Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Deviation Presentation
Hochgeladen von
yogendra0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
471 Ansichten14 Seitendeviation process uploaded
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
PPTX, PDF, TXT oder online auf Scribd lesen
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldendeviation process uploaded
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als PPTX, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
471 Ansichten14 SeitenDeviation Presentation
Hochgeladen von
yogendradeviation process uploaded
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als PPTX, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
Sie sind auf Seite 1von 14
Deviation and root cause analysis in Pharma
• 1. Title: Deviation and Root Cause Analysis Content
• Deviation and Type of Deviation
• Regulatory expectation
• Basic process flow for Deviation handling
• Root Cause Analysis Tools and Technique for Root
Cause
• 2. WHAT IS DEVIATION? Deviation is a departure from a
documented standard or procedure Deviations are measured
differences between observed value and expected or normal
value for a process or product condition, or a departure from
approved procedure or established standard or specification
There are two types of deviations
• 1)Planned Deviation : Planned deviations, which are described,
and pre-approved deviation from the current operational
document/system, covering a specified period of time or number
of batches. Planned deviation shall be approved before execution
• 2)Unplanned Deviation: Unplanned deviations also called as incident.
It is defined as unplanned or uncontrolled event in the form of non-
compliance from the designed systems or procedures at any stage of
manufacturing, packaging, testing, holding and storage of drug
product due to system failure or equipment breakdown or manual
error. WHY INVEISTIGATE DEVIATION? To prevent reoccurrence
Failures are cost to company Failures can have adverse health impact
on the consumers if go undetected To identify the cause and take
corrective actions To identify other similar situations and take
preventive actions Continuous improvement Regulatory requirement
• 3. Regulatory Expectation
• “Any unexplained discrepancy…shall be thoroughly
investigated…The investigation shall extend to other batches
…that can have been associated with the specific failure or
discrepancy. A written record of the investigation shall be made
and shall include the conclusions and follow-up 21 CFR 211.192
•“Any deviations from instructions or procedures should be
avoided as far as possible. If a deviation occurs, it should be
approved in writing by a competent person…”
• Any significant deviations [from defined procedures
and instructions] are fully recorded and investigated EC
Guide to GMP, Chapter 5 (5.15)
• Any deviation from established procedures should be
documented and explained. Critical deviations should
be investigated, and the investigation and its
conclusions should be documented. ICHQ7A
• The organization should ensure process outputs, products, and services
that do not conform to requirements are identified and controlled to
prevent unintended use or delivery. The organization should take
appropriate action based on nature of nonconformity and its impact on
conformity of products and services. This is applicable also to
nonconforming products and services detected after delivery of products
during or after provision of service ISO 9001:2015,Clause 8.7 When a
deviation occurs the responsible firm must undertake and investigation to
determine what went wrong and what damage, if any , the product might
have suffered.
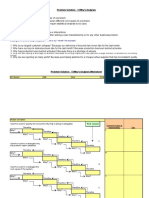
• 4. Basic Process flow for Deviation handling
Identification of deviation Immediate correction &
initial impact assessment (Containment action)
Define and classified deviation Major :Impact on
product quality Critical: Impact on product quality,
safety & efficacy Minor: No impact on product
quality, safety & efficacy
•Impact Assessment
•Corrections & closure of incident
•Impact Assessment
•Investigation •Corrections / CAPA
•Closure of incident
•CAPA implementation & effectiveness check
Related to what? When and Where? What is the
extent? What are the immediate action taken Any
interim control
• 5. Root Cause Analysis
• Root cause analysis(RCA) is a method that used to address a deviation
or non conformance in order to get to the true root cause of the
problem.
• RCA is application of a series of well known technique which can
produce a systematic, quantified and documented approach to the
identification, under stand and resolution of under causes.
• As a PROCESS it is more effective when it’s adequately defined,
provisioned with appropriate resources, and performed by trained
personnel.
• Goals - Failure identification - Failure analysis - Failure
resolution
• Iterative Process: - Complete prevention of recurrence
by a single intervention is not always possible. Basic
steps involved in Root Cause Analysis Define Event
Gather data Investigation Identify the Root Causes
Eliminate items that are not root causes
Recommendation s CAPA Improvement
• 6. RCA Tools and Technique
• Brainstorming A creative approach to generate a high volume of ideas
free of criticism and judgment.
• What are the rules?
• Every idea is captured.
• Ideas are written as said.
• No comments, discussion, or criticism.
• Everyone contributes.
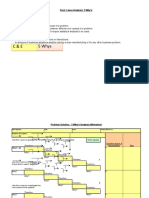
• Five Whys? The 5 Whys is a questions‐asking method used to explore the
cause/effect relationships underlying a particular problem. Ultimately, the
goal of applying the 5 Whys method is to determine a root cause of a
defect or problem. Keep asking Why till you reach root cause
• Cause and Effect Diagram Technique to graphically identify and organize
many possible causes of a problem Advantages - Helps to discover the
most likely ROOT CAUSES of a problem Teach a team to reach a common
understanding of a problem. Fishbone Analysis Components : - Head
of a Fish : Problem or Effect Horizontal Branches : Causes Sub –
branches : Reason
•THANKING YOU
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Root Cause Analysis & Action PlanningDokument56 SeitenRoot Cause Analysis & Action Planningsatyendra kumar100% (2)
- Pharmacology Drug Chart: Drug Name Receptor Therapeutic Uses Adverse EffectsDokument18 SeitenPharmacology Drug Chart: Drug Name Receptor Therapeutic Uses Adverse EffectsPadmavathy Naidu Chokkapu100% (2)
- Design Thinking TutorialDokument51 SeitenDesign Thinking Tutorialjoca200892% (12)
- Deviation & OOSDokument56 SeitenDeviation & OOSRakeshNoch keine Bewertungen
- Quality Assurance (QA) Management Procedures: By: Pharma Tips - Views: 14415 - Date: 06-May-2012Dokument6 SeitenQuality Assurance (QA) Management Procedures: By: Pharma Tips - Views: 14415 - Date: 06-May-2012SrinivasNoch keine Bewertungen
- 5 Whys Analysis SheetDokument3 Seiten5 Whys Analysis SheetTanvi SharmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Determining The Root Cause of A Problem: Approved For Public ReleaseDokument22 SeitenDetermining The Root Cause of A Problem: Approved For Public ReleaseLucia M. AceroNoch keine Bewertungen
- 5 Whys 5 Whys C & E C & E: Root-Cause Analysis: 5 Why'sDokument6 Seiten5 Whys 5 Whys C & E C & E: Root-Cause Analysis: 5 Why'ssalva100% (1)
- Equipment Logbook 2 2Dokument7 SeitenEquipment Logbook 2 2Belazouz BoualemNoch keine Bewertungen
- 5 WHYs Root Cause AnalysisDokument2 Seiten5 WHYs Root Cause AnalysisDwi SurantoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Change ControlDokument7 SeitenChange ControlPrince MoniNoch keine Bewertungen
- 014 Quality Unit Roles and ResponsibilitiesDokument35 Seiten014 Quality Unit Roles and ResponsibilitiesSIRAJ KP100% (1)
- Sun Moon Pharma Documents ProcedureDokument11 SeitenSun Moon Pharma Documents ProcedureSagar ChavanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Root Cause AnalysisDokument20 SeitenRoot Cause AnalysisAjit Bhosale100% (1)
- The Art of Root Cause Analysis: Back To BasicsDokument1 SeiteThe Art of Root Cause Analysis: Back To BasicsNasser KunjuNoch keine Bewertungen
- 5 Whys Analysis Sheet 06.01.16Dokument3 Seiten5 Whys Analysis Sheet 06.01.16Joydeep ChakrabortyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Root Cause Analysis - VVGGG Cases PDFDokument54 SeitenRoot Cause Analysis - VVGGG Cases PDFnorthbride2008Noch keine Bewertungen
- SOP-000182638 Phase 1b Investigation ChecklistDokument3 SeitenSOP-000182638 Phase 1b Investigation ChecklistSebastian LopezNoch keine Bewertungen
- OOS Guidance OverviewDokument48 SeitenOOS Guidance OverviewAnjamSoodNoch keine Bewertungen
- Example RA For Transport To Regulated MarketsDokument7 SeitenExample RA For Transport To Regulated MarketsDoan Chi ThienNoch keine Bewertungen
- Out of Specifications IIDokument39 SeitenOut of Specifications IIHaekal Ramadhan100% (1)
- 2 Process Validation QandA Version 4 (June 2011) - Adopted 18th PPWG Meeting PDFDokument4 Seiten2 Process Validation QandA Version 4 (June 2011) - Adopted 18th PPWG Meeting PDFVishal SomaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- JAGSONPAL HOLD TIME STUDYDokument3 SeitenJAGSONPAL HOLD TIME STUDYAshok Lenka100% (2)
- Change Control ProcedureDokument19 SeitenChange Control ProcedureyogendraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Change Control ProcedureDokument19 SeitenChange Control ProcedureyogendraNoch keine Bewertungen
- How To Use The 5-Whys For Root Cause AnalysisDokument10 SeitenHow To Use The 5-Whys For Root Cause AnalysisSlim100% (2)
- Sop Fumigation Vapour Hydrogen Peroxide-H2o2 VHPDokument6 SeitenSop Fumigation Vapour Hydrogen Peroxide-H2o2 VHPMohamed FetouhNoch keine Bewertungen
- Annual Products ReviewDokument12 SeitenAnnual Products ReviewMubeen Khan100% (1)
- Root Cause Analysis Tools Ishikawa 5 Whys GuideDokument32 SeitenRoot Cause Analysis Tools Ishikawa 5 Whys GuideBRO HAFIZNoch keine Bewertungen
- Problem Analysis MethodsDokument24 SeitenProblem Analysis MethodsFrank Calberg0% (1)
- Auoclave Validation ProtocolDokument20 SeitenAuoclave Validation Protocolyogendra67% (3)
- PICS Inspection QC LabDokument18 SeitenPICS Inspection QC LabMax HuangNoch keine Bewertungen
- BiteSizedTraining ProblemSolvingDokument13 SeitenBiteSizedTraining ProblemSolvingAnielaLTC100% (2)
- Labaid Pharmaceuticals Limited: Deviation Control Status Open Closed TotalDokument33 SeitenLabaid Pharmaceuticals Limited: Deviation Control Status Open Closed TotalgolamnobiNoch keine Bewertungen
- MICLAB 150 Initial Investigation of Out of Specification (OOS) Results in Microbiological LaboratoryDokument11 SeitenMICLAB 150 Initial Investigation of Out of Specification (OOS) Results in Microbiological Laboratoryspp100% (1)
- SOP for Handling Out of Trend Pharmaceutical ResultsDokument3 SeitenSOP for Handling Out of Trend Pharmaceutical ResultsMubarak PatelNoch keine Bewertungen
- 007 Out of SpecificationDokument12 Seiten007 Out of Specificationmarkandey gupta100% (2)
- Water for Injection Generation System RequirementsDokument14 SeitenWater for Injection Generation System Requirementsyogendra100% (2)
- Sterile Drug Insp CPGM 7356-002a - Ora - Lao-Nm 9-10-15 - Emc Lao FinalDokument54 SeitenSterile Drug Insp CPGM 7356-002a - Ora - Lao-Nm 9-10-15 - Emc Lao Finaltito1628100% (1)
- Out of SpecificationDokument7 SeitenOut of SpecificationMichelle Morgan LongstrethNoch keine Bewertungen
- OOS InvestigationsDokument20 SeitenOOS InvestigationsShanePooleNoch keine Bewertungen
- Handling of Deviation: Dr. A. AmsavelDokument34 SeitenHandling of Deviation: Dr. A. Amsavelsandro CardosoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Quality Risk Management - The Pharmaceutical Experience PDFDokument25 SeitenQuality Risk Management - The Pharmaceutical Experience PDFChiorean Ioana100% (1)
- Understanding QA System in Pharma Industry - 23092020Dokument31 SeitenUnderstanding QA System in Pharma Industry - 23092020Anggia Bia Amanda100% (1)
- Cleaning Validation (CV) Procedure and Protocol - Guideline SOPsDokument30 SeitenCleaning Validation (CV) Procedure and Protocol - Guideline SOPsDeepakNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lab Notebook Policy SOPDokument9 SeitenLab Notebook Policy SOPmrpicasso0% (1)
- User Requirement Specification for Pure Steam GenerationDokument14 SeitenUser Requirement Specification for Pure Steam Generationyogendra75% (4)
- User Requirement Specification for Pure Steam GenerationDokument14 SeitenUser Requirement Specification for Pure Steam Generationyogendra75% (4)
- User Requirement Specification for Pure Steam GenerationDokument14 SeitenUser Requirement Specification for Pure Steam Generationyogendra75% (4)
- Annual Product Quality Review Data Summary and TrendsDokument1 SeiteAnnual Product Quality Review Data Summary and Trendsnasreen anjumNoch keine Bewertungen
- Supervisor On-Boarding: Root Cause Analysis 101Dokument36 SeitenSupervisor On-Boarding: Root Cause Analysis 101Anson GarganianNoch keine Bewertungen
- 01 LC Vibratory Sifter 01Dokument2 Seiten01 LC Vibratory Sifter 01Ravi YadavNoch keine Bewertungen
- Laboratory Investigation and Report Form Part A: (Ref. SOP LAB-055.)Dokument4 SeitenLaboratory Investigation and Report Form Part A: (Ref. SOP LAB-055.)Ira NurjannahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Laboratory Investigation RequirementsDokument16 SeitenLaboratory Investigation RequirementsSebastian LopezNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Report On 5w S and 1h Root Cause and PDokument23 SeitenA Report On 5w S and 1h Root Cause and PalexrferreiraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sop For Technology TransferDokument3 SeitenSop For Technology TransferDolly Bijani100% (3)
- VAL 090 Equipment Validation Guideline Sample PDFDokument2 SeitenVAL 090 Equipment Validation Guideline Sample PDFsiva sankarNoch keine Bewertungen
- SOP For Handling of Out of Specification Results in Microbiological Testing - Pharmaceutical GuidelinesDokument4 SeitenSOP For Handling of Out of Specification Results in Microbiological Testing - Pharmaceutical Guidelinesalnzeer omerNoch keine Bewertungen
- 3-Test Report of Amlodipine Besilate 3Dokument1 Seite3-Test Report of Amlodipine Besilate 3ShagorShagorNoch keine Bewertungen
- Purified Water Distribution System URSDokument11 SeitenPurified Water Distribution System URSyogendra0% (1)
- Purified Water Distribution System URSDokument11 SeitenPurified Water Distribution System URSyogendra0% (1)
- FDA Inspection Observations of Beacon Hill Medical PharmacyDokument9 SeitenFDA Inspection Observations of Beacon Hill Medical Pharmacyvijayns_250355172Noch keine Bewertungen
- 001 How To Use The 5-Whys For Root Cause AnalysisDokument9 Seiten001 How To Use The 5-Whys For Root Cause AnalysisAbd ZouhierNoch keine Bewertungen
- 02 LC of Double Cone Blender 02Dokument2 Seiten02 LC of Double Cone Blender 02Ravi YadavNoch keine Bewertungen
- 01.collection, Storage and Control of Reserve Samples For Drug ProductsDokument4 Seiten01.collection, Storage and Control of Reserve Samples For Drug ProductsBejoy KarimNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hold Time Study SOP Indian Pharma 1Dokument3 SeitenHold Time Study SOP Indian Pharma 1ziadddNoch keine Bewertungen
- SOP of Sanitation of PW SystemDokument6 SeitenSOP of Sanitation of PW Systemanon_350461302100% (1)
- Process Validation Protocol (500 MG Tablet)Dokument6 SeitenProcess Validation Protocol (500 MG Tablet)Mohammed Zubair100% (1)
- QCD-036-01 Good Chromatography PracticesDokument12 SeitenQCD-036-01 Good Chromatography Practicesarnab rayNoch keine Bewertungen
- 50 Quick Retrospectives SampleDokument28 Seiten50 Quick Retrospectives SampleSampat SundayNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hold Time Study GuidelineDokument4 SeitenHold Time Study GuidelineYousifNoch keine Bewertungen
- URS For Water For Injection Storage and Distribution SystemDokument19 SeitenURS For Water For Injection Storage and Distribution Systemyogendra100% (2)
- 10 - Design and Performance QualificationDokument8 Seiten10 - Design and Performance Qualificationsainzb83Noch keine Bewertungen
- Annual Product Review Developing An SOPDokument26 SeitenAnnual Product Review Developing An SOPanants2567% (3)
- Good Documentation Practices - IVT - JVTDokument7 SeitenGood Documentation Practices - IVT - JVTdcharliesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Protocol For The Conduct of Stability StudiesDokument4 SeitenProtocol For The Conduct of Stability StudiesManish shankarpure100% (1)
- Sterile Pharmaceutical ProductsDokument62 SeitenSterile Pharmaceutical ProductsTaesup Byun50% (6)
- QRQC Training ProtocolDokument52 SeitenQRQC Training ProtocolSudhagar P100% (1)
- TEMPLATE FOR OPERATIONAL QUALIFICATION PROTOCOL - Pharmaceutical GuidanceDokument7 SeitenTEMPLATE FOR OPERATIONAL QUALIFICATION PROTOCOL - Pharmaceutical GuidanceMSL India100% (2)
- SOP For Handling of Market ComplaintDokument32 SeitenSOP For Handling of Market Complaintsubbu_281Noch keine Bewertungen
- Winthrox QC checklistDokument5 SeitenWinthrox QC checklistanoushia alviNoch keine Bewertungen
- OOS调差Dokument17 SeitenOOS调差Smartishag BediakoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Oecd ArchivingDokument24 SeitenOecd ArchivingNicolas Quero CarvajalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Access Control To GMP AreaDokument4 SeitenAccess Control To GMP AreaNishit SuvaNoch keine Bewertungen
- SMF Update SOLITAIRE PDFDokument35 SeitenSMF Update SOLITAIRE PDFmaheshNoch keine Bewertungen
- Guidlines On Recall by CDSCODokument28 SeitenGuidlines On Recall by CDSCONAVNEET BAGGA100% (1)
- Annual Product Quality Review (APQR) SOP - PharmaBDokument14 SeitenAnnual Product Quality Review (APQR) SOP - PharmaBrehmat ali100% (1)
- VAL-085 Process Validation Guideline SampleDokument2 SeitenVAL-085 Process Validation Guideline SampleVizit31Noch keine Bewertungen
- Helix Pharma (Private) Limited: Validation ProtocolDokument4 SeitenHelix Pharma (Private) Limited: Validation Protocolziauddin bukhari0% (2)
- Annual Products ReviewDokument5 SeitenAnnual Products Reviewmainart50% (2)
- Good Distribution Practices A Complete Guide - 2021 EditionVon EverandGood Distribution Practices A Complete Guide - 2021 EditionNoch keine Bewertungen
- Data Integrity and Compliance: A Primer for Medical Product ManufacturersVon EverandData Integrity and Compliance: A Primer for Medical Product ManufacturersNoch keine Bewertungen
- NGVF 2016 D1.T2.4.1 Gordon Farquharson WFI - New PH Eur Production Specification PDFDokument39 SeitenNGVF 2016 D1.T2.4.1 Gordon Farquharson WFI - New PH Eur Production Specification PDFParth PatelNoch keine Bewertungen
- HVAC Installation Qualification ReportDokument26 SeitenHVAC Installation Qualification ReportyogendraNoch keine Bewertungen
- NGVF 2016 D1.T2.4.1 Gordon Farquharson WFI - New PH Eur Production Specification PDFDokument39 SeitenNGVF 2016 D1.T2.4.1 Gordon Farquharson WFI - New PH Eur Production Specification PDFParth PatelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Personalhygiene 120531235008 Phpapp01Dokument41 SeitenPersonalhygiene 120531235008 Phpapp01Mar JinitaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Data Integrity Agon - Part 10-Warning Letters AnalysisDokument12 SeitenData Integrity Agon - Part 10-Warning Letters AnalysisyogendraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Revision R3Dokument6 SeitenRevision R3yogendraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Oms 2018Dokument424 SeitenOms 2018ROBINNoch keine Bewertungen
- PICs Annex1 Consultation Document Dec. 2017Dokument50 SeitenPICs Annex1 Consultation Document Dec. 2017DholakiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Revision R3Dokument6 SeitenRevision R3yogendraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Oms 2018Dokument424 SeitenOms 2018ROBINNoch keine Bewertungen
- Trending Causes Marine IncidentsDokument10 SeitenTrending Causes Marine IncidentsVinod DsouzaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Solve The Real Problem Using Root Cause Analysis Grace Duffy, John Moran, and William RileyDokument10 SeitenSolve The Real Problem Using Root Cause Analysis Grace Duffy, John Moran, and William RileyChandrashekar ChiruthaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Understanding the 5 Whys Root Cause Analysis MethodDokument9 SeitenUnderstanding the 5 Whys Root Cause Analysis MethodnelsonNoch keine Bewertungen
- IshikawaDokument16 SeitenIshikawaJohn DoeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Problem > Root Cause - 5 Whys AnalysisDokument3 SeitenProblem > Root Cause - 5 Whys AnalysisVasant bhoknalNoch keine Bewertungen
- 5 Whys Root Cause Analysis TemplateDokument2 Seiten5 Whys Root Cause Analysis TemplateLeventNoch keine Bewertungen
- Root Cause Investigation Tool Problem Solution - 5 Why's Analysis Benefits of The 5 WhysDokument2 SeitenRoot Cause Investigation Tool Problem Solution - 5 Why's Analysis Benefits of The 5 WhysBiswaranjan KarNoch keine Bewertungen
- 5 WhysDokument7 Seiten5 WhysRanjini RaoNoch keine Bewertungen
- RCA-Adapting 5-Whys, Fishbone, and Other Methods in PROACT - Reliability Center IncDokument7 SeitenRCA-Adapting 5-Whys, Fishbone, and Other Methods in PROACT - Reliability Center IncHafsa JalalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assignment EPDDokument33 SeitenAssignment EPDChấn Nguyễn100% (6)
- What you're proposingDokument3 SeitenWhat you're proposingappleappsNoch keine Bewertungen