Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Revenue Cycle
Hochgeladen von
Nurrin DarOriginaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Revenue Cycle
Hochgeladen von
Nurrin DarCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Chapter 12
The Revenue Cycle: Sales to Cash Collections
Copyright © 2012 Pearson Education
12-1
Learning Objectives
Describe the basic business activities and related
information processing operations performed in the
revenue cycle.
Discuss the key decisions that need to be made in the
revenue cycle, and identify the information needed to
make those decisions.
Identify major threats in the revenue cycle, and evaluate
the adequacy of various control procedures for dealing
with those threats.
Copyright © 2012 Pearson Education 12-2
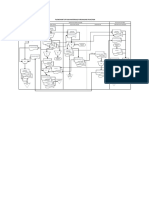
The Revenue Cycle
Copyright © 2012 Pearson Education 12-3
The Revenue Cycle
Provides goods and services to customers
Collects cash in payment for those sales
Primary Objective:
Provide the right product
In the right place
At the right time for the right price
Copyright © 2012 Pearson Education 12-4
Revenue Cycle Activities
1. Sales order entry
2. Shipping
3. Billing
4. Cash collections
Copyright © 2012 Pearson Education 12-5
General Revenue Cycle Threats
Inaccurate or invalid master data
Unauthorized disclosure of sensitive information
Loss or destruction of master data
Poor performance
Copyright © 2012 Pearson Education 12-6
General Revenue Cycle Controls
Data processing integrity controls
Restriction of access to master data
Review of all changes to master data
Access controls
Encryption
Backup and disaster recovery procedures
Managerial reports
Copyright © 2012 Pearson Education 12-7
Sales Order Entry
1. Take order
2. Check and approve credit
3. Check inventory availability
Copyright © 2012 Pearson Education 12-8
Sales Order Threats
Incomplete/inaccurate orders
Invalid orders
Uncollectible accounts
Stockouts or excess inventory
Loss of customers
Copyright 2012 © Pearson Education 12-9
Sales Order Entry Controls
Data entry edit controls (see Perpetual inventory control
Chapter 10) system
Restriction of access to Use of bar-codes or RFID
master data
Training
Digital signatures or written
signatures Periodic physical counts of
inventory
Credit limits
Sales forecasts and activity
Specific authorization to reports
approve sales to new
customers or sales that CRM systems, self-help Web
exceed a customer’s credit sites, and proper evaluation
limit of customer service ratings
Aging of accounts
receivable
Copyright © 2012 Pearson Education 12-10
Shipping
1. Picking and packing the order
2. Shipping the order
Copyright © 2012 Pearson Education 12-11
Shipping Threats
Picking the wrong items or the wrong quantity
Theft of inventory
Shipping errors (delay or failure to ship, wrong quantities,
wrong items, wrong addresses, duplication)
Copyright © 2012 Pearson Education 12-12
Shipping Controls
Bar-code and RFID Reconciliation of shipping
technology documents with sales orders,
picking lists, and packing
Reconciliation of picking lists slips
to sales order details
Use RFID systems to identify
Restriction of physical delays
access to inventory
Data entry via bar-code
Documentation of all scanners and RFID
inventory transfers
Data entry edit controls (if
RFID and bar-code shipping data entered on
technology terminals)
Periodic physical counts of Configuration of ERP system
inventory and reconciliation to prevent duplicate
to recorded quantities shipments
Copyright © 2012 Pearson Education 12-13
Billing
1. Invoicing
2. Updating accounts receivable
Copyright © 2012 Pearson Education 12-14
Billing Threats
Failure to bill
Billing errors
Posting errors in accounts receivable
Inaccurate or invalid credit memos
Copyright © 2012 Pearson Education 12-15
Billing Controls
Separation of billing and Data entry controls
shipping functions
Reconciliation of batch totals
Periodic reconciliation of
invoices with sales orders, Mailing of monthly statements to
picking tickets, and shipping customers
documents
Reconciliation of subsidiary
Configuration of system to accounts to general ledger
automatically enter pricing data
Segregation of duties of credit
Restriction of access to pricing memo authorization from both
master data sales order entry and customer
account maintenance
Data entry edit controls
Configuration of system to block
Reconciliation of shipping credit memos unless there is
documents (picking tickets, bills either corresponding
of lading, and packing list) to documentation of return of
sales orders damaged goods or specific
authorization by management
Copyright © 2012 Pearson Education 12-16
Cash Collections Threats
1. Theft of cash
2. Cash flow problems
Copyright © 2012 Pearson Education 12-17
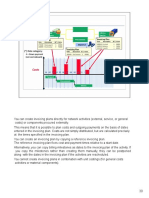
Cash Collection Controls
Separation of cash handling function from accounts receivable and credit functions
Regular reconciliation of bank account with recorded amounts by someone
independent of cash collections procedures
Use of EFT, FEDI, and lockboxes to minimize handling of customer payments by
employees
Prompt, restrictive endorsement of all customer checks
Having two people open all mail likely to contain customer payments
Use of cash registers
Daily deposit of all cash receipts
Lockbox arrangements, EFT, or credit cards
Discounts for prompt payment by customers
Cash flow budgets
Copyright © 2012 Pearson Education 12-18
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- The Operational Auditing Handbook: Auditing Business and IT ProcessesVon EverandThe Operational Auditing Handbook: Auditing Business and IT ProcessesBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (4)
- Accounting Information System A Complete Guide - 2020 EditionVon EverandAccounting Information System A Complete Guide - 2020 EditionBewertung: 1 von 5 Sternen1/5 (1)
- Bonds Payable by J. GonzalesDokument7 SeitenBonds Payable by J. GonzalesGonzales JhayVeeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Inventory valuation Complete Self-Assessment GuideVon EverandInventory valuation Complete Self-Assessment GuideBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1)
- Cash With AnsDokument6 SeitenCash With AnsHhhhhNoch keine Bewertungen
- At at 1st Preboard Oct08Dokument12 SeitenAt at 1st Preboard Oct08Czarina CasallaNoch keine Bewertungen
- At - (14) Internal ControlDokument13 SeitenAt - (14) Internal ControlLorena Joy Aggabao100% (2)
- Computerised Accounting Practice Set Using Xero Online Accounting: Australian EditionVon EverandComputerised Accounting Practice Set Using Xero Online Accounting: Australian EditionNoch keine Bewertungen
- ACT1202.Case Study 1 - StudentDokument6 SeitenACT1202.Case Study 1 - StudentKeight NuevaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 3 CISDokument20 SeitenChapter 3 CISGwen Sula LacanilaoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ais Chapter 4Dokument6 SeitenAis Chapter 4Pandu Rangarao100% (1)
- Click Here For Answers: ACC 400 Final ExamDokument4 SeitenClick Here For Answers: ACC 400 Final Examclickme12Noch keine Bewertungen
- Management Reporting A Complete Guide - 2019 EditionVon EverandManagement Reporting A Complete Guide - 2019 EditionNoch keine Bewertungen
- Naqdown FinalsDokument6 SeitenNaqdown FinalsMJ YaconNoch keine Bewertungen
- Apm Assignment 5 Team 6-1Dokument11 SeitenApm Assignment 5 Team 6-1Nicholas Mega100% (1)
- Operational Auditing A Complete Guide - 2021 EditionVon EverandOperational Auditing A Complete Guide - 2021 EditionNoch keine Bewertungen
- ch02 Beams10e TBDokument22 Seitench02 Beams10e TBbabycatine100% (3)
- 10.2 Using CaattsDokument38 Seiten10.2 Using CaattsPauline MercadoNoch keine Bewertungen
- KY-385 KUCHEF Multi-Cooker IM-V1.2Dokument40 SeitenKY-385 KUCHEF Multi-Cooker IM-V1.2al83rt777750% (2)
- Auditing Theory Test BankDokument26 SeitenAuditing Theory Test Bankdfgmlk dsdwNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 18 Policies Estimates and ErrorsDokument28 SeitenChapter 18 Policies Estimates and ErrorsHammad Ahmad100% (1)
- Chapter 14Dokument20 SeitenChapter 14Kad Saad67% (3)
- Romney Ais13 PPT 13Dokument11 SeitenRomney Ais13 PPT 13Aj PotXzs ÜNoch keine Bewertungen
- PSA-800 Special Consideration - Audits of FSs Prepared in Accord With Special Purpose FrameworksDokument18 SeitenPSA-800 Special Consideration - Audits of FSs Prepared in Accord With Special Purpose FrameworkscolleenyuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Corporate Financial Analysis with Microsoft ExcelVon EverandCorporate Financial Analysis with Microsoft ExcelBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (1)
- Topic 11 Audit of Payroll & Personnel CycleDokument14 SeitenTopic 11 Audit of Payroll & Personnel Cyclebutirkuaci100% (1)
- Hall Asia Edition PP - ch01Dokument41 SeitenHall Asia Edition PP - ch01Vince Paolo Alicaya AcidoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Auditing in Computer Environment in WordDokument2 SeitenAuditing in Computer Environment in WordLotte CabreraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 5. Audit of Investments, Hedging Instruments, and Related Revenues - Handout - T21920 (Final)Dokument9 SeitenUnit 5. Audit of Investments, Hedging Instruments, and Related Revenues - Handout - T21920 (Final)Alyna JNoch keine Bewertungen
- Accounting Information SystemDokument12 SeitenAccounting Information Systembea6089Noch keine Bewertungen
- Value Chain Management Capability A Complete Guide - 2020 EditionVon EverandValue Chain Management Capability A Complete Guide - 2020 EditionNoch keine Bewertungen
- 07 TQMDokument32 Seiten07 TQMimran27pk50% (2)
- CPA Review Notes 2019 - Audit (AUD)Von EverandCPA Review Notes 2019 - Audit (AUD)Bewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (10)
- Auditor - S Report Lecture NotesDokument4 SeitenAuditor - S Report Lecture NotesJosh TorcedoNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Difference Between Financial and Managerial AccountingDokument1 SeiteThe Difference Between Financial and Managerial AccountingJonna LynneNoch keine Bewertungen
- Specialized IndustriesDokument107 SeitenSpecialized IndustriesCristine Joyce ValdezNoch keine Bewertungen
- SYNTHESISDokument8 SeitenSYNTHESISMark Stanley PangoniloNoch keine Bewertungen
- Auditing QuestionsDokument10 SeitenAuditing Questionssalva8983Noch keine Bewertungen
- Atkinson Management Accounting 6eDokument22 SeitenAtkinson Management Accounting 6esalamoov100% (2)
- Auditing Pre Week Quizzer 2Dokument26 SeitenAuditing Pre Week Quizzer 2rascalflatts_16Noch keine Bewertungen
- Audit Evidence Multiple ChoiceDokument6 SeitenAudit Evidence Multiple Choicerandom17341Noch keine Bewertungen
- 13 Positive Accounting Theory Bab XiiDokument18 Seiten13 Positive Accounting Theory Bab XiiasaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1.1 Assignment1 Internal Audit and The Audit Committee and Types of AuditDokument4 Seiten1.1 Assignment1 Internal Audit and The Audit Committee and Types of AuditXexiannaNoch keine Bewertungen
- AP04 05 Audit of IntangiblesDokument8 SeitenAP04 05 Audit of IntangibleseildeeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 1-7 - Tugas Kelompok Kelas BDokument3 SeitenChapter 1-7 - Tugas Kelompok Kelas BJana WrightNoch keine Bewertungen
- Auditing Expenditure CycleDokument16 SeitenAuditing Expenditure CycleShane Nuss RedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Auditors Report On Financial StatementDokument4 SeitenAuditors Report On Financial StatementKafonyi JohnNoch keine Bewertungen
- AIS01Dokument49 SeitenAIS01Fitriyah Az-zahraaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Legal Environment of Philippine Business and Management - Midterm ExaminationsDokument2 SeitenLegal Environment of Philippine Business and Management - Midterm ExaminationsMaanParrenoVillarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Topic 5a - Audit of Property - Plant and EquipmentDokument20 SeitenTopic 5a - Audit of Property - Plant and EquipmentLANGITBIRUNoch keine Bewertungen
- Substantive Tests of Transactions and Account Balances EditedDokument85 SeitenSubstantive Tests of Transactions and Account Balances EditedPiaElemos100% (2)
- 01 TQMDokument40 Seiten01 TQMimran27pk100% (1)
- Tugas Audit Forensik Week 14Dokument11 SeitenTugas Audit Forensik Week 14juppa Saroha Purba100% (2)
- Testbank Ch01 02 REV Acc STD PDFDokument7 SeitenTestbank Ch01 02 REV Acc STD PDFheldiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 16 Environmental CostDokument34 SeitenChapter 16 Environmental CostAngga100% (1)
- Financial Accounting I: Incoming 2 Year MAY 30 - 31, 2016Dokument27 SeitenFinancial Accounting I: Incoming 2 Year MAY 30 - 31, 2016Desteen StormNoch keine Bewertungen
- The East Pacific Merchandising Corporation vs. The Director of Patents and Luis P. PellicerDokument31 SeitenThe East Pacific Merchandising Corporation vs. The Director of Patents and Luis P. PellicerRalph HonoricoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Kuis PDFDokument4 SeitenKuis PDFZhay Anty0% (1)
- Ecoborder Brown L Shaped Landscape Edging (6-Pack) - The Home Depot CanadaDokument4 SeitenEcoborder Brown L Shaped Landscape Edging (6-Pack) - The Home Depot Canadaming_zhu10Noch keine Bewertungen
- Ccs (Conduct) RulesDokument3 SeitenCcs (Conduct) RulesKawaljeetNoch keine Bewertungen
- All Bom HC CircularsDokument55 SeitenAll Bom HC CircularsSkk IrisNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1st Quarterly Exam Questions - TLE 9Dokument28 Seiten1st Quarterly Exam Questions - TLE 9Ronald Maxilom AtibagosNoch keine Bewertungen
- Xxxxacca Kısa ÖzzetttDokument193 SeitenXxxxacca Kısa ÖzzetttkazimkorogluNoch keine Bewertungen
- AideD&D n5 Basse-Tour (Suite Pour Un Diamant)Dokument7 SeitenAideD&D n5 Basse-Tour (Suite Pour Un Diamant)Etan KrelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Walmart GRRDokument174 SeitenWalmart GRRPatricia DillonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Planning & Managing Inventory in Supply Chain: Cycle Inventory, Safety Inventory, ABC Inventory & Product AvailabilityDokument24 SeitenPlanning & Managing Inventory in Supply Chain: Cycle Inventory, Safety Inventory, ABC Inventory & Product AvailabilityAsma ShoaibNoch keine Bewertungen
- Capstone Project Final Report - PatanjaliDokument60 SeitenCapstone Project Final Report - PatanjaliSharvarish Nandanwar0% (1)
- Lessons 1 and 2 Review IBM Coursera TestDokument6 SeitenLessons 1 and 2 Review IBM Coursera TestNueNoch keine Bewertungen
- SBI ProjectDokument82 SeitenSBI Projectchandan sharmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Leonardo Roth, FLDokument2 SeitenLeonardo Roth, FLleonardorotharothNoch keine Bewertungen
- Investor PDFDokument3 SeitenInvestor PDFHAFEZ ALINoch keine Bewertungen
- Finacle - CommandsDokument5 SeitenFinacle - CommandsvpsrnthNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2018 Saln VangieDokument2 Seiten2018 Saln VangieWilliam BalalaNoch keine Bewertungen
- SHS Business Finance Chapter 2Dokument24 SeitenSHS Business Finance Chapter 2Ji BaltazarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pledge, REM, Antichresis DigestsDokument43 SeitenPledge, REM, Antichresis DigestsAnonymous fnlSh4KHIgNoch keine Bewertungen
- GADokument72 SeitenGABang OchimNoch keine Bewertungen
- Management Accounting Perspective: © Mcgraw-Hill EducationDokument12 SeitenManagement Accounting Perspective: © Mcgraw-Hill Educationabeer alfalehNoch keine Bewertungen
- Business CombinationDokument20 SeitenBusiness CombinationabhaybittuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Part 3 Toeic WritingDokument33 SeitenPart 3 Toeic WritingNguyen Thi Kim ThoaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Flowchart of Raw Materials Purchasing FunctionDokument1 SeiteFlowchart of Raw Materials Purchasing Function05. Ariya ParendraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tez PortalDokument1 SeiteTez Portalkiran BawadkarNoch keine Bewertungen
- SAP InvoiceDokument86 SeitenSAP InvoicefatherNoch keine Bewertungen
- How To Use Oracle Account Generator For Project Related TransactionsDokument40 SeitenHow To Use Oracle Account Generator For Project Related Transactionsapnambiar88Noch keine Bewertungen
- Q4M1Dokument54 SeitenQ4M1Klyn AgananNoch keine Bewertungen
- Antoine Cited Money LaunderingDokument74 SeitenAntoine Cited Money Launderingcorina_maria_eneNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sources of Finance: Ib Business & Management A Course Companion (2009) P146-157 (Clark Edition)Dokument54 SeitenSources of Finance: Ib Business & Management A Course Companion (2009) P146-157 (Clark Edition)sshyamsunder100% (1)