Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Concrete Foundation Wall Design
Hochgeladen von
Severino Jr. Salera0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
25 Ansichten10 SeitenThe document discusses the design of concrete foundation walls. It outlines several objectives of foundation wall design including transferring load to the earth, providing strength to prevent settlement, resisting lateral soil pressure and wind/seismic forces, and isolating moisture. It also discusses considerations like withstanding erosion, proper embedment and height/width ratios, and providing lateral support. Common building materials for foundation walls are described as concrete, masonry, and wood. An example reinforced concrete foundation wall design problem is then presented.
Originalbeschreibung:
Originaltitel
Concrete Foundation Wall Design.pptx
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
PPTX, PDF, TXT oder online auf Scribd lesen
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenThe document discusses the design of concrete foundation walls. It outlines several objectives of foundation wall design including transferring load to the earth, providing strength to prevent settlement, resisting lateral soil pressure and wind/seismic forces, and isolating moisture. It also discusses considerations like withstanding erosion, proper embedment and height/width ratios, and providing lateral support. Common building materials for foundation walls are described as concrete, masonry, and wood. An example reinforced concrete foundation wall design problem is then presented.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als PPTX, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
25 Ansichten10 SeitenConcrete Foundation Wall Design
Hochgeladen von
Severino Jr. SaleraThe document discusses the design of concrete foundation walls. It outlines several objectives of foundation wall design including transferring load to the earth, providing strength to prevent settlement, resisting lateral soil pressure and wind/seismic forces, and isolating moisture. It also discusses considerations like withstanding erosion, proper embedment and height/width ratios, and providing lateral support. Common building materials for foundation walls are described as concrete, masonry, and wood. An example reinforced concrete foundation wall design problem is then presented.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als PPTX, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
Sie sind auf Seite 1von 10
Concrete Foundation
Wall Design
Caduyac, May Ann
Olasiman, Marrianie O.
Foundation Wall
O Provides support for the entire
structure you are building
O Should be planned and constructed
carefully as they are probably the most
important part of the structure
OBJECTIVES OF FOUNDATION WALL
DESIGN:
O To transfer the load of the building to the footing or
directly to the earth
O To provide adequate strength, in combination with the
footing when required, to prevent differential
settlement
O To provide adequate resistance to shear and bending
stresses resulting from lateral soil pressure
O To provide anchorage for the above-grade
structure to resist wind or seismic forces
O To provide a moisture-resistant barrier to
below-ground habitable space, in accordance
with the building code
O To isolate non-moisture-resistant building
materials from the ground
Foundation Wall Design
Considerations
O Foundation wall shall be design to be
withstand erosion, fast-moving water,
other factors affecting those types of
walls.
Embedment and Height/Width
O A foundation wall should be built in such a
way that the top of the footing shall be no
higher than the depth of erosion and scour
O Foundation Wall require lateral support from
the floor system and diaphragm, and
connections to the top of the walls must be
detailed properly
O Foundation walls should be constructed high
enough, so the bottom of the floor is above
the design flood elevation.
O concrete foundation walls typically are a
nominal 6, 8, or 10 inches thick. The typical
concrete compressive strength used in
residential construction is 2,500 or 3,000 psi,
although other strengths are available.
Building Materials for Foundation
Walls
O Foundation walls can be built from almost
any material, but concrete, masonry and
wood are predominant
O Concrete foundation must be reinforced,
and the concrete mix must be a high-
strength, low water-to-cement ratio
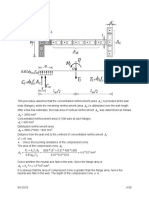
O Reinforced Concrete Foundation Wall Design
O Given Service loads
Live load (L) = 1000 plf
Dead load (D) = 750 plf
Moment at top = 0
Concrete weight = 150 pcf
Backfill material = 60 pcf (equivalent fluid density)
Wall thickness = 8 in
Wall height = 10 ft
Unbalanced backfill height = 8 ft
f'c = 3,000 psi
fy = 60,000 psi
O Assume axial load is in middle one-third of wall. Find If one No. 5
bar at 24 inches on center vertically is adequate for the load
combination, U = 1.2D + 1.6H + 1.6L (chapter 3, table 3.1) when
rebar is placed 3 inches from outer face of wall (d=5 in).
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Tall Buildings: The Proceedings of a Symposium on Tall Buildings with Particular Reference to Shear Wall Structures, Held in the Department of Civil Engineering, University of Southampton, April 1966Von EverandTall Buildings: The Proceedings of a Symposium on Tall Buildings with Particular Reference to Shear Wall Structures, Held in the Department of Civil Engineering, University of Southampton, April 1966A. CoullBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (1)
- Aalami CI Mar03 PaperDokument7 SeitenAalami CI Mar03 PaperWalter CastilloNoch keine Bewertungen
- Critical Excitation Methods in Earthquake EngineeringVon EverandCritical Excitation Methods in Earthquake EngineeringBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1)
- The Life of Structures: Physical TestingVon EverandThe Life of Structures: Physical TestingG.S.T ArmerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Probabilistic service life model of RC structures subjected to the combined effect of chloride-induced corrosion and cyclic loadingVon EverandProbabilistic service life model of RC structures subjected to the combined effect of chloride-induced corrosion and cyclic loadingNoch keine Bewertungen
- Capacity Based DesignDokument12 SeitenCapacity Based DesignnagarajuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Anchorage of Reinforcing BarsDokument148 SeitenAnchorage of Reinforcing BarsAntonette Marie ElgarioNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1714 Deep Beams Concept Applications Assumptions A Differences Between Deep A Simple BeamsDokument3 Seiten1714 Deep Beams Concept Applications Assumptions A Differences Between Deep A Simple BeamsNikhil Babaria0% (2)
- Roof Sheathing TolerancesDokument46 SeitenRoof Sheathing TolerancesLeonichevNoch keine Bewertungen
- Earthquake isolation method with variable natural frequencyVon EverandEarthquake isolation method with variable natural frequencyNoch keine Bewertungen
- CRSI The Designer's ResponsibilityDokument16 SeitenCRSI The Designer's ResponsibilityAdam Jones100% (1)
- Slender Wall Byslender Wall DesignDokument4 SeitenSlender Wall Byslender Wall DesignDiquanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Poroelastic StructuresVon EverandPoroelastic StructuresG. CederbaumNoch keine Bewertungen
- Structural Analysis of Historic ConstructionsDokument6 SeitenStructural Analysis of Historic ConstructionsChinmay KaranNoch keine Bewertungen
- Designing Tall Buildings Structure As Architecture-103-134Dokument32 SeitenDesigning Tall Buildings Structure As Architecture-103-134Milka VincentiyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Advanced Opensees Algorithms, Volume 1: Probability Analysis Of High Pier Cable-Stayed Bridge Under Multiple-Support Excitations, And LiquefactionVon EverandAdvanced Opensees Algorithms, Volume 1: Probability Analysis Of High Pier Cable-Stayed Bridge Under Multiple-Support Excitations, And LiquefactionNoch keine Bewertungen
- Braced Frameworks: An Introduction to the Theory of StructuresVon EverandBraced Frameworks: An Introduction to the Theory of StructuresNoch keine Bewertungen
- Limit State Design of Reinforced Concrete by VergheseDokument566 SeitenLimit State Design of Reinforced Concrete by VerghesePRADEEPYADAVIITGNoch keine Bewertungen
- Design of Concrete Shell Roofs For Amphi TheatreDokument58 SeitenDesign of Concrete Shell Roofs For Amphi TheatreGuru Raja100% (1)
- Composite Special Moment Frames 2020Dokument71 SeitenComposite Special Moment Frames 2020Camilo SoteloNoch keine Bewertungen
- Full Text 01Dokument325 SeitenFull Text 01YashNoch keine Bewertungen
- Structure SyllabusDokument25 SeitenStructure SyllabuspraveennagarajanNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Perspective On The Seismic Design of Precast Concrete Structures in New ZealandDokument21 SeitenA Perspective On The Seismic Design of Precast Concrete Structures in New Zealandunix0123Noch keine Bewertungen
- Footing Soil Pressure From Biaxial LoadingDokument18 SeitenFooting Soil Pressure From Biaxial LoadingSon NguyenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Structural Elements for Architects and Builders: Design of Columns, Beams, and Tension Elements in Wood, Steel, and Reinforced ConcreteVon EverandStructural Elements for Architects and Builders: Design of Columns, Beams, and Tension Elements in Wood, Steel, and Reinforced ConcreteNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2006 - Krahn - The Purpose of Numerical ModelingDokument3 Seiten2006 - Krahn - The Purpose of Numerical Modelinghartonowu0% (1)
- Concrete Slender Wall DesignDokument9 SeitenConcrete Slender Wall Designamokhta100% (1)
- Seismic Masonry Guide 2nd Edition Oct 2018 R1 Split 4Dokument71 SeitenSeismic Masonry Guide 2nd Edition Oct 2018 R1 Split 4Eduardo Martinez CaleroNoch keine Bewertungen
- Structural Analysis A Unified Classical and Matrix ApproachDokument866 SeitenStructural Analysis A Unified Classical and Matrix ApproachHariHaranNoch keine Bewertungen
- Performance and Practice For Earthquake Resistance: of IsDokument8 SeitenPerformance and Practice For Earthquake Resistance: of IsJUAN PABLO FUENTESNoch keine Bewertungen
- SEISMIC DESIGN Priestley PDFDokument22 SeitenSEISMIC DESIGN Priestley PDFRoger Julian MenaNoch keine Bewertungen
- CONCRETE STRUCTURES by Mehdi Setareh & Robert Darvas 2nd. Springer International Publishing (2017) - CopiarDokument6 SeitenCONCRETE STRUCTURES by Mehdi Setareh & Robert Darvas 2nd. Springer International Publishing (2017) - CopiarMilagros M. SanchezNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2170Dokument2 Seiten2170Jhesus GarciaNoch keine Bewertungen
- ASDIP Concrete Users ManualDokument27 SeitenASDIP Concrete Users ManualKarl PacalaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Behaviour of Building Structures Subjected to Progressive CollapseVon EverandBehaviour of Building Structures Subjected to Progressive CollapseNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nonlinear Static and Dynamic Analysis of ReinforceDokument179 SeitenNonlinear Static and Dynamic Analysis of ReinforceCésarEspinozaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Optimal Design of Flexural Systems: Beams, Grillages, Slabs, Plates and ShellsVon EverandOptimal Design of Flexural Systems: Beams, Grillages, Slabs, Plates and ShellsBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (1)
- Summerized Technology PDFDokument44 SeitenSummerized Technology PDFAnonymous sWro8YW100% (1)
- Dynamic Analysis of Multistoreyed Frame Shear Wall Building Considering SSIDokument50 SeitenDynamic Analysis of Multistoreyed Frame Shear Wall Building Considering SSIEditor IJTSRD100% (1)
- Wind Engineering 1983 3C: Proceedings of the Sixth international Conference on Wind Engineering, Gold Coast, Australia, March 21-25, And Auckland, New Zealand, April 6-7 1983; held under the auspices of the International Association for Wind EngineeringVon EverandWind Engineering 1983 3C: Proceedings of the Sixth international Conference on Wind Engineering, Gold Coast, Australia, March 21-25, And Auckland, New Zealand, April 6-7 1983; held under the auspices of the International Association for Wind EngineeringJ.D. HolmesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Masonary Design Working StressDokument21 SeitenMasonary Design Working Stresstaz_taz3Noch keine Bewertungen
- PCDokument491 SeitenPCVaibhav Gorad100% (2)
- Lateral Force CollectorsDokument11 SeitenLateral Force Collectorsx620Noch keine Bewertungen
- Plastic Analysis of Beams and Frames 1Dokument9 SeitenPlastic Analysis of Beams and Frames 1Fan ZhangNoch keine Bewertungen
- Timber Formwork DesignDokument12 SeitenTimber Formwork DesignMaiwand KhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Analysis of G+30 Highrise Buildings by Using Etabs For Various Frame Sections in ZoneIV and ZoneV PDFDokument15 SeitenAnalysis of G+30 Highrise Buildings by Using Etabs For Various Frame Sections in ZoneIV and ZoneV PDFK.ANISHNoch keine Bewertungen
- Factors Affecting Selection of Foundation For BuildingsDokument5 SeitenFactors Affecting Selection of Foundation For BuildingsJaisurya SharmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Friction Pendulum System - A Parametric Study of Friction CoefficientDokument3 SeitenFriction Pendulum System - A Parametric Study of Friction CoefficientIJSTENoch keine Bewertungen
- Seismic Design of Steel StructuresDokument55 SeitenSeismic Design of Steel StructuresAndrea LitzNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tower Design-Chapter 2-Pile Caps Design-Nada ZarrakDokument37 SeitenTower Design-Chapter 2-Pile Caps Design-Nada ZarrakNadaZarrakNoch keine Bewertungen
- Siting Agricultural Waste Management SystemsDokument38 SeitenSiting Agricultural Waste Management SystemsSeverino Jr. SaleraNoch keine Bewertungen
- 7-Direct Seeding and TransplantingDokument43 Seiten7-Direct Seeding and TransplantingSeverino Jr. SaleraNoch keine Bewertungen
- EO ART 160 Implementing Guidelines - Revised 1Dokument5 SeitenEO ART 160 Implementing Guidelines - Revised 1Severino Jr. SaleraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Threshing: Rice Competitiveness Enhancement FundDokument57 SeitenThreshing: Rice Competitiveness Enhancement FundSeverino Jr. SaleraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Principles and Systems of Land PreparationDokument91 SeitenPrinciples and Systems of Land PreparationSeverino Jr. Salera100% (1)
- School HeadsDokument37 SeitenSchool HeadsSeverino Jr. SaleraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Summary, Conclusions and Recommendations Summary of FindingsDokument5 SeitenSummary, Conclusions and Recommendations Summary of FindingsSeverino Jr. SaleraNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2K CERTIFICATES (Board Review)Dokument4 Seiten2K CERTIFICATES (Board Review)Severino Jr. SaleraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bohol Island State University PDFDokument2 SeitenBohol Island State University PDFSeverino Jr. SaleraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 2Dokument27 SeitenChapter 2Severino Jr. SaleraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Forest Utilization Engineering: C. Fiber Saturation PointDokument12 SeitenForest Utilization Engineering: C. Fiber Saturation PointSeverino Jr. Salera100% (1)
- Vocabulary List Year 6 Unit 10Dokument2 SeitenVocabulary List Year 6 Unit 10Nyat Heng NhkNoch keine Bewertungen
- CM760 E-Brochure HemobasculaDokument6 SeitenCM760 E-Brochure Hemobasculajordigs50Noch keine Bewertungen
- 5 Axis Lesson 2 PDFDokument36 Seiten5 Axis Lesson 2 PDFPC ArmandoNoch keine Bewertungen
- 6 CHDokument27 Seiten6 CHjafariNoch keine Bewertungen
- GROZ Tools & Equipment 2018Dokument3 SeitenGROZ Tools & Equipment 2018ayush bansalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Harmonic Distortion CSI-VSI ComparisonDokument4 SeitenHarmonic Distortion CSI-VSI ComparisonnishantpsbNoch keine Bewertungen
- Jsa - Cable TerminationDokument4 SeitenJsa - Cable TerminationSantos Rex73% (15)
- Lease Contract AddendumDokument1 SeiteLease Contract AddendumjasonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lust V Animal Logic MSJ OppositionDokument34 SeitenLust V Animal Logic MSJ OppositionTHROnlineNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lynette Hawkins, BMG Awesome InsightDokument2 SeitenLynette Hawkins, BMG Awesome Insightawesomei100% (1)
- Raul C. Cosare v. Broadcom Asia Inc. and Dante ArevaloDokument4 SeitenRaul C. Cosare v. Broadcom Asia Inc. and Dante ArevaloRam Migue SaintNoch keine Bewertungen
- UNDCO Disability Inclusion Strategy 2022 - 2025Dokument28 SeitenUNDCO Disability Inclusion Strategy 2022 - 2025Nelson MichmeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Suplayer Metal Working Sipil and Fabrication: Company ProfileDokument10 SeitenSuplayer Metal Working Sipil and Fabrication: Company ProfileRuntian TeaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Virtual Asset Insurance Risk Analysis - OneDegreeDokument3 SeitenVirtual Asset Insurance Risk Analysis - OneDegreeShaarang BeganiNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Study On Impact of Acne Vulgaris On Quality of LifeDokument7 SeitenA Study On Impact of Acne Vulgaris On Quality of LifeIJAR JOURNALNoch keine Bewertungen
- Diesel Oil Matters 70 YrsDokument1 SeiteDiesel Oil Matters 70 YrsingsespinosaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Defining The Audiovisual IndustryDokument20 SeitenDefining The Audiovisual IndustryAyoub Ait MahmoudNoch keine Bewertungen
- Standard Operating Procedure Template - Single PageDokument1 SeiteStandard Operating Procedure Template - Single PagetesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Remedies FlowDokument44 SeitenRemedies Flowzeebeelo100% (1)
- Metrologic Colombia S.A.S. Medellín Medellín Colombia: Oferta Economica CO20233ADokument3 SeitenMetrologic Colombia S.A.S. Medellín Medellín Colombia: Oferta Economica CO20233AJulian MoraNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2 SpecificationDokument20 Seiten2 Specificationprithvi614710Noch keine Bewertungen
- GFCO Certification ManualDokument72 SeitenGFCO Certification Manualatila117Noch keine Bewertungen
- Uniarch Network Video Recorders User Manual-V1.00Dokument99 SeitenUniarch Network Video Recorders User Manual-V1.00amurjiantoNoch keine Bewertungen
- BrochureDokument8 SeitenBrochurevacmanilaNoch keine Bewertungen
- MCMCHistoryDokument18 SeitenMCMCHistoryAli S.Noch keine Bewertungen
- Treatment of Dairy Waste Water Using Adsorbents From Solid WasteDokument7 SeitenTreatment of Dairy Waste Water Using Adsorbents From Solid WasteIJRASETPublicationsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Flexi Multiradio Introduction - Sharing SessionDokument96 SeitenFlexi Multiradio Introduction - Sharing SessionRobby MiloNoch keine Bewertungen
- National Knowledge Commision and Its Implication in Higher EducationDokument73 SeitenNational Knowledge Commision and Its Implication in Higher Educationabhi301280100% (1)
- An Introduction To SAP Business One CloudDokument14 SeitenAn Introduction To SAP Business One CloudBharathkumar PalaniveluNoch keine Bewertungen
- TUF-2000M User Manual PDFDokument56 SeitenTUF-2000M User Manual PDFreinaldoNoch keine Bewertungen