Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Molecular Structure and Bonding Types
Hochgeladen von
asimshiekh0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
9 Ansichten15 Seitenit is about chemistry presentation
Originaltitel
Chemistry
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
PPTX, PDF, TXT oder online auf Scribd lesen
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenit is about chemistry presentation
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als PPTX, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
9 Ansichten15 SeitenMolecular Structure and Bonding Types
Hochgeladen von
asimshiekhit is about chemistry presentation
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als PPTX, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
Sie sind auf Seite 1von 15
Structure of molecules
Why atoms react
Chemical bonds
Types of bonds
Intermolecular forces
Nature of bonding and properties
Chemical bond
• Force of attraction between atoms that holds
them together
• Octet rule
• Duplet rule
• 3-ways to complete octet
Types of chemical bonds
• Ionic bond
• Colvalent bond
• Coordinate covalent bond
• Metallic bond
Ionic bond
• The bond which forms by complete transfer of
electron from one atom to another atom
• NaCl
• Na (Ne)
• Cl(Ar)
• Exo
Covalent bond
• The bond which is formed by mutual sharing of
electrons is called covalent bond
• Types
• 1)single covalent bond
• H2,Cl2,CH4 etc
• 2)double covalent bond
• O2,C2H4 etc
• 3)triple covalent bond
• N2,C2H2 etc
• Coordinate covalent bond
• The bond in which bond pair is donated by
only one bonded atom
• Acceptor
• Donor
• NH4,NH3+BF3
Polar and non polar covalent bond
• Non polar
• Covalent bond between 2 similar atoms
• H2, Cl2 etc
• Polar
• Covalent bond between 2 different atoms
• HCl,H2O etc
• Ionic or covalent
• Electronegativity difference 1.7
Metallic bond
• The bond between metal atoms due to free
electrons
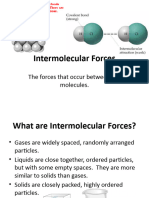
Intermolecular forces
• The weak forces between molecules are called
intermolecular forces
• HCll 17 kj HClg
• 430 kj to break chemical bond
Dipole dipole interaction
• When partial positive and partial nagative
molecules locate at different positions they
arranged themselves in way that partial
positive charge attract partial nagative charge
and the force exist is dipole dipole interaction
• HCl
Hydrogen bonding
• When partially positive charged hydrogen
atom of one molecule attracts and forms a
bond with the partially negatively charged
atom of the other molecule the bonding is
called hydrogen bonding
• H2O etc
• Physical properties water and alcohol boiling
points
• Ice and water density
Nature of bonding and properties
• Ionic bond
• Properties
• Crystalline solids
• Conductance
• High melting and boiling points
• Solubility
Covalent bond
• Properties
• Low melting and boiling points
• Solubility
• Conductance
• Large molecules have high melting and boiling
points
Polar and non polar compounds
• Conductance
• Solubility
Coordinate covalent compounds
• Solubility
• Rigid
• Metals properties
• Maleable and ductile
• Cations
• Conductors
• High melting and boiling points
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Turbo Generator Project ReportDokument40 SeitenTurbo Generator Project Reportthegopal100% (2)
- 66kv Earthing System R-1 (For Print Out)Dokument8 Seiten66kv Earthing System R-1 (For Print Out)g_nraja100% (1)
- Polar Bonds and Polar MoleculesDokument29 SeitenPolar Bonds and Polar Moleculesshin100% (1)
- Retainingwall bs8110Dokument11 SeitenRetainingwall bs8110unionewNoch keine Bewertungen
- GSNH Science Lessons on ElectricityDokument4 SeitenGSNH Science Lessons on ElectricityMaám Rosemary B. LandanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Carbon Compounds and Chemical Bonds Chm457Dokument83 SeitenCarbon Compounds and Chemical Bonds Chm457kumukhrizNoch keine Bewertungen
- INTRODUCTION TO CHEMICAL BONDINGDokument96 SeitenINTRODUCTION TO CHEMICAL BONDINGgsharkzNoch keine Bewertungen
- IM ForcesDokument46 SeitenIM ForcesdanielayskiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chemical Bond & Molecular GeometryDokument129 SeitenChemical Bond & Molecular GeometryAlexNoch keine Bewertungen
- Practicaldistillationcontrol 140307141500 Phpapp01Dokument549 SeitenPracticaldistillationcontrol 140307141500 Phpapp01syedmuhammadtariqueNoch keine Bewertungen
- Solids, Liquids, Gases, ReviewDokument5 SeitenSolids, Liquids, Gases, ReviewnettextsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ionic, Covalent and Metallic Bonding ExplainedDokument21 SeitenIonic, Covalent and Metallic Bonding ExplainedMustafa ghazanfarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bonding TheoriesDokument31 SeitenBonding TheoriesMatthew HallNoch keine Bewertungen
- CHM1102 - Lecture 15 BondingDokument17 SeitenCHM1102 - Lecture 15 BondingEwartNoch keine Bewertungen
- Diploma in Engineering: Chemistry Covalent BondingDokument18 SeitenDiploma in Engineering: Chemistry Covalent BondingOscar Kelvin NsituNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2 Chemical Bonding 1Dokument78 Seiten2 Chemical Bonding 1MilanellePintoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bonding & Chemical Interactions GuideDokument13 SeitenBonding & Chemical Interactions Guidehussein MohammedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lewis Acids and BasesDokument7 SeitenLewis Acids and BasesGrad OanaNoch keine Bewertungen
- IMFA and Chemical BondingDokument137 SeitenIMFA and Chemical BondingEnna SertNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physical Science Lesson 2 - Intramolecular Forces of AttractionDokument26 SeitenPhysical Science Lesson 2 - Intramolecular Forces of Attractionrainjarrenperegrino13298Noch keine Bewertungen
- Chemical Bonds: Lecturer: Dr. Yayooo Course Title: Organic ChemistryDokument50 SeitenChemical Bonds: Lecturer: Dr. Yayooo Course Title: Organic Chemistryyayooo200450% (2)
- AS Chemistry - States of MatterDokument25 SeitenAS Chemistry - States of MatterwilsonconcepcionNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chemical Bonding (Ionic and Covalent Bond)Dokument32 SeitenChemical Bonding (Ionic and Covalent Bond)Krystene coronelNoch keine Bewertungen
- ChemistryDokument8 SeitenChemistryVvnikovNoch keine Bewertungen
- Intermolecular Forces Explaining Liquid PropertiesDokument49 SeitenIntermolecular Forces Explaining Liquid PropertiesdNoch keine Bewertungen
- Intermolecular ForcesDokument17 SeitenIntermolecular ForcesNursherina AsanjiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture 1 114Dokument20 SeitenLecture 1 114rakingbulugbe194Noch keine Bewertungen
- Kimia Kristal - 1Dokument37 SeitenKimia Kristal - 1Wana KimhanbinNoch keine Bewertungen
- 3.2 Chemical BondsDokument13 Seiten3.2 Chemical BondsKenix ChanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chemical Bonding: Second Year ScienceDokument20 SeitenChemical Bonding: Second Year Scienceapi-406307933Noch keine Bewertungen
- CHEM111 Week 4.2 - Chemical Bonds and Compounds Part 2 - Covalent Bond ModelDokument17 SeitenCHEM111 Week 4.2 - Chemical Bonds and Compounds Part 2 - Covalent Bond ModelKharl Roei SalvadorNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture 3Dokument32 SeitenLecture 3Quang TrườngNoch keine Bewertungen
- Non Metalic Substances and Covalent BondingDokument47 SeitenNon Metalic Substances and Covalent Bonding42h47n5zvrNoch keine Bewertungen
- CP The Covalent BondDokument13 SeitenCP The Covalent BondShielo Marie CardinesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Covalent BondingDokument26 SeitenCovalent BondinghahaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chemistry Module TwoDokument111 SeitenChemistry Module TwoGreg YianniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Topic 3 Chemical BondDokument26 SeitenTopic 3 Chemical BondAidah HanidaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Engineering MaterialsDokument24 SeitenEngineering MaterialsBakhtyar AhmedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chemistry Exam Notes Semester 2Dokument37 SeitenChemistry Exam Notes Semester 2AnjaliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chemical BondingDokument37 SeitenChemical BondingJenifer TaniaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Structure and BondingDokument72 SeitenStructure and BondingUnknownKidNoch keine Bewertungen
- NSSCAS Chemistry Theme 1 Topic 1.3 - Updated 20 October 2020Dokument59 SeitenNSSCAS Chemistry Theme 1 Topic 1.3 - Updated 20 October 2020Peter KudumoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Week 2 - Compounds and Chemical BondsDokument35 SeitenWeek 2 - Compounds and Chemical BondsKaye Selene Raphaelle SyNoch keine Bewertungen
- BondingDokument39 SeitenBondingKen LiNoch keine Bewertungen
- STRUCTURE AND BONDING PowerPoint For Fourth Form.Dokument54 SeitenSTRUCTURE AND BONDING PowerPoint For Fourth Form.tsteadmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- How Atoms BondDokument32 SeitenHow Atoms BondemilyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter - 4 Types of Chemical BondingDokument32 SeitenChapter - 4 Types of Chemical BondingMadhur ShrivastavaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Polar and Nonpolar Bonds ExplainedDokument11 SeitenPolar and Nonpolar Bonds ExplainedJoseph Patrick F MaglaqueNoch keine Bewertungen
- Result CardDokument52 SeitenResult CardfoziaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chemical Components and Bonds in CellsDokument29 SeitenChemical Components and Bonds in Cellsmina catNoch keine Bewertungen
- Building Blocks of MatterDokument18 SeitenBuilding Blocks of MatterPaul AckermannNoch keine Bewertungen
- Technical English IDokument52 SeitenTechnical English IeleazarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Covalent Bonding QuestionsDokument31 SeitenCovalent Bonding QuestionsSU CHENG LAM, CAREY F4S (36)Noch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 1: Organic Chemistry IntroductionDokument66 SeitenChapter 1: Organic Chemistry IntroductionmissyashimNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chemical BondingDokument14 SeitenChemical BondingMarisol BravoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chemical Bonding/ Macromolecules: Dr. BryanDokument72 SeitenChemical Bonding/ Macromolecules: Dr. BryanAlisha WallerNoch keine Bewertungen
- NOTES - 8.4 - Polar Bonds - NEW - SlideshowDokument34 SeitenNOTES - 8.4 - Polar Bonds - NEW - SlideshowElsayed ElazazyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Types of Chemical Bonds ExplainedDokument24 SeitenTypes of Chemical Bonds ExplainedRamon EnsendenciaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Module 3: Chemical Bonding and NomenclatureDokument11 SeitenModule 3: Chemical Bonding and NomenclatureJay Mark CapanangNoch keine Bewertungen
- Atomic BondingDokument19 SeitenAtomic BondingSabir AliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chemical BondingDokument22 SeitenChemical BondingshamsvocesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Intermolecular ForcesDokument16 SeitenIntermolecular Forcesmaricon pocheNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1 NotesDokument8 Seiten1 NotesillegiblecaptchaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chemical BondingDokument25 SeitenChemical Bondingmaxwell amponsahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chemical Bonding: Understanding The Forces that Hold Molecules Together.Von EverandChemical Bonding: Understanding The Forces that Hold Molecules Together.Noch keine Bewertungen
- PT2.3 Mirrors Answer SheetDokument6 SeitenPT2.3 Mirrors Answer SheetMarionne HerreraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physics 4 O LevelDokument3 SeitenPhysics 4 O LevelChrispin Msofe100% (1)
- Introduction to Structural AnalysisDokument2 SeitenIntroduction to Structural AnalysisMelvin EsguerraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Novel Procedure For Coproduction of Ethyl Acetate and N-ButylDokument7 SeitenNovel Procedure For Coproduction of Ethyl Acetate and N-ButylYiğit ErkulNoch keine Bewertungen
- Psychrometric Charts (Humidity Chart)Dokument7 SeitenPsychrometric Charts (Humidity Chart)ccami709Noch keine Bewertungen
- Ac GeneratorDokument2 SeitenAc Generatoryashwanth.s10aNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Critical Analysis of The Erasmus Bridge:: Christopher J. HewettDokument10 SeitenA Critical Analysis of The Erasmus Bridge:: Christopher J. HewettAndik Mardiyanto MellodyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Graph of ProjectileDokument9 SeitenGraph of ProjectileMd AzharuddinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Max Xi Ma CatalogDokument64 SeitenMax Xi Ma CatalogAngel GuillormeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Math2089 (Num) NotesDokument14 SeitenMath2089 (Num) NotesHellen ChenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lab Report 5Dokument9 SeitenLab Report 5Leo Marcelo Villalba100% (1)
- Electrochemical Determination of Gatifloxacin, Moxifloxacin and Sparfloxacin Fluoroquinolonic Antibiotics On Glassy Carbon Electrode in Pharmaceutical FormulationsDokument4 SeitenElectrochemical Determination of Gatifloxacin, Moxifloxacin and Sparfloxacin Fluoroquinolonic Antibiotics On Glassy Carbon Electrode in Pharmaceutical FormulationsEmilia Peralta MolinaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bridgmanita PDFDokument2 SeitenBridgmanita PDFAnibal Urango AlcantaraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction to Computer Graphics ApplicationsDokument11 SeitenIntroduction to Computer Graphics ApplicationsSachin NarangNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ball Screw General CatalogDokument490 SeitenBall Screw General CatalogMax NovaxNoch keine Bewertungen
- Optical CommunicationDokument5 SeitenOptical CommunicationSaiviswanth BoggarapuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Caterpillar ELC Coolant Longest PerformanceDokument2 SeitenCaterpillar ELC Coolant Longest PerformancePETROTECHMECONoch keine Bewertungen
- D Flip FlopDokument5 SeitenD Flip FlopNaveen Kumar RavillaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction and Basic Concepts: Fluid Mechanics: Fundamentals and ApplicationsDokument21 SeitenIntroduction and Basic Concepts: Fluid Mechanics: Fundamentals and ApplicationsAhmedalaal LotfyNoch keine Bewertungen
- DIRECT SHEAR TEST TITLEDokument19 SeitenDIRECT SHEAR TEST TITLESaid-Mansour MohamedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Earth Air Heat Exchanger PerformanceDokument4 SeitenEarth Air Heat Exchanger Performanceviraj shettyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Donkr Rational Bankroll Management Part2Dokument7 SeitenDonkr Rational Bankroll Management Part2kustad33Noch keine Bewertungen
- Daftar PustakaDokument7 SeitenDaftar PustakaUlul AlbabNoch keine Bewertungen
- 11 Multicomponent Distillation Case StudyDokument12 Seiten11 Multicomponent Distillation Case StudyTNoch keine Bewertungen
- WaterFlowMeter Catalogue PDFDokument2 SeitenWaterFlowMeter Catalogue PDFjaianit89Noch keine Bewertungen