Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Ureterocele
Hochgeladen von
Nadia Dwiputri0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
63 Ansichten18 SeitenUreterocele is a cystic dilatation of the distal ureter that occurs more often in women. It results from delayed canalization during embryogenesis causing obstruction. Ureteroceles can be intravesical or prolapsed and located orthotopically or ectopically. Clinical signs include urinary retention, hematuria, infection, and abdominal pain. Ureteral duplication is a common congenital abnormality where an extra ureter is present. It can cause issues like reflux, infection, and hydronephrosis if the ureter inserts abnormally or becomes obstructed. Ureteral ectopia is when the ureter terminates in an abnormal location outside the bladder
Originalbeschreibung:
Pptx
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
PPTX, PDF, TXT oder online auf Scribd lesen
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenUreterocele is a cystic dilatation of the distal ureter that occurs more often in women. It results from delayed canalization during embryogenesis causing obstruction. Ureteroceles can be intravesical or prolapsed and located orthotopically or ectopically. Clinical signs include urinary retention, hematuria, infection, and abdominal pain. Ureteral duplication is a common congenital abnormality where an extra ureter is present. It can cause issues like reflux, infection, and hydronephrosis if the ureter inserts abnormally or becomes obstructed. Ureteral ectopia is when the ureter terminates in an abnormal location outside the bladder
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als PPTX, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
63 Ansichten18 SeitenUreterocele
Hochgeladen von
Nadia DwiputriUreterocele is a cystic dilatation of the distal ureter that occurs more often in women. It results from delayed canalization during embryogenesis causing obstruction. Ureteroceles can be intravesical or prolapsed and located orthotopically or ectopically. Clinical signs include urinary retention, hematuria, infection, and abdominal pain. Ureteral duplication is a common congenital abnormality where an extra ureter is present. It can cause issues like reflux, infection, and hydronephrosis if the ureter inserts abnormally or becomes obstructed. Ureteral ectopia is when the ureter terminates in an abnormal location outside the bladder
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als PPTX, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
Sie sind auf Seite 1von 18
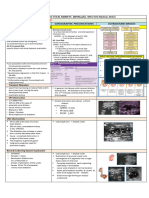
Ureterocele
Ureterocele is cystic dilatation of the
intravesical segment of the distal ureter
Occurs in 1 per 4000 population and often
occurs in women (4-7 times compared to
men)
Etiology
• It is non inherited or genetic disorder
• Delayed canalization of Chwalla membrane
(membrane that separate the ureteric bud
from the urogenital sinus) during
embryogenesis which causes obstruction of
the ureteric orifice
Classifications
a. According to position
Intravesical ureterocel and Prolapsing
b. According to the location of ureteric orifice
Orthotopic (25%) and Ectopic (75%)
c. According to renal collecting system
Single system and duplex system
Clinical Sign
• Urinary retention
• Hematuria
• Abdominal distention
• Abdominal or colic pain
• Urinary tract infection
Ureteral Duplication
• Most common congenital renal abnormality,
1 : 125 of birth
• Incomplete ureteral duplication, in which one
common ureter enters the bladder
• Complete ureteral duplication, in which two
ureters ipsilaterally enter the bladder
In cases of ureteral duplication where the
ureteral bud arises twice, the lower-pole
ureter integrates with the bladder earlier than
expected and, as a result, is carried into a
more superolateral position. Thus, the distal
ureter is poorly supported by the trigone and
has a shorter intramural tunnel, both of which
situations increase the likelihood of VUR.
Clinical sign
Commonly asymptomatic, but the
symptoms occur when something happen like
obstruction, reflux, infection, etc
• Hydronephrosis
• Urinary tract infection
• Vesicoureteral reflux
Ureter Ectopic
Ureteral ectopia is defined as a ureter that
terminates into an abnormal location.
Instead of draining into the bladder, the
ureteral orifice is located in the urethra,
vagina, uterus (in woman) or ductus deferens,
seminal vesicles, urethra (in man)
In ureteral duplication, two ipsilateral ureteral buds
migrate separately and simultaneously toward the
urogenital sinus.
Ectopia of one or both ureters may occur; however,
ectopia of only the upper pole ureter is usually
present, because it is the second ureter to be
incorporated onto the trigone. Its late arrival to the
urogenital sinus causes the migrating mesonephric
duct to carry the ureter to an abnormal location
outside the bladder
• Urinary track infection
• Incontinence
• Vesicoureteral reflux
• Abdominal pain and swelling
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- ANA Recognized Terminologies and Data Element SetsDokument5 SeitenANA Recognized Terminologies and Data Element SetsBlair WoodsenNoch keine Bewertungen
- ORE - UK Dental Reference BooksDokument4 SeitenORE - UK Dental Reference BooksKisshore ReddyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Untitled - Susan BlumDokument65 SeitenUntitled - Susan BlumnewNoch keine Bewertungen
- Manual of Clinical DieteticsDokument7 SeitenManual of Clinical Dieteticsandi agung0% (1)
- HydronephrosisDokument12 SeitenHydronephrosisChithra SajuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ohmeda Modulus II Plus Anesthesia Machine - Service and User ManualDokument213 SeitenOhmeda Modulus II Plus Anesthesia Machine - Service and User ManualRoger86% (7)
- Info DcsDokument9 SeitenInfo DcsKhei Laqui SNNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pediatric Urology HDokument54 SeitenPediatric Urology HAlaa A. AbdelrahimNoch keine Bewertungen
- Congenital Anomalies of Kidney and Urinary TractDokument53 SeitenCongenital Anomalies of Kidney and Urinary TractDoctor peds100% (1)
- Pediatric Urological Disorders: Professor Adel Al-HunayanDokument44 SeitenPediatric Urological Disorders: Professor Adel Al-Hunayanmarina_shawkyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Congenital Anomalies of Urinary BladderDokument102 SeitenCongenital Anomalies of Urinary Bladdernancy voraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Genitiurinary2: Kidneys and UreterDokument101 SeitenGenitiurinary2: Kidneys and UreterFiza MushtaqNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ureteral Duplication and UreterocelesDokument8 SeitenUreteral Duplication and UreterocelesEster Elisabeth WoworNoch keine Bewertungen
- 20 - Pediatric Urinary DisordersDokument62 Seiten20 - Pediatric Urinary DisordersKhaalid AbdirahmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Congenital Anomalies of Ureter BladderDokument17 SeitenCongenital Anomalies of Ureter BladderAfiq SabriNoch keine Bewertungen
- Scrotal AbnormalitiesDokument6 SeitenScrotal AbnormalitiesmoominjunaidNoch keine Bewertungen
- Congenital Anomaly: Dr. Yacobda H. Sigumonrong, SpuDokument89 SeitenCongenital Anomaly: Dr. Yacobda H. Sigumonrong, Spuangelica gloryNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mnlkaxi QH: Manisha M.Sc. NursingDokument57 SeitenMnlkaxi QH: Manisha M.Sc. NursingManisha ShakyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 82-Articles Content-317-1-10-20200917Dokument7 Seiten82-Articles Content-317-1-10-20200917Devi Permata SariNoch keine Bewertungen
- Uro PedsooDokument9 SeitenUro Pedsoomotasem.med120Noch keine Bewertungen
- 10 13 PBDokument72 Seiten10 13 PBViandra DewiNoch keine Bewertungen
- LO Kidney Week 5Dokument51 SeitenLO Kidney Week 5chloeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Posterior Urethral ValveDokument6 SeitenPosterior Urethral ValveMustafa AadanNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2.obstruction of The Urinary TractDokument22 Seiten2.obstruction of The Urinary TractAkli JahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pathology of The Urinary BladderDokument58 SeitenPathology of The Urinary BladderamyNoch keine Bewertungen
- UTI in PregnancyDokument33 SeitenUTI in Pregnancyyusufkiduchu8Noch keine Bewertungen
- Xv-B.pathologic Fetal Kidneys 2017Dokument8 SeitenXv-B.pathologic Fetal Kidneys 2017jamiladeguzmanabcdefghijklmNoch keine Bewertungen
- Vesico Ureteric Reflex: By: DR Sonam Moderator: DR AbhishekDokument14 SeitenVesico Ureteric Reflex: By: DR Sonam Moderator: DR Abhisheksourabh jakharNoch keine Bewertungen
- Microbial Diseases of The Urinary System: Yemane Weldu (MSC., Assistant Professor)Dokument65 SeitenMicrobial Diseases of The Urinary System: Yemane Weldu (MSC., Assistant Professor)Lidiya TeshomeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Categories of Malformations: Anomalies of Number, Volume and Structure Ascent, Form and Fusion, Rotation andDokument3 SeitenCategories of Malformations: Anomalies of Number, Volume and Structure Ascent, Form and Fusion, Rotation andÁngel Parra CominoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Urinary System 06Dokument43 SeitenUrinary System 06damclfNoch keine Bewertungen
- Duplex Collecting SystemDokument7 SeitenDuplex Collecting SystemAnda Tri SuhandaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 31 Uro Hydrocele 111211112520 Phpapp02Dokument6 Seiten31 Uro Hydrocele 111211112520 Phpapp02ppc_20Noch keine Bewertungen
- CAKUTDokument50 SeitenCAKUTsantosh subediNoch keine Bewertungen
- NMT11 Urology Special NoteDokument36 SeitenNMT11 Urology Special NoteYiba Zul100% (4)
- Obstructive Uropathy: Nitha. K 2 Year MSC NursingDokument67 SeitenObstructive Uropathy: Nitha. K 2 Year MSC NursingNITHA KNoch keine Bewertungen
- Infections of The Urinary Genirouty TractDokument4 SeitenInfections of The Urinary Genirouty Tractfifa nasrul ummahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Anomalies of The KidneysDokument19 SeitenAnomalies of The KidneysOmotosho DavidNoch keine Bewertungen
- I. Objectives For Students' Independent StudiesDokument5 SeitenI. Objectives For Students' Independent StudiesFokeerbux ZyadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Umbilicalabnor MalitiesDokument53 SeitenUmbilicalabnor MalitiesAlicia TjinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Background KarunkelDokument2 SeitenBackground KarunkeldatascribdyesNoch keine Bewertungen
- RenalDokument150 SeitenRenalHoe TeohNoch keine Bewertungen
- Congenital Urological Conditions - Dr. HawkarDokument38 SeitenCongenital Urological Conditions - Dr. HawkarBashar KhalilNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nizzah Gus Idk1 EpispadiasDokument22 SeitenNizzah Gus Idk1 EpispadiasLuthfan Dio Satria BachriNoch keine Bewertungen
- Apn and Malformations of TheDokument54 SeitenApn and Malformations of TheRyan KadavilNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ureterocele 130919225917 Phpapp02Dokument23 SeitenUreterocele 130919225917 Phpapp02Marcelo Bravo CortesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Modern Management of Renal Colic: 14 Urology SeminarDokument4 SeitenModern Management of Renal Colic: 14 Urology SeminarAliNoch keine Bewertungen
- LO Kidney 5.2Dokument4 SeitenLO Kidney 5.2Dapot SianiparNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pediatric EmergencyDokument66 SeitenPediatric EmergencyWaseem MoukhtarNoch keine Bewertungen
- HydronephrosisDokument6 SeitenHydronephrosisJamaluddin Ahmad A.MNoch keine Bewertungen
- Week 5Dokument12 SeitenWeek 5Marcellina AwingNoch keine Bewertungen
- Colon, Rectum and AnusDokument30 SeitenColon, Rectum and AnusKiara GovenderNoch keine Bewertungen
- Renal Concept MapDokument8 SeitenRenal Concept MapXtine CajiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Uroperitoneum in FoalsDokument13 SeitenUroperitoneum in FoalsPhantom HassanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mrcs UrologyDokument78 SeitenMrcs UrologyAdebisiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Vesicoureteral RefluxDokument4 SeitenVesicoureteral RefluxPrasetya Ismail PermadiNoch keine Bewertungen
- VESICOLITHIASISDokument17 SeitenVESICOLITHIASISilma aulia zahra0% (1)
- Bladder Outlet Obstruction in Children PDFDokument64 SeitenBladder Outlet Obstruction in Children PDFalaaNoch keine Bewertungen
- (2020) Goldman-Cecil Medicine - Approach To The Patient With Urinary Tract InfectionDokument23 Seiten(2020) Goldman-Cecil Medicine - Approach To The Patient With Urinary Tract InfectionMiftahurrohmat AlmaasahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Urinary SystemDokument18 SeitenUrinary SystemAbdusaburNoch keine Bewertungen
- L7 Urethra, Congenital Anomalies &injuriesDokument10 SeitenL7 Urethra, Congenital Anomalies &injurieswww.owaisarbNoch keine Bewertungen
- +ascariasisDokument16 Seiten+ascariasisDr. SAMNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Simple Guide to Disorders of Pelvic Floor Organs, Diagnosis, Treatment and Related ConditionsVon EverandA Simple Guide to Disorders of Pelvic Floor Organs, Diagnosis, Treatment and Related ConditionsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fetal BehaviourDokument1 SeiteFetal BehaviourJuan José Espinoza OsoresNoch keine Bewertungen
- 484-Article Text-2583-1-10-20210630Dokument8 Seiten484-Article Text-2583-1-10-20210630Nova RizkenNoch keine Bewertungen
- JGCA JPN Classification 3rd EngDokument12 SeitenJGCA JPN Classification 3rd EngLiz PesantesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Midwifery Pharmacology-9Dokument1 SeiteMidwifery Pharmacology-9georgeloto12Noch keine Bewertungen
- Machines That Save Lives in The Intensive Care Unit: The Ultrasonography MachineDokument10 SeitenMachines That Save Lives in The Intensive Care Unit: The Ultrasonography MachineCirstea Marina-alinaNoch keine Bewertungen
- HCP Chapterwise MCQ FinalDokument36 SeitenHCP Chapterwise MCQ Finalsudeep kulkarni100% (7)
- Small Animal Maternal Behavior and Its AberrationsDokument4 SeitenSmall Animal Maternal Behavior and Its AberrationsPablo Herreros UbaldeNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Newborn Infant: A Missing Stage in Developmental PsychologyDokument17 SeitenThe Newborn Infant: A Missing Stage in Developmental PsychologyJunia RahmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- SIBO Breath Test (Lactulose #900-C) : Z180487 For Accession #Dokument2 SeitenSIBO Breath Test (Lactulose #900-C) : Z180487 For Accession #VICENTENoch keine Bewertungen
- Breastfeeding Exclusively and Iron Deficiency Anemia During The First 6 Months of AgeDokument5 SeitenBreastfeeding Exclusively and Iron Deficiency Anemia During The First 6 Months of AgeDimas Fauzan TanpabasabasiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pediatrics 2002 Ballard E63Dokument8 SeitenPediatrics 2002 Ballard E63dentistalitNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dele PrioDokument10 SeitenDele PriomonmonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Endotracheal IntubationDokument14 SeitenEndotracheal IntubationajayvarvalaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Instrumental Analysis of Swallowing - PDF / KUNNAMPALLIL GEJODokument65 SeitenInstrumental Analysis of Swallowing - PDF / KUNNAMPALLIL GEJOKUNNAMPALLIL GEJO JOHNNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ketamine Psychedelic Psychotherapy: Focus On Its Pharmacology PHDokument59 SeitenKetamine Psychedelic Psychotherapy: Focus On Its Pharmacology PHMartin Girard100% (1)
- The Uses and Limitations of The Fetal Biophysical Profile.Dokument18 SeitenThe Uses and Limitations of The Fetal Biophysical Profile.Diego Ortecho100% (1)
- Case Study-Chronic TonsillitisDokument7 SeitenCase Study-Chronic TonsillitisJonalyn TumanguilNoch keine Bewertungen
- And Employee Satisfaction Survey in Kulwanti HospitalDokument52 SeitenAnd Employee Satisfaction Survey in Kulwanti HospitalAfaq Sana100% (1)
- Final Surgery RevisionDokument195 SeitenFinal Surgery RevisionAbdulziz Al-jedaieNoch keine Bewertungen
- Keeping Birth Normal: Position StatementDokument3 SeitenKeeping Birth Normal: Position StatementCatur ErtyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chlamydia: Chlamydia Rapid Test Device (Swab/Urine)Dokument3 SeitenChlamydia: Chlamydia Rapid Test Device (Swab/Urine)Cristhian CuviNoch keine Bewertungen
- Words of Wisdom From and To PhlebotomistsDokument7 SeitenWords of Wisdom From and To PhlebotomistsDanhil RamosNoch keine Bewertungen
- Kendra Squires Final ResumeDokument2 SeitenKendra Squires Final ResumeKendra SquiresNoch keine Bewertungen
- Abrasio PlacentaDokument3 SeitenAbrasio Placentamuhammad azamNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2017-02-13 (10) PaintedDokument355 Seiten2017-02-13 (10) PaintedhsmanNoch keine Bewertungen