Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Specialty Plastics: Polyvinylfluoride (PVF)
Hochgeladen von
Akash Yadav0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
19 Ansichten14 SeitenOriginaltitel
PVF.ppt
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
PPT, PDF, TXT oder online auf Scribd lesen
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als PPT, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
19 Ansichten14 SeitenSpecialty Plastics: Polyvinylfluoride (PVF)
Hochgeladen von
Akash YadavCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als PPT, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
Sie sind auf Seite 1von 14
SPECIALTY PLASTICS
Polyvinylfluoride
(PVF)
CORPORATE TRAINING AND PLANNING
CH2-CHF
n
Polyvinylfluoride (PVF)
Polyvinylfluoride was commercialized by Du Pont in the
early sixties. The monomer is manufactured by adding
hydrogen fluoride to acetylene.
CORPORATE TRAINING AND PLANNING
Structure and General Properties
The crystalline melting point is 198°C and the
molecular weight is 5x104 to 2x105.
Many properties of PVF resemble those of PVC (low
water absorption, resistance to hydrolysis, separation
of HF at elevated temperature).
The smaller F atoms result in a higher degree of
crystallinity.
The flame resistance is poorer than that of PVC; PVF
continues to burn slowly after ignition.
CORPORATE TRAINING AND PLANNING
Availability
PVF is supplied only as film, weakly oriented
or biaxially stretched film is available.
Transition Temperatures
The glass transition temperature is - 20 °C,
the crystalline melting temperature 198 °C.
CORPORATE TRAINING AND PLANNING
Optical Properties
PVF films are transparent to visible and UV
light.
In the infrared region radiation with
wavelengths between 7 and l2 mm is absorbed.
The refractive index n20D is 1.45. Three
optical axes must be differentiated for
oriented films.
CORPORATE TRAINING AND PLANNING
Chemical Properties
Resistance to Chemicals
PVF is resistant to acids, alkaline solutions and
many solvents at room temperature.
It is unaffected by boiling in carbon
tetrachloride, benzene, acetone and methyl
ethyl ketone.
The resistance lies between that of PTFE and
PCTFE.
CORPORATE TRAINING AND PLANNING
Flammability
PVF burns slowly, i.e. its fire performance is
somewhat poorer than that of PVC-U.
Toxicological Assessment
PVF is suitable for use with foodstuffs and
is physiologically inert.
CORPORATE TRAINING AND PLANNING
Processing-1
• PVF is supplied only as film.
• It can be compression molded.
• Cast film is made by pouring a mixture of 25 to
40% PVF and 75 to 60% dimethyl sulfoxide on
to a platen and heating to 130 °C for a short
time.
• The paste-like mixture can also be extruded in
hot oil at 160°C.
• PVF films can be welded by heat impulse or high
frequency.
CORPORATE TRAINING AND PLANNING
Processing-2
• Organosols (g-butyrolactone) can also be
extruded in a water bath.
• High transparency films are obtained by
briefly heating the film to 250 °C and
quenching rapidly.
• Biaxial stretching is carried out in warm
solvents (g-butyrolactone, dimethyl
acetamide).
• PVF films can be welded by heat impulse or
high frequency.
CORPORATE TRAINING AND PLANNING
Typical Applications
The high weathering resistance of PVF makes
it suitable for outdoor use as roof covering,
cladding, pipe insulation, green houses, solar
collectors (transparent to UV).
Corrosion protection for metal panels, plywood
and insulating board, road signs, packaging
film, shrink tube.
CORPORATE TRAINING AND PLANNING
Trade Names
Kel-F (3M Co., US)
KF Piezo Film (Kureha Chem. Ind., IP)
Tedlar (Du Pont de Nemours, US)
CORPORATE TRAINING AND PLANNING
Further Reading
1. BRYDSON, J.A, Plastics Material, Butterworth
Heinemann, oxford, New Delhi (2005)
2. DOMININGHAUS.H, Plastics for Engineering,
Hanser publishers, Munich, New York (1998)
3. CHARLESS A . HARPER, Modern Plastics Hand
Book McGraw –Hill, New York (1999)
CORPORATE TRAINING AND PLANNING
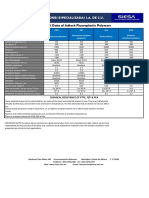
Table 1 Guide values of properties of Fluorine containing polymers
Properties Units PTFE FEP PCTFE PVF PVDF
Density g/cm3 2.15-2.20 2.12-2.17 2.10-2.12 1.38-1.57 1.7
Water absorption (23°C, 24h) % 0.04
Mechanical
Tensile strength N/mm2 25-36 22-28 32-40 49-127 46
Elongation at break % 350-550 250-330 128-175 115-250 100-400
Tensile modulus of elasticity N/mm2 408 350 1050-2110 1800 840
Notched impact strength Ft lb/in 3 No break 2.5-2.7 No break
Thermal
Melting Point °C 327 290 216 198 171
Service temperature short-term 300 250 180
in air
without mechanical long-term 250 205 150 150 100-120
loading
Glass transition temperature °C 127 45 -20 40
Heat deflection temperature °C 121 70 126
Coefficient of linear expansion between 0 and 100 80 60 20 85
K-1.10.-6
50°C
Specific heat capacity kJ/kg K 1.0 1.2 0.9
Thermal conductivity W/mK 0.25 0.25 0.22
Table 1 Guide values of properties of Fluorine containing polymers
Properties Units PTFE FEP PCTFE PVF PVDF
Electrical
Volume resistivity Wcm >1018 >2.1018 >1.20.1018 3.1013 2.1014
Surface resistance W 1017 1017 1016
Dielectric constant <2.1 2.1 2.3-2.7 8.5 7.72
Dissipation factor, tan d (103Hz) 0.0002 0.0002 0.023-0.027 0.015 0.018
Dielectric strength kV/mm 600-800 800 450-550
Tracking resistance class C 600 600 600
Flammability (ASTM D65) Non flammable Non flammable Non flammable Non flammable Non flammable
Clarity opaque Transparent -
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Polyvinylchloride — 2: Main Lectures Presented at the Second International Symposium on Polyvinylchloride, Lyon-Villeurbanne, France, 5 - 9 July 1976Von EverandPolyvinylchloride — 2: Main Lectures Presented at the Second International Symposium on Polyvinylchloride, Lyon-Villeurbanne, France, 5 - 9 July 1976A. GuyotNoch keine Bewertungen
- PeekDokument23 SeitenPeekwamikshahidrizviNoch keine Bewertungen
- Poly Phenylene Oxide (PPO) : Corporate Training and PlanningDokument27 SeitenPoly Phenylene Oxide (PPO) : Corporate Training and PlanningAkash YadavNoch keine Bewertungen
- ETFE Vs ECTFE PDFDokument2 SeitenETFE Vs ECTFE PDFpinkNoch keine Bewertungen
- Vitralit 1650 English Tds Panacol AdhesiveDokument4 SeitenVitralit 1650 English Tds Panacol Adhesivetito3007Noch keine Bewertungen
- Teflon (PTFE) Data SheetDokument1 SeiteTeflon (PTFE) Data SheetMarisa Yuni Nur AzizaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Technical Data Sheet Teflon (Ptfe) : (Polytetrafluoroethylene Resin)Dokument1 SeiteTechnical Data Sheet Teflon (Ptfe) : (Polytetrafluoroethylene Resin)Dharmendra DubeyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Epofine 184-Finehard 907 - Acc 062Dokument4 SeitenEpofine 184-Finehard 907 - Acc 062Karishma PrabhuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Epofine 205 - Finehard 905 - Flex 040 - Acc 061Dokument4 SeitenEpofine 205 - Finehard 905 - Flex 040 - Acc 061Karishma PrabhuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Epofine 221 - Finehard 964 - Accelerator 070Dokument4 SeitenEpofine 221 - Finehard 964 - Accelerator 070Karishma PrabhuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Technical Data of Adtech Fluoroplastic Polymers: Servicios E Importaciones Especializadas S.A. de C.VDokument1 SeiteTechnical Data of Adtech Fluoroplastic Polymers: Servicios E Importaciones Especializadas S.A. de C.VEdgar LucianoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Exact 8201Dokument2 SeitenExact 8201Kashif MuhammadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Epofine 6071A80/ Finecure 197/ Finecure 190/ Finehard 986/ Accelerator 062 Toughened PrepregDokument5 SeitenEpofine 6071A80/ Finecure 197/ Finecure 190/ Finehard 986/ Accelerator 062 Toughened PrepregKarishma PrabhuNoch keine Bewertungen
- UHMW Mechanical Properties: Comparison of Dynamic Coefficient of Friction On Polished SteelDokument4 SeitenUHMW Mechanical Properties: Comparison of Dynamic Coefficient of Friction On Polished SteeldangdinhthyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Repsol Alcudia PE046Dokument1 SeiteRepsol Alcudia PE046armandoestavanquitoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Manual Tecnico de Tuberias de PVC y CPVC-GFDokument48 SeitenManual Tecnico de Tuberias de PVC y CPVC-GFluis claudio c, vieiraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Geomat Tech Data SheetDokument1 SeiteGeomat Tech Data SheetclangatNoch keine Bewertungen
- HFX 500P Rev 6 - 2018 PDFDokument2 SeitenHFX 500P Rev 6 - 2018 PDFMuhammad Shabbir AwanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Colpoly 7172 TDSDokument2 SeitenColpoly 7172 TDSKristjan PosavecNoch keine Bewertungen
- Data Sheet Schott® Borofloat: Chemical PropertiesDokument2 SeitenData Sheet Schott® Borofloat: Chemical PropertiesDiego SaenzNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2.slide 1Dokument52 Seiten2.slide 1Radhashyam GiriNoch keine Bewertungen
- ABS N Fisa TehnicaDokument1 SeiteABS N Fisa TehnicaFloare de PrimavaraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Polyethylene Properties - VinidexDokument8 SeitenPolyethylene Properties - VinidexalexNoch keine Bewertungen
- Engineering Materials Data SheetDokument6 SeitenEngineering Materials Data Sheetrajarao1234Noch keine Bewertungen
- Ultradur: Product InformationDokument3 SeitenUltradur: Product InformationirisNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ultradur B2520Dokument2 SeitenUltradur B2520Phung LucNoch keine Bewertungen
- Colpoly 739 S TDSDokument2 SeitenColpoly 739 S TDSKristjan PosavecNoch keine Bewertungen
- PPO SlideDokument29 SeitenPPO SlideRadhashyam GiriNoch keine Bewertungen
- 4x-Datasheet BONDiT B-481Dokument4 Seiten4x-Datasheet BONDiT B-481Marco BrolloNoch keine Bewertungen
- Epofine 556 FR/ FInehard 951Dokument3 SeitenEpofine 556 FR/ FInehard 951Karishma Prabhu100% (1)
- En Iso Mattex Geomatt TB - I-25!08!2013Dokument1 SeiteEn Iso Mattex Geomatt TB - I-25!08!2013FarhatNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fluon® ETFE Film - Advanced Fluoropolymer Film-V0.1Dokument10 SeitenFluon® ETFE Film - Advanced Fluoropolymer Film-V0.1White_rabbit2885764Noch keine Bewertungen
- F F O P L: Epofine - 205 / Finehard - 951Dokument3 SeitenF F O P L: Epofine - 205 / Finehard - 951Karishma PrabhuNoch keine Bewertungen
- F F O P L: Epofine - 740 / Finehard - 918 / Accelerator - 062Dokument4 SeitenF F O P L: Epofine - 740 / Finehard - 918 / Accelerator - 062Karishma Prabhu100% (1)
- Pds Ready T4plus Int enDokument2 SeitenPds Ready T4plus Int endafaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Technical Data Sheet G-10: General DescriptionDokument1 SeiteTechnical Data Sheet G-10: General Descriptionbahtiar affandyNoch keine Bewertungen
- 15 Processing of Refractory Carbides An 1996 Handbook of Refractory CarbidDokument33 Seiten15 Processing of Refractory Carbides An 1996 Handbook of Refractory CarbidWilson SCKUDLAREKNoch keine Bewertungen
- Epofine 556 - Finehard 22962Dokument5 SeitenEpofine 556 - Finehard 22962Karishma PrabhuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Elantas 50VTDokument4 SeitenElantas 50VTAjay AbrahamNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2017 Kynar Wire and Cable SolutionsDokument8 Seiten2017 Kynar Wire and Cable SolutionsKaarthicNatarajanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ace Mersen Armylor 2 Ptfe Pfa Lined Pipes DinDokument32 SeitenAce Mersen Armylor 2 Ptfe Pfa Lined Pipes DinClaire GrecoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Epofine 404 - Finehard 2404Dokument3 SeitenEpofine 404 - Finehard 2404Karishma PrabhuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pala 652 e 02 15Dokument3 SeitenPala 652 e 02 15Carmen LinaresNoch keine Bewertungen
- Halene - H : Technical Data SheetDokument1 SeiteHalene - H : Technical Data SheetDaya Shanker PalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Teflon Af Product InfoDokument3 SeitenTeflon Af Product Infod5969660Noch keine Bewertungen
- Ultradur® B 6550 LN en SI - Product DatasheetDokument2 SeitenUltradur® B 6550 LN en SI - Product Datasheetnoto.sugiartoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Colpoly 7167 TDSDokument2 SeitenColpoly 7167 TDSKristjan PosavecNoch keine Bewertungen
- Colpoly 7167 8A TDSDokument2 SeitenColpoly 7167 8A TDSKristjan PosavecNoch keine Bewertungen
- Winpower International Limited: ApplicationDokument2 SeitenWinpower International Limited: ApplicationAHMED YOUSEFNoch keine Bewertungen
- Iso Dis 23936-2appendix+a08Dokument33 SeitenIso Dis 23936-2appendix+a08Abel Lopez JoachinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Colpoly 768 TDSDokument2 SeitenColpoly 768 TDSKristjan PosavecNoch keine Bewertungen
- Spacesaver: Thermal Insulation For Pitched Roof Joist ApplicationsDokument2 SeitenSpacesaver: Thermal Insulation For Pitched Roof Joist ApplicationsAlex RNoch keine Bewertungen
- Epofine 740 - Finehard 5200Dokument4 SeitenEpofine 740 - Finehard 5200Karishma PrabhuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Barniz DolpsDokument3 SeitenBarniz DolpsCordero FranciscoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Colpoly 736 WAT TDSDokument2 SeitenColpoly 736 WAT TDSKristjan PosavecNoch keine Bewertungen
- UHMWPE ProductsDokument4 SeitenUHMWPE Productsmchan1965Noch keine Bewertungen
- Huamei Spec Sheets - 2018Dokument1 SeiteHuamei Spec Sheets - 2018Phan LongNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ultramid A3X2G5 Crni PDFDokument2 SeitenUltramid A3X2G5 Crni PDFOvidiu ChertesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Technical Data Sheet Polycarbonate: Benefits ApplicationsDokument2 SeitenTechnical Data Sheet Polycarbonate: Benefits ApplicationsjackNoch keine Bewertungen
- Product Data Sheet: EnglishDokument3 SeitenProduct Data Sheet: EnglishsyamprasadNoch keine Bewertungen
- 0 0 20 May 2015 1624470301PFR ManavChemicals PDFDokument16 Seiten0 0 20 May 2015 1624470301PFR ManavChemicals PDFAkash YadavNoch keine Bewertungen
- Trevor Pope. Stator Rubber Innovation Vs ApplicationDokument11 SeitenTrevor Pope. Stator Rubber Innovation Vs ApplicationAkash YadavNoch keine Bewertungen
- Astm8.3 Plastic PDFDokument206 SeitenAstm8.3 Plastic PDFAkash YadavNoch keine Bewertungen
- D3574 11 PDFDokument149 SeitenD3574 11 PDFAkash YadavNoch keine Bewertungen
- Short-Chain Chlorinated Paraffins (SCCPS) PDFDokument11 SeitenShort-Chain Chlorinated Paraffins (SCCPS) PDFAkash YadavNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chlorinated Paraffin Wax - Manufacturing Plant PDFDokument6 SeitenChlorinated Paraffin Wax - Manufacturing Plant PDFAkash Yadav0% (1)
- Effect of Metal Oxides As AcivatorDokument13 SeitenEffect of Metal Oxides As AcivatorAkash YadavNoch keine Bewertungen
- Is 10810 10 1984 PDFDokument6 SeitenIs 10810 10 1984 PDFAkash YadavNoch keine Bewertungen
- Akrochem Perioxide Comparison HalfDokument1 SeiteAkrochem Perioxide Comparison HalfAkash YadavNoch keine Bewertungen
- Coupling: SilaneDokument5 SeitenCoupling: SilaneAkash YadavNoch keine Bewertungen
- Blend Term DefinitionDokument14 SeitenBlend Term DefinitionAkash YadavNoch keine Bewertungen
- Urea & Melamine Formaldehyde ResinsDokument33 SeitenUrea & Melamine Formaldehyde ResinsAkash Yadav50% (2)
- CH CH CH - CH CL CL N N: PolymerizationDokument40 SeitenCH CH CH - CH CL CL N N: PolymerizationAkash YadavNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sector Wise End Use Applications of Plastics: Corporate Training and PlanningDokument24 SeitenSector Wise End Use Applications of Plastics: Corporate Training and PlanningAkash YadavNoch keine Bewertungen
- Part B - Type Questions: Corporate Training and PlanningDokument19 SeitenPart B - Type Questions: Corporate Training and PlanningAkash YadavNoch keine Bewertungen
- Epoxy Resins: Corporate Training and PlanningDokument53 SeitenEpoxy Resins: Corporate Training and PlanningAkash YadavNoch keine Bewertungen
- AdditivesDokument148 SeitenAdditivesAkash Yadav100% (2)
- Unsaturated Polyester1 ResinsDokument74 SeitenUnsaturated Polyester1 ResinsAkash YadavNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bonding of Untreated Cellulose Fibers To Natural RubberDokument10 SeitenBonding of Untreated Cellulose Fibers To Natural RubberAkash YadavNoch keine Bewertungen
- AdditivesDokument148 SeitenAdditivesAkash Yadav100% (2)
- CH CH C CH CH - C N N: PolymerizationDokument16 SeitenCH CH C CH CH - C N N: PolymerizationAkash YadavNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tensile and Tear Behavior of Anisotropic Double Networks of A Black-Filled Natural Rubber VulcanizateDokument15 SeitenTensile and Tear Behavior of Anisotropic Double Networks of A Black-Filled Natural Rubber VulcanizateAkash YadavNoch keine Bewertungen
- Viton Related Chemicals Handling PrecautionsDokument22 SeitenViton Related Chemicals Handling PrecautionsrplNoch keine Bewertungen
- AkasDokument12 SeitenAkasAkash YadavNoch keine Bewertungen
- PPG Aerospace Ca70451Dokument2 SeitenPPG Aerospace Ca70451aldiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Material For Handling Chlorine ChemicalsDokument38 SeitenMaterial For Handling Chlorine ChemicalsanishsrNoch keine Bewertungen
- Design of RCC PierDokument10 SeitenDesign of RCC Piervijayunity40% (5)
- Assignment Base On: Study On Some Fabric Faults During Processing.Dokument5 SeitenAssignment Base On: Study On Some Fabric Faults During Processing.MD Nazrul IslamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Periodic Table of ElementsDokument1 SeitePeriodic Table of ElementsNicola ViradorNoch keine Bewertungen
- Armaflex Tube Insulation CatalogueDokument4 SeitenArmaflex Tube Insulation CatalogueRiyas UdheenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Laser Plastic Welding 101Dokument30 SeitenLaser Plastic Welding 101Josh BrownNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ancon - Masonry Support PDFDokument38 SeitenAncon - Masonry Support PDFESNoch keine Bewertungen
- Corrosion Resistance of Surface Treated 42crmo4 Steel: D. Kusmič, V. Hrubý, L. BachárováDokument6 SeitenCorrosion Resistance of Surface Treated 42crmo4 Steel: D. Kusmič, V. Hrubý, L. BachárovárachidradouaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- What Is The Difference Between The Hardness, Toughness, Resilience, and Stiffness of Materials - QuoraDokument5 SeitenWhat Is The Difference Between The Hardness, Toughness, Resilience, and Stiffness of Materials - QuoraUdit AgarwalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Astm E1131 08 Tga PDFDokument5 SeitenAstm E1131 08 Tga PDFThomas Sørensen Quaade100% (1)
- Group 13 Occurrences, Extraction and Uses (Multiple Choice)Dokument3 SeitenGroup 13 Occurrences, Extraction and Uses (Multiple Choice)kionaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Column JacketingDokument3 SeitenColumn Jacketinganonymousupldr666100% (1)
- Complete Amphetamine SyntheseDokument14 SeitenComplete Amphetamine Synthesejtbrownstone100% (2)
- Unomax - Catalogue (300922) - CompressedDokument79 SeitenUnomax - Catalogue (300922) - Compressedkarthik_jsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chicken LonganisaDokument3 SeitenChicken LonganisaLemuel Jr MitchaoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Effects of Mineralogy On Thermo-Hydro-Mechanical Parameters of MX80 BentoniteDokument6 SeitenEffects of Mineralogy On Thermo-Hydro-Mechanical Parameters of MX80 BentonitemazharNoch keine Bewertungen
- MIL-H-6875H Heat Treatment of Steel, Process For (SS by SAE-AMS-H-6875)Dokument29 SeitenMIL-H-6875H Heat Treatment of Steel, Process For (SS by SAE-AMS-H-6875)320338100% (4)
- Fastmarkets Risi Price Assessments All Forest MarketsDokument287 SeitenFastmarkets Risi Price Assessments All Forest MarketsAkil KaziNoch keine Bewertungen
- Exxon IP 5-3-1 Pressure Testing of Unfired Pressure VesselsDokument2 SeitenExxon IP 5-3-1 Pressure Testing of Unfired Pressure Vesselshcsharma1967Noch keine Bewertungen
- Fibres PPT 1Dokument19 SeitenFibres PPT 1rajesh duaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Widening EstimateDokument76 SeitenWidening EstimateSangram MundeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tyre PyrolysisDokument12 SeitenTyre PyrolysisviswamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Water Treatment Management - Quality ControlDokument6 SeitenWater Treatment Management - Quality ControlChilaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Research On Distinctive Classifications and Mitigation of Shrinkage in Prestressed ConcreteDokument31 SeitenResearch On Distinctive Classifications and Mitigation of Shrinkage in Prestressed ConcreteFlorence AgsaludNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lab Ex 6 FinalDokument6 SeitenLab Ex 6 FinalPytharix CaineNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fosroc Cemtop GP Advanced SpecDokument2 SeitenFosroc Cemtop GP Advanced SpecmrameshceNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Study On Durability Properties of Geopolymer Concrete Using Flyash and GgbsDokument13 SeitenA Study On Durability Properties of Geopolymer Concrete Using Flyash and Ggbsbala rajuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Reinforced Concrete and Masonry StructurDokument821 SeitenReinforced Concrete and Masonry StructurHarley FrenchNoch keine Bewertungen
- Threading Inserts: Now in To Conquer ISO S MaterialsDokument32 SeitenThreading Inserts: Now in To Conquer ISO S MaterialsAchmad Arifudin HidayatullohNoch keine Bewertungen