Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Arrangement by The Nervous System and Hormones
Hochgeladen von
agustin savitry0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
5 Ansichten5 SeitenThe document summarizes the arrangement of the digestive system by the nervous system and hormones. It discusses the enteric nervous system which regulates gastrointestinal motility and secretion. It also discusses the autonomic nervous system which influences gastrointestinal motility. It then explains the four groups of hormones that influence digestion: 1) Actual hormones like cholecystokinine and gastrin that influence secretion, motility, and growth, 2) Hormone candidates like motilin, 3) Paracrine factors like somatostatin and prostaglandins, and 4) Neurocrine peptides like VIP that stimulate the enteric nervous system.
Originalbeschreibung:
sistem saraf
Originaltitel
Saraf Dan Hormon
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
PPTX, PDF, TXT oder online auf Scribd lesen
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenThe document summarizes the arrangement of the digestive system by the nervous system and hormones. It discusses the enteric nervous system which regulates gastrointestinal motility and secretion. It also discusses the autonomic nervous system which influences gastrointestinal motility. It then explains the four groups of hormones that influence digestion: 1) Actual hormones like cholecystokinine and gastrin that influence secretion, motility, and growth, 2) Hormone candidates like motilin, 3) Paracrine factors like somatostatin and prostaglandins, and 4) Neurocrine peptides like VIP that stimulate the enteric nervous system.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als PPTX, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
5 Ansichten5 SeitenArrangement by The Nervous System and Hormones
Hochgeladen von
agustin savitryThe document summarizes the arrangement of the digestive system by the nervous system and hormones. It discusses the enteric nervous system which regulates gastrointestinal motility and secretion. It also discusses the autonomic nervous system which influences gastrointestinal motility. It then explains the four groups of hormones that influence digestion: 1) Actual hormones like cholecystokinine and gastrin that influence secretion, motility, and growth, 2) Hormone candidates like motilin, 3) Paracrine factors like somatostatin and prostaglandins, and 4) Neurocrine peptides like VIP that stimulate the enteric nervous system.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als PPTX, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
Sie sind auf Seite 1von 5
8.
Arrangement by the nervous
system and hormones
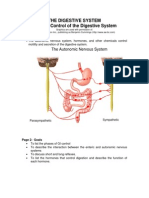
A. The nervous system
1. Enteric nervous system (Intrinsic)
- Pleksus mientrikus auerbach
To regulate motor function or motility of gastrointestinal
wall. But on the sphincter it inhibits plain muscle
contraction of the sphincter to experience relaxation so
that food can enter the next segment of the gastrointestinal
tract
- Submucous plexus
To regulate gastrointestinal secretion and control of
submucosal smooth muscle activity. Subtle submucous
muscle contractions result in folds of the mucosa whose
function is to expand the absorption area.
2. Autonomic nervous system (extrinsic)
- Parasympathetic for increased gastrointestinal motility, its
stimulation increases the activity of enteric nervous system,
except sphincter.
- Sympathetic also for increased motility but few (low activity)
B. Hormones
Can be divided into 4 groups :
1. The actual hormone
- Cholecystokinine
to increase the contraction of the bladder so
that the fluid is pushed out, stimulating the
secretion of pancreas digestive enzymes. In the
stomach, this hormone inhibits the emptying
of the contents of the stomach into the
duodenum. The goal is to take time on the
duodenum to digest the fat present in it.
- Secretion
to stimulate the secretion of bicarbonate from the
pancreas and bile which is useful to neutralize the
acidic chemistry, inhibits gastric acid secretion, the
growth of the pancreatic exocrine gland.
- Gastrin Secretion
to stimulate gastric acid secretion by oxintic cells,
the growth of oxintic cells.
- Gastric inhibitory peptide
To inhibits gastric acid secretion, slows the
emptying of the stomach
2. Hormone Candidates
- Motilin to stimulate the motility of the stomach and duodenum
- Pancreas polypeptide for inhibition or inhibition of secretion in the pancreas
- Enteroglukagon, possibly to increase blood glucose levels
3. Paracrine
- Somatostasin to inhibit the release of almost all the digestive system
peptide hormones.
- Prostaglandins to increase blood flow, increase secretion of mucus and
bicarbonate ions from the gastric mucosa
- Histamine to stimulate gastric secretion by oxintic cells
4. Neurocrine
Peptides that stimulate enteric nervous system and its producing cells are
called neuroendocrine cells.
- Vasoactive peptide inhibitory (VIP) function for relaxation of circular muscles
including sphincter, stimulates bowel and pancreatic secretions
- Bombesin to stimulate the gastric mucosa to secrete gastrin hormones
- Enfekalin to stimulate smooth muscle contraction of the digestive system and
inhibit intestinal secretion
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Control of DigestionDokument5 SeitenControl of DigestionMichael NyaongoNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2.6 Kontrol Saraf Hormon DigestivusDokument19 Seiten2.6 Kontrol Saraf Hormon DigestivusDewi Kartika SariNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture-5 Hormonal Regulation of Intestinal MotilityDokument4 SeitenLecture-5 Hormonal Regulation of Intestinal Motilityمرتضى حسين عبدNoch keine Bewertungen
- Digestive/Endocrine Answer KeyDokument10 SeitenDigestive/Endocrine Answer KeykmulqsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biopharmaceutics-01 AssignmentDokument14 SeitenBiopharmaceutics-01 AssignmentRA TanvirNoch keine Bewertungen
- Regulation of GIT ProcessesDokument16 SeitenRegulation of GIT ProcessesMuneeb Ur RehmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gi Hormones: Dr. Sharon M. PDokument50 SeitenGi Hormones: Dr. Sharon M. PAleenaNoch keine Bewertungen
- DigestionDokument187 SeitenDigestionJane Andrea Christiano Djianzonie100% (1)
- Metabolism (Ncm-216)Dokument10 SeitenMetabolism (Ncm-216)Sofronio OmboyNoch keine Bewertungen
- SGD - DigestiveDokument4 SeitenSGD - DigestiveSerious LeoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nur Syahirah Binti Mohd Yusri A170291: Nama Dan No. MatrikDokument9 SeitenNur Syahirah Binti Mohd Yusri A170291: Nama Dan No. MatrikSyahirah YusriNoch keine Bewertungen
- ControlDokument12 SeitenControlSirVietaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dr. ChintanDokument60 SeitenDr. ChintanWaqar AhmedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physiology of The PancreasDokument4 SeitenPhysiology of The PancreasKetan PatelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physiology, Lecture 8, GIT 2 (Stomach) (Slides)Dokument24 SeitenPhysiology, Lecture 8, GIT 2 (Stomach) (Slides)Ali Al-Qudsi100% (2)
- Pendahuluan Gi SystemDokument21 SeitenPendahuluan Gi SystemdeasyahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gastric Juice RegulationDokument22 SeitenGastric Juice Regulationjanuian75% (4)
- GIT Lec 4Dokument36 SeitenGIT Lec 4Kim Sa-buNoch keine Bewertungen
- Digestion & Digestive SystemDokument27 SeitenDigestion & Digestive SystemAam BhortaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture 10: Gastric Secretion & Its Regulation: Functions of StomachDokument8 SeitenLecture 10: Gastric Secretion & Its Regulation: Functions of StomachBoody KhalilNoch keine Bewertungen
- Digestive System: Freshmen Year Program Medical School Universitas Islam Bandung 2011-2012Dokument125 SeitenDigestive System: Freshmen Year Program Medical School Universitas Islam Bandung 2011-2012deasyahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Digestive SystemDokument7 SeitenDigestive SystemEva BrendaNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Digestive System: Cont'd (From Swallowing)Dokument56 SeitenThe Digestive System: Cont'd (From Swallowing)Jerilee SoCute WattsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hormonal Control of GitDokument42 SeitenHormonal Control of GitM. Shahin Uddin KazemNoch keine Bewertungen
- Digestive Hormones and EnzymesDokument2 SeitenDigestive Hormones and EnzymesTiannaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bsczo 301Dokument386 SeitenBsczo 301JjelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physio 6. Digestive System 6Dokument21 SeitenPhysio 6. Digestive System 6Xena XenaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Digestive System Best NoteDokument45 SeitenDigestive System Best NoteVarsha Mol MohananNoch keine Bewertungen
- Topic 1 MetaDokument68 SeitenTopic 1 MetaArvin LazarteNoch keine Bewertungen
- Animal Hormones and Their Functions: Balete, Berida, BorromeoDokument88 SeitenAnimal Hormones and Their Functions: Balete, Berida, BorromeoRessabela Juniper FayneNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gastric SecretionDokument45 SeitenGastric SecretionAzeeza Elya100% (1)
- Anatomy and PhysiologyDokument4 SeitenAnatomy and PhysiologyJohn Rey Abad67% (3)
- The Role of Enzymes in The Digestive SystemDokument2 SeitenThe Role of Enzymes in The Digestive SystemJeanAnzurezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gastric SecretionDokument36 SeitenGastric SecretionammuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gastrointestinal Physiology: By: Zewdu JimaDokument77 SeitenGastrointestinal Physiology: By: Zewdu JimaZewdu Jima100% (1)
- BiologyDokument12 SeitenBiologyvidottma kolheNoch keine Bewertungen
- Digestive System-1Dokument3 SeitenDigestive System-1elinandreaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture 48,49 GIT-Liver Parts 1 and 2Dokument65 SeitenLecture 48,49 GIT-Liver Parts 1 and 2yebadem228Noch keine Bewertungen
- Digestive System: Overview of The Digestive System Physiology of Digestion and AbsorptionDokument26 SeitenDigestive System: Overview of The Digestive System Physiology of Digestion and AbsorptionTemz HlubyNoch keine Bewertungen
- PancreasDokument36 SeitenPancreasANZC-chetana singhNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gastrointestinal HormonesDokument5 SeitenGastrointestinal Hormonesanjali.jha1909Noch keine Bewertungen
- Git Kpbi NisaDokument62 SeitenGit Kpbi NisaaristadevyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 15 Digestive System: Give The Function and Mechanism of Secretion of Salivary Juice?Dokument24 Seiten15 Digestive System: Give The Function and Mechanism of Secretion of Salivary Juice?Bhavin ChangelaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Digestive System 1Dokument45 SeitenDigestive System 1dmutethia68Noch keine Bewertungen
- DigestiveDokument74 SeitenDigestiveLeah Magbago RemolisanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physiology of GIT (2) (Autosaved)Dokument67 SeitenPhysiology of GIT (2) (Autosaved)RISALATUL KHOIROTUNISANoch keine Bewertungen
- Digestion of FoodDokument25 SeitenDigestion of FoodJaymee GonzalesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Digestive SystemDokument8 SeitenDigestive SystemAnamta AkhtarNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Digestive System: G.R. Pitts, PH.D., J.R. Schiller, Ph.D. and James F. Thompson, PH.DDokument54 SeitenThe Digestive System: G.R. Pitts, PH.D., J.R. Schiller, Ph.D. and James F. Thompson, PH.DAchmadPrihadianto100% (1)
- The Digestive System: Dr. Ali EbneshahidiDokument46 SeitenThe Digestive System: Dr. Ali EbneshahidiNirmala BandooNoch keine Bewertungen
- Medical Physiology: Gastro-Intestinal SystemDokument192 SeitenMedical Physiology: Gastro-Intestinal SystemKamal AhmedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Digestive System: A. Def'nDokument14 SeitenDigestive System: A. Def'nRahardian Gusta PatriaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Salivary SecretionDokument10 SeitenSalivary SecretionMahadi Hasan KhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gastrointestinal Tract HormonesDokument10 SeitenGastrointestinal Tract HormonesKevin SangNoch keine Bewertungen
- Updated Imp For Section - 10 On DigestionDokument6 SeitenUpdated Imp For Section - 10 On DigestionJethalal GadaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gastrointestinal System, FK, 2013Dokument72 SeitenGastrointestinal System, FK, 2013gabriellafelisaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Regulation of DigestionDokument11 SeitenRegulation of DigestionMichael NyaongoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cpy 521 - 122630Dokument41 SeitenCpy 521 - 122630onyibor joshuaNoch keine Bewertungen
- GASTRODokument94 SeitenGASTROriskyy1100% (1)
- Healthy Habits for Managing & Reversing Prediabetes: 100 Simple, Effective Ways to Prevent and Undo PrediabetesVon EverandHealthy Habits for Managing & Reversing Prediabetes: 100 Simple, Effective Ways to Prevent and Undo PrediabetesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Blood Classification SysemDokument5 SeitenBlood Classification Sysemagustin savitryNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Brain: The Brain Can Be Roughly Split Into Four Lobes, Shown As Green, Purple, Yellow and Pink in This PictureDokument4 SeitenThe Brain: The Brain Can Be Roughly Split Into Four Lobes, Shown As Green, Purple, Yellow and Pink in This Pictureagustin savitryNoch keine Bewertungen
- Arrangement by The Nervous System and HormonesDokument2 SeitenArrangement by The Nervous System and Hormonesagustin savitryNoch keine Bewertungen
- Arrangement by The Nervous System and HormonesDokument2 SeitenArrangement by The Nervous System and Hormonesagustin savitryNoch keine Bewertungen
- PhysioEx Exercise 11 Activity 4 - MD3N3Dokument4 SeitenPhysioEx Exercise 11 Activity 4 - MD3N3Dorlisca Montes GarcesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gi PhysiologyDokument21 SeitenGi PhysiologyNoreen Orro BernalNoch keine Bewertungen
- THE FETUS and PLACENTADokument50 SeitenTHE FETUS and PLACENTAKyla CalsoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Marjorie A. Carganilla BSN 3-2 Pathophysiology of Urinaryy Tract Infection Precipitating FactorsDokument8 SeitenMarjorie A. Carganilla BSN 3-2 Pathophysiology of Urinaryy Tract Infection Precipitating FactorsMarjorie CarganillaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Digestion Board Game - Tiered Task Sheet-2Dokument5 SeitenDigestion Board Game - Tiered Task Sheet-2api-295423685Noch keine Bewertungen
- Urinary System PDFDokument27 SeitenUrinary System PDFfiona100% (3)
- Igcse Biology Revision Finale!!Dokument143 SeitenIgcse Biology Revision Finale!!sohaila ibrahim100% (1)
- How Do Phagocytes Work in The BodyDokument2 SeitenHow Do Phagocytes Work in The Bodykei04086100% (1)
- Medical AstrologyDokument2 SeitenMedical Astrologyabhi16Noch keine Bewertungen
- LORESCA - BB Ratio Activity 2Dokument14 SeitenLORESCA - BB Ratio Activity 2Kaycee Gretz LorescaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cell JunctionsDokument40 SeitenCell JunctionsAhmad MursyidNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assessment of AbdomenDokument99 SeitenAssessment of AbdomenKeid ReumaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Molecular Genetics of Endometrial CancerDokument31 SeitenMolecular Genetics of Endometrial CancerJoju SebastianNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2021 ISFM Consensus Guidelines On The Collection and Administration of Blood and Blood Products in CatsDokument23 Seiten2021 ISFM Consensus Guidelines On The Collection and Administration of Blood and Blood Products in CatsNurul Izzatul AnnisaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Muscular System Study Guide 2015 AnswersDokument16 SeitenMuscular System Study Guide 2015 AnswersLinet HuchuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Jove-84-51214 - Vasectomy, Mouse ModelDokument8 SeitenJove-84-51214 - Vasectomy, Mouse ModelGia KuteliaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Orbit Arpita 111 (1) (New)Dokument31 SeitenOrbit Arpita 111 (1) (New)WALID HOSSAINNoch keine Bewertungen
- Transfusion in Emergency Room by DR Prannoy George, Department of Emergency Medicine, Amrita Institute of Medical Sciences, Kochi, KeralaDokument41 SeitenTransfusion in Emergency Room by DR Prannoy George, Department of Emergency Medicine, Amrita Institute of Medical Sciences, Kochi, KeralaAETCM Emergency medicineNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bowel Obstruction Case StudyDokument11 SeitenBowel Obstruction Case StudyFatimah Batool NawazNoch keine Bewertungen
- DPP - Anatomy of Flowering PlantsDokument10 SeitenDPP - Anatomy of Flowering PlantsRitika GochhaitNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cells Exploration ActivitiesDokument32 SeitenCells Exploration ActivitiesSay KhoNoch keine Bewertungen
- MGR Medical University MS ENT Basic Sciences March 2009 Question Paper With SolutionDokument44 SeitenMGR Medical University MS ENT Basic Sciences March 2009 Question Paper With SolutionDr. T. Balasubramanian100% (4)
- Contribution of Endoscopic Ultrasound in Pancreatic MassesDokument6 SeitenContribution of Endoscopic Ultrasound in Pancreatic MassesIJAR JOURNALNoch keine Bewertungen
- HydrocephalusDokument40 SeitenHydrocephalusAstrid Sabirin100% (1)
- Haematology - An Illustrated Colour Text, 4th Edition - 2Dokument132 SeitenHaematology - An Illustrated Colour Text, 4th Edition - 2蔡季霖100% (1)
- Malpresentations and MalpositionsDokument14 SeitenMalpresentations and MalpositionsAsteway MesfinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gold DPP of Human Reproduction by Garima GoelDokument7 SeitenGold DPP of Human Reproduction by Garima Goelgargmahek904Noch keine Bewertungen
- Connective TissueDokument62 SeitenConnective Tissuehnm mnhNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gas Exchange in Humans: Multiple-Choice QuestionsDokument56 SeitenGas Exchange in Humans: Multiple-Choice QuestionsZ s2021 4C Ma Ka Ki Margaret 4C16Noch keine Bewertungen
- BloodDokument24 SeitenBloodapi-310193189Noch keine Bewertungen