Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Presentation1. AEC GeoTech LANDFILL
Hochgeladen von
Ayan Borgohain0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
20 Ansichten22 Seiten1) A landfill is a carefully designed structure built into or on top of the ground that isolates trash from the surrounding environment using liners and daily soil coverings.
2) Landfills must follow operating requirements like using appropriate cover materials, monitoring air and groundwater quality, and controlling run-on and run-off. Site selection criteria includes sufficient land area and volume, and being located away from water sources and residential areas.
3) Landfill liners create barriers between waste and the environment and drain leachate for collection and treatment. Liners can be single, composite, or double layers. Landfill gas is produced in different phases as waste breaks down anaerobically over time.
Originalbeschreibung:
Originaltitel
Presentation1. AEC GeoTech LANDFILL.pptx
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
PPTX, PDF, TXT oder online auf Scribd lesen
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument melden1) A landfill is a carefully designed structure built into or on top of the ground that isolates trash from the surrounding environment using liners and daily soil coverings.
2) Landfills must follow operating requirements like using appropriate cover materials, monitoring air and groundwater quality, and controlling run-on and run-off. Site selection criteria includes sufficient land area and volume, and being located away from water sources and residential areas.
3) Landfill liners create barriers between waste and the environment and drain leachate for collection and treatment. Liners can be single, composite, or double layers. Landfill gas is produced in different phases as waste breaks down anaerobically over time.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als PPTX, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
20 Ansichten22 SeitenPresentation1. AEC GeoTech LANDFILL
Hochgeladen von
Ayan Borgohain1) A landfill is a carefully designed structure built into or on top of the ground that isolates trash from the surrounding environment using liners and daily soil coverings.
2) Landfills must follow operating requirements like using appropriate cover materials, monitoring air and groundwater quality, and controlling run-on and run-off. Site selection criteria includes sufficient land area and volume, and being located away from water sources and residential areas.
3) Landfill liners create barriers between waste and the environment and drain leachate for collection and treatment. Liners can be single, composite, or double layers. Landfill gas is produced in different phases as waste breaks down anaerobically over time.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als PPTX, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
Sie sind auf Seite 1von 22
Presented by:
Ayan Ansha Borgohain
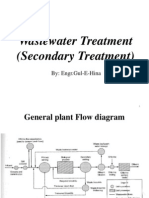
INTRODUCTION
What is a Landfill ?
A Landfill is a carefully designed structure
built into or on top of the ground in which
trash is isolated from the surrounding
environment. This isolation is
accomplished with a bottom liner and a
daily covering of soil. A Sanitary Landfill
uses a clay liner and a Municipal Solid
Waste (MSW) Landfill uses a
synthetic(plastic) liner.
Operating Requirements:
Use of appropriate Cover Material for the
landfill.
Disease Vector Control.
Monitoring of air and groundwater quality.
Run-on and Run-off control systems.
Record keeping requirements.
Site Selection Criteria:
Land area and volume must be sufficient
enough so that the landfill can serve for the
projected number of years.
Irrigation pipelines and water supply wells
should not be situated close to the
boundary of the landfill.
Residential Development should be
planned far away from the landfill.
Agricultural Lands should not be used for
landfill development.
Liner Systems
Landfill liners are designed to create a
barrier between the waste and the
environment, and to drain the leachate to
collection and treatment facilities.
Liners may be of 3 types:
1) Single
2) Composite
3) Double
Single Liner
Composite Liner
Double Liner
Landfill gas production
Phase 1:
Aerobic phase.
Biodegradable components undergo
microbial decomposition.
Once pH drops below 15%, anaerobic
organisms are cultivated.
Phase 2:
Anaerobic phase.
pH of landfill cells drops down.
Phase 3:
This is the second anaerobic phase.
pH of landfill liquid drops to around -5.
Increased amount of CO2 within voids.
Metals and other inorganic constituents are
solubilised.
Dissolution of organic acids in leachate.
Phase 4:
Methane fermentation phase.
pH increases and stabilizes at around 6.8 to 8.
BOD, COD and leachate conductivity reduces.
Metals which were soluble previously begin to
precipitate.
Phase 5:
Maturation phase.
Rate of gas generation decreases.
The occurrence of these phases depend on distribution of
organic components in landfill cell, availability of
nutrients, moisture content of waste and degree of
initial compaction.
Landfill gas production in
different phases
Treatment , Storage and Disposal
Facilities (TSDF)
Waste Analysis:
o Parameters to be analysed.
o Safe sampling methods.
o Labelling.
o Repeatability of tests.
o Standardization of tests.
o Trained personnel to handle equipment
and hazardous substances.
Hazardous Waste Landfills:
o Double liner.
o Double leachate collection removal
systems.
o Leak detection systems.
o Monitoring storm water run-on and run-off.
o Monitoring wind dispersal.
Incineration of Hazardous Waste:
There are 3 factors which ensure the
completeness of combustion in an
incinerator:
Temperature of combustion chamber.
Length of time for which the wastes are
maintained.
Turbulence (degree of mixing).
Type of Incinerators
Liquid Injector
Incinerator:
o Advantages-
Few moving parts and less
maintenance.
Capability to incinerate a
wide variety of wastes.
o Disadvantages-
Only capable of combusting
liquids and slurries.
Feed nozzles tend to clog.
Rotary Kiln Incinerator:
It consist of a rotating cylinder mounted at slight inclined from ground
level. Waste in the form of liquids, slurries or solids are fed.
Moving Grate Incinerator:
It is also referred to as MSW incinerator. It allows more efficient and
complete combustion. A single moving grate incinerator can handle up
to 35 metric tonnes of waste/hour and can operate for ~ 8000
hours/year.
Fixed Hearth
Incinerator:
These are extensively used
for combustion of bulk
solid and liquid waste
from medical or
municipal facilities. A
controlled flow of
combustion air is
introduced up through
the hearth(floor) and the
bottom ash is removed
by dumping the parts
into a water bath.
Fluidized Bed
Incinerator:
In a fluidized bed
incinerator, the bed part
is separated into
combustion and heat
absorption cells. It offers
isothermal combustion
with temperature of
operation being in the
range of 750-1000°C.
Thank You
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- 2949 HSE Risk Register - 2013-06-16 RevD1-VB FreeDokument3 Seiten2949 HSE Risk Register - 2013-06-16 RevD1-VB Freesalic201388% (8)
- Physical, Chemical & Biological: Design of Facilities For Treatment of Waste WaterDokument118 SeitenPhysical, Chemical & Biological: Design of Facilities For Treatment of Waste WaterAseem Vivek Masih100% (1)
- Dictionary of Water and Waste ManagementVon EverandDictionary of Water and Waste ManagementBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (3)
- Manhole ScheduleDokument5 SeitenManhole ScheduleSher AliNoch keine Bewertungen
- WEEE Rec in Umicore SmelterDokument1 SeiteWEEE Rec in Umicore Smeltercd20047gaikerNoch keine Bewertungen
- IO SummaryDokument8 SeitenIO SummaryVineeth VKNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture 9 - Water PollutionDokument42 SeitenLecture 9 - Water PollutionCiara Crew100% (1)
- Report OF Sewage Treatment PlantDokument17 SeitenReport OF Sewage Treatment PlantSanand Karwa100% (3)
- Report BODDokument16 SeitenReport BODMuhammad Aimi100% (1)
- Biotower 001 PDFDokument3 SeitenBiotower 001 PDFIsmael KhalilNoch keine Bewertungen
- Trickling Filters PDFDokument16 SeitenTrickling Filters PDFJohnclaude ChamandiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 2Dokument95 SeitenUnit 2rangaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Landfills: Design and OperationDokument31 SeitenLandfills: Design and OperationRao AliAshir100% (1)
- Chapter 6 - 24 Oct 17Dokument74 SeitenChapter 6 - 24 Oct 17Jiana NasirNoch keine Bewertungen
- Septic TankDokument55 SeitenSeptic TankAslam Laghari100% (1)
- Landfill DesignDokument45 SeitenLandfill DesignLareebNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture 12 - Waste Water Treatment MethodsDokument41 SeitenLecture 12 - Waste Water Treatment MethodsUsman KhalidNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gas Chromatography AmmoniaDokument10 SeitenGas Chromatography AmmoniacurlychemNoch keine Bewertungen
- Activated Sludge ProcessDokument28 SeitenActivated Sludge Processusmansherdin100% (2)
- Disposal of WastesDokument53 SeitenDisposal of WastesPriya Sharma100% (1)
- Admission Test Exam Question Sep 2018Dokument3 SeitenAdmission Test Exam Question Sep 2018masud64% (11)
- CH 4 Sewage TreatmentDokument134 SeitenCH 4 Sewage TreatmentGetu BogaleNoch keine Bewertungen
- Trickling FiltersDokument16 SeitenTrickling FiltersGunnar AgarwalNoch keine Bewertungen
- EPCLectureNotes Solid Waste2Dokument6 SeitenEPCLectureNotes Solid Waste2Harshini Reddy B.Noch keine Bewertungen
- PCT Pollution Control Technology (M REHAN TAHIR) - Waste Water TreatmentDokument71 SeitenPCT Pollution Control Technology (M REHAN TAHIR) - Waste Water Treatmentrehan263Noch keine Bewertungen
- Leachate Treatment-Km-Impart-Km5Dokument53 SeitenLeachate Treatment-Km-Impart-Km5manoj kumar GNoch keine Bewertungen
- 41 Solid Waste ManagementDokument55 Seiten41 Solid Waste ManagementAgnes Kindo100% (1)
- Anaerobic Biological Treatment For Municipal WasteDokument48 SeitenAnaerobic Biological Treatment For Municipal WasteU19CH076 ZEELKUMAR PATEL SVNITNoch keine Bewertungen
- Topic: Composting (Lecture 3) : National University of Science and TechnologyDokument27 SeitenTopic: Composting (Lecture 3) : National University of Science and TechnologyprincekamutikanjoreNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture 12 Trickling FilterDokument7 SeitenLecture 12 Trickling FilterAs MihNoch keine Bewertungen
- Disposal of Solid Waste ManagementDokument13 SeitenDisposal of Solid Waste ManagementBhavani Challa100% (1)
- Solid Waste BiotechnologyDokument7 SeitenSolid Waste Biotechnologyani putkaradzeNoch keine Bewertungen
- WAWE Material Unit VDokument19 SeitenWAWE Material Unit VArul GanapathyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 5Dokument114 SeitenUnit 5sethupathy ANoch keine Bewertungen
- High Rate Bio Trickling FiltersDokument11 SeitenHigh Rate Bio Trickling FiltersFriends of the Atlantic Coast Watch NewsletNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Portion of The Activated Sludge, From The Secondary Clarifier Is Returned To Mix With The Effluents of Primary Clarifier.Dokument21 SeitenA Portion of The Activated Sludge, From The Secondary Clarifier Is Returned To Mix With The Effluents of Primary Clarifier.Náģå Rájú ÇhïmąţäNoch keine Bewertungen
- Case 01Dokument19 SeitenCase 01Rushanth ChandraboseNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bio ToiletDokument31 SeitenBio Toiletmoon missionNoch keine Bewertungen
- Industrial and Hazardous Waste Management Week 7Dokument35 SeitenIndustrial and Hazardous Waste Management Week 7MUHABBAT SHAHNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture 14Dokument24 SeitenLecture 14Tejas MhaiskarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture 4, 5 and 6 WWTDokument113 SeitenLecture 4, 5 and 6 WWTWariyo GalgaloNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 34Dokument36 SeitenUnit 34SHAH JILNoch keine Bewertungen
- Astewater Reatment Lant DesignDokument2 SeitenAstewater Reatment Lant Designas3ateNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sewage Treatment: Chapter Four: (Part Two) Secondary/Biological and Tertiary Wastewater TreatmentDokument41 SeitenSewage Treatment: Chapter Four: (Part Two) Secondary/Biological and Tertiary Wastewater Treatmentmarshet berhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1 Landfill Design ConsiderationsDokument41 Seiten1 Landfill Design ConsiderationsShanSaharNoch keine Bewertungen
- Week 9-CHEM4015-CIVE4140-2023-2024Dokument44 SeitenWeek 9-CHEM4015-CIVE4140-2023-2024Nitin RautNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sludge ManagementDokument37 SeitenSludge ManagementcivilkudumbamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Untitled MDokument25 SeitenUntitled MKrishnaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Wastewate TreatmentDokument68 SeitenWastewate Treatment21pwche1592Noch keine Bewertungen
- BNR Process BendigoDokument6 SeitenBNR Process Bendigobansa79Noch keine Bewertungen
- Municipal Solid Waste ManagementDokument59 SeitenMunicipal Solid Waste ManagementShivansh ThakurNoch keine Bewertungen
- Industrial Wastewater Treatment-DisposalDokument37 SeitenIndustrial Wastewater Treatment-DisposalSajedur Rahman SetuNoch keine Bewertungen
- PP Problem 5 (8-11)Dokument3 SeitenPP Problem 5 (8-11)Fadrian OktoriNoch keine Bewertungen
- Main UASB ReactorDokument23 SeitenMain UASB ReactorsasisNoch keine Bewertungen
- Building ServicesDokument16 SeitenBuilding ServicesTamanna PanditaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Evs Unit-2&3Dokument17 SeitenEvs Unit-2&3Jeeva JeevaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Midterm Exam Answers 2-3-4Dokument7 SeitenMidterm Exam Answers 2-3-4Aslıhan KayaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Final PPT Sa ps1Dokument23 SeitenFinal PPT Sa ps1Alnor Latabat AlontoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Wastewatertreatment 130204082216 Phpapp02Dokument55 SeitenWastewatertreatment 130204082216 Phpapp02CakEmUsNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Dranco Technology: A Unique Digestion Technology For Solid Organic WasteDokument7 SeitenThe Dranco Technology: A Unique Digestion Technology For Solid Organic Wastemime840% (1)
- Landfill: Design and Operation: Arushe Tickoo M. TechDokument30 SeitenLandfill: Design and Operation: Arushe Tickoo M. Techsakthivel duraisamyNoch keine Bewertungen
- 7 Wastewater Treatment Systems Week 7Dokument41 Seiten7 Wastewater Treatment Systems Week 7Divyashini MohanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture 31Dokument9 SeitenLecture 31Naga Varshini MeenakshisundaramNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sewage Treatment PlantDokument34 SeitenSewage Treatment PlantAthi MNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cycle 9 & 10Dokument23 SeitenCycle 9 & 10Yasewn KALAWANTNoch keine Bewertungen
- Wastewater Treatment: On Completion of This Segment You Should BeDokument57 SeitenWastewater Treatment: On Completion of This Segment You Should BeGourav MehtaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Inside the Pill Bottle: A Comprehensive Guide to the Pharmaceutical IndustryVon EverandInside the Pill Bottle: A Comprehensive Guide to the Pharmaceutical IndustryNoch keine Bewertungen
- Aviation Industry and Sustainability ChallengesDokument12 SeitenAviation Industry and Sustainability Challengesbrightness419Noch keine Bewertungen
- Vigan CityDokument3 SeitenVigan CityAfflict TionNoch keine Bewertungen
- Material Safety Data Sheet Ecol Lube HTDokument4 SeitenMaterial Safety Data Sheet Ecol Lube HTfs1640Noch keine Bewertungen
- Cce 408Dokument4 SeitenCce 408Neetor TendekayiNoch keine Bewertungen
- GTZ Proklima Natural RefrigerantsDokument208 SeitenGTZ Proklima Natural RefrigerantsПетар УрџановNoch keine Bewertungen
- Current Fields & Career of Civil Engineering - 4Dokument20 SeitenCurrent Fields & Career of Civil Engineering - 4More ReadNoch keine Bewertungen
- 7 Ways To Protects The EnvironmentDokument16 Seiten7 Ways To Protects The EnvironmentHikariNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sampling and Field Testing at Wastewater Treatment FacilitiesDokument11 SeitenSampling and Field Testing at Wastewater Treatment FacilitiesSundarapandiyan SundaramoorthyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Analysis of The Book of KellsDokument17 SeitenAnalysis of The Book of KellsVornicu NicoletaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Acid Rain - Can Chalk Dissolve? - Results TableDokument4 SeitenAcid Rain - Can Chalk Dissolve? - Results TablecgNoch keine Bewertungen
- CH 10 - MicroDokument41 SeitenCH 10 - MicroRitika NandaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Post Completion IEMC ReportDokument29 SeitenPost Completion IEMC ReportAtta'ullah Bhatt'iNoch keine Bewertungen
- If I Were Harry Potter - Task 4 School ArticelDokument2 SeitenIf I Were Harry Potter - Task 4 School ArticelFitri AfiqNoch keine Bewertungen
- VOCs in Hanoi and HCMCDokument8 SeitenVOCs in Hanoi and HCMCblackangel1603Noch keine Bewertungen
- Acid RainDokument7 SeitenAcid RainAnoshKhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Residential Wastewater Heat RecoveryDokument6 SeitenResidential Wastewater Heat RecoveryMReza AdiliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Best Management Practices For Treating Waste Polyester-Resin and GelcoatDokument4 SeitenBest Management Practices For Treating Waste Polyester-Resin and GelcoatTaraknath MukherjeeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Environmental Decision MakingDokument140 SeitenEnvironmental Decision MakingManik Kumar100% (1)
- MoEF IIFM Thermal Power PlantsDokument122 SeitenMoEF IIFM Thermal Power PlantsVishal SIngh100% (1)
- Reduce Research PaperDokument17 SeitenReduce Research PaperTata Duero LachicaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lesson Plan Title: Go With The Flow Objectives / UnderstandingsDokument4 SeitenLesson Plan Title: Go With The Flow Objectives / Understandingsapi-212877977Noch keine Bewertungen
- 50% Construction Documents: Jacobs Medical Center East Campus Bed TowerDokument35 Seiten50% Construction Documents: Jacobs Medical Center East Campus Bed TowerSoumitra GuptaNoch keine Bewertungen