Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
CHP 1
Hochgeladen von
Iraj AmirOriginaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
CHP 1
Hochgeladen von
Iraj AmirCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
1–1
Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education
1–2
Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education
Teaching Methodology
Quizzes
05%
Assignments
10%
Class Participation 1–3
05%
Project and Presentation
10%
Midterm
30%
Final term
40%
•C A S E S T U D Y
•C L A S S A C T I V I T I E S I N D I V I D U A L G R O U P
•B O O K R E A D I N G
•A R T I C L E A N D I N F O G R A P H I C S
•V I D E O S
Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education
Introduction to Human Resource
Management
Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education 1–4
LEARNING OUTCOMES
1. Explain what human resource management is and how
it relates to the management process.
2. Show with examples why human resource management
is important to all managers.
3. Illustrate the human resources responsibilities of line
and staff (HR) managers.
4. Briefly discuss and illustrate each of the important
trends influencing human resource management.
5. List and briefly describe important trends in human
resource management.
6. Define and give an example of evidence-based human
resource management.
7. Outline the plan of this book.
Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education 1–5
The Management Process
1–6
Planning
Controlling Organizing
Leading
Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education
Staffing/People Management/Personnel
Management/HRM
1–7
Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education
Human Resource Management Processes
1–8
Acquisition
Fairness Training
Human
Resource
Management
Health and Safety (HRM) Appraisal
Labor Relations Compensation
Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education
Human Resource Management at Work
1–9
What Is Human Resource Management (HRM)?
The process of acquiring, training, appraising, and
compensating employees, and of attending to their labor
relations, health and safety, and fairness concerns.
Organization
People with formally assigned roles who work together to
achieve the organization’s goals.
Manager
The person responsible for accomplishing the organization’s
goals, and who does so by managing the efforts of the
organization’s people.
Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education
Personnel Aspects of a Manager’s Job
1–
10
Conducting job analyses
Planning labor needs and recruiting job candidates
Selecting job candidates
Orienting and training new employees
Managing wages and salaries
Providing incentives and benefits
Appraising performance
Communicating
Training and developing managers
Building employee commitment
Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education
Personnel Mistakes
1–
11
Hire the wrong person for the job
Experience high turnover
Have your people not doing their best
Waste time with useless interviews
Have your firm in court because of discriminatory
actions
Have your firm cited by OSHA for unsafe practices
Have some employees think their salaries are unfair and
inequitable relative to others in the organization
Allow a lack of training to undermine your department’s
effectiveness
Commit any unfair labor practices
Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education
Line and Staff Aspects of HRM
1–
12
Line Manager
Is authorized (has line authority) to direct the work of
subordinates and is responsible for accomplishing the
organization’s tasks.
Staff Manager
Assists and advises line managers.
Has functional authority to coordinate personnel
activities and enforce organization policies.
Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education
Line Managers’ HRM Responsibilities
1–
13
1. Placing the right person on the right job
2. Starting new employees in the organization (orientation)
3. Training employees for jobs that are new to them
4. Improving the job performance of each person
5. Gaining creative cooperation and developing smooth
working relationships
6. Interpreting the firm’s policies and procedures
7. Controlling labor costs
8. Developing the abilities of each person
9. Creating and maintaining department morale
10. Protecting employees’ health and physical condition
Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education
Human Resource Managers’ Duties
1–
14
Functions of
HR Managers
Line Function Coordinative Staff Functions
Line Authority Function Staff Authority
Implied Authority Functional Authority Innovator/Advocacy
Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education
Human Resource Specialties
1–
15
Recruiter
Labor relations
specialist EEO coordinator
Human
Resource
Specialties
Training specialist Job analyst
Compensation
manager
Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education
Trends Shaping Human Resource
Management
1–
16
Globalization
and Competition
Trends
Indebtedness
(“Leverage”) and Technological
Deregulation Trends
Trends in HR
Management
Workforce and
Trends in the
Demographic
Nature of Work
Trends
Economic
Challenges and
Trends
Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education
FIGURE 1–4 Trends Shaping Human Resource Management
Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education 1–17
Trends in the Nature of Work
1–
18
Changes in How We Work
High-Tech Service Knowledge Work
Jobs Jobs and Human Capital
Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education
Workforce and Demographic Trends
1–
19
Demographic Trends
Generation “Y”
Trends Affecting
Human Resources
Retirees
Nontraditional Workers
Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education
Important Trends in HRM
1–
20
The New HR
Managers
Strategic High-Performance
HRM Human Work Systems
Resource
Management
Evidence-Based Trends Managing
HRM Ethics
HR
Certification
Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education
Meeting Today’s HRM Challenges
1–
21
The New Human Resource
Managers
Acquire broader
Find new ways to
Focus more on business
provide
“big picture” knowledge and
transactional
(strategic) issues new HRM
services
proficiencies
Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education
TABLE 1–2 Some Technological Applications to Support HR
Technology How Used by HR
Application service providers ASPs provide software application, for instance, for processing
(ASPs) and technology employment applications. The ASPs host and manage the services
outsourcing for the employer from their own remote computers
Web portals Employers use these, for instance, to enable employees to sign up
for and manage their own benefits packages and to update their
personal information
Streaming desktop video Used, for instance, to facilitate distance learning and training or to
provide corporate information to employees quickly and
inexpensively
Internet- and network- Used to track employees’ Internet and e-mail activities or to monitor
monitoring software their performance
Electronic signatures Legally valid e-signatures that employers use to more expeditiously
obtain signatures for applications and record keeping
Electronic bill presentment Used, for instance, to eliminate paper checks and to facilitate
and payment payments to employees and suppliers
Data warehouses and Help HR managers monitor their HR systems. For example, they
computerized analytical make it easier to assess things like cost per hire, and to compare
programs current employees’ skills with the firm’s projected strategic needs
Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education 1–22
High-Performance Work Systems
1–
23
Increase productivity and performance by:
Recruiting, screening and hiring more effectively
Providing more and better training
Paying higher wages
Providing a safer work environment
Linking pay to performance
Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education
Evidence-Based HRM
1–
24
Providing Evidence for
HRM Decision Making
Actual Existing Research
measurements data studies
Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education
Managing Ethics
1–
25
Ethics
Standards that someone uses to decide
what his or her conduct should be
HRM-related Ethical Issues
Workplace safety
Security of employee records
Employee theft
Affirmative action
Comparable work
Employee privacy rights
Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education
HR Certification
1–
26
HR is becoming more professionalized.
Society for Human Resource Management
(SHRM)
SHRM’s Human Resource Certification Institute (HRCI)
SPHR (Senior Professional in HR) certificate
GPHR (Global Professional in HR) certificate
PHR (Professional in HR) certificate
Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education
The Plan of This Book: Basic Themes
1–
27
HRM is the responsibility of every manager.
The workforce is becoming increasingly diverse.
Current economic challenges require that HR
managers develop new and better skills to effectively
and efficiently deliver and manage HR services.
The intensely competitive nature of business today
means human resource managers must defend their
plans and contributions in measurable terms.
Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education
FIGURE 1–10 Strategy and the Basic Human Resource Management Process
Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education 1–28
KEY TERMS
organization
manager
management process
human resource management (HRM)
authority
line authority
staff authority
line manager
staff manager
functional authority
globalization
human capital
Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education 1–29
All rights reserved. No part of this publication may be reproduced,
stored in a retrieval system, or transmitted, in any form or by any
means, electronic, mechanical, photocopying, recording, or
otherwise, without the prior written permission of the publisher.
Printed in the United States of America.
Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education 1–30
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Von EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Bewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (98)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceVon EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (895)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeVon EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (5794)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingVon EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (399)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaVon EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (266)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeVon EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (537)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureVon EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (474)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItVon EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (838)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceVon EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (588)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryVon EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (231)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerVon EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (271)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyVon EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (2259)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealVon EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (73)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersVon EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (344)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnVon EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (234)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaVon EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (45)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreVon EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Von EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Bewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesVon EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (821)
- Tutorial 6Dokument3 SeitenTutorial 6Lai Qing YaoNoch keine Bewertungen
- WellaPlex Technical 2017Dokument2 SeitenWellaPlex Technical 2017Rinita BhattacharyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Kamal: Sales and Marketing ProfessionalDokument3 SeitenKamal: Sales and Marketing ProfessionalDivya NinaweNoch keine Bewertungen
- PEA Comp Study - Estate Planning For Private Equity Fund Managers (ITaback, JWaxenberg 10 - 10)Dokument13 SeitenPEA Comp Study - Estate Planning For Private Equity Fund Managers (ITaback, JWaxenberg 10 - 10)lbaker2009Noch keine Bewertungen
- Name of The Business-Rainbow Blooms LLC. Executive SummaryDokument17 SeitenName of The Business-Rainbow Blooms LLC. Executive SummaryAhamed AliNoch keine Bewertungen
- WFM 5101 Watershed Hydrology: Shammi HaqueDokument18 SeitenWFM 5101 Watershed Hydrology: Shammi HaquejahirNoch keine Bewertungen
- Papalia Welcome Asl 1 Guidelines 1 1Dokument14 SeitenPapalia Welcome Asl 1 Guidelines 1 1api-403316973Noch keine Bewertungen
- Catch Up RPHDokument6 SeitenCatch Up RPHபிரதீபன் இராதேNoch keine Bewertungen
- Philpost RRDokument6 SeitenPhilpost RRGene AbotNoch keine Bewertungen
- Genie PDFDokument277 SeitenGenie PDFOscar ItzolNoch keine Bewertungen
- 16-ELS-Final-Module 16-08082020Dokument18 Seiten16-ELS-Final-Module 16-08082020jeseca cincoNoch keine Bewertungen
- 377 Situational Expression Advanced Level Test Quiz Online Exercise With Answers 1Dokument7 Seiten377 Situational Expression Advanced Level Test Quiz Online Exercise With Answers 1zdravkamajkicNoch keine Bewertungen
- FM Testbank-Ch18Dokument9 SeitenFM Testbank-Ch18David LarryNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 3 Depreciation - Sum of The Years Digit MethodPart 4Dokument8 SeitenChapter 3 Depreciation - Sum of The Years Digit MethodPart 4Tor GineNoch keine Bewertungen
- Die Openbare BeskermerDokument3 SeitenDie Openbare BeskermerJaco BesterNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2021-01-01 - Project (Construction) - One TemplateDokument1.699 Seiten2021-01-01 - Project (Construction) - One TemplatemayalogamNoch keine Bewertungen
- D.O. 221-A - Application Form (Renewal)Dokument1 SeiteD.O. 221-A - Application Form (Renewal)Karl PagzNoch keine Bewertungen
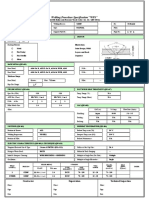
- Wps For Carbon Steel THK 7.11 GtawDokument1 SeiteWps For Carbon Steel THK 7.11 GtawAli MoosaviNoch keine Bewertungen
- ABHIGYAN 2020 E-InvitationDokument2 SeitenABHIGYAN 2020 E-Invitationchirag sabhayaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Iroquois Clothes and WampumDokument3 SeitenIroquois Clothes and Wampumapi-254323856Noch keine Bewertungen
- Walton Finance Way Strategy (MO)Dokument12 SeitenWalton Finance Way Strategy (MO)AshokNoch keine Bewertungen
- IGCSE 0408 Unseen Poem QuestionsDokument5 SeitenIGCSE 0408 Unseen Poem QuestionsMenon HariNoch keine Bewertungen
- History of Old English GrammarDokument9 SeitenHistory of Old English GrammarAla CzerwinskaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Science Grade 10 (Exam Prep)Dokument6 SeitenScience Grade 10 (Exam Prep)Venice Solver100% (3)
- Schermer 1984Dokument25 SeitenSchermer 1984Pedro VeraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Model DPR & Application Form For Integrated RAS PDFDokument17 SeitenModel DPR & Application Form For Integrated RAS PDFAnbu BalaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Black Hole Safety Brochure Trifold FinalDokument2 SeitenBlack Hole Safety Brochure Trifold Finalvixy1830Noch keine Bewertungen
- Turnbull CV OnlineDokument7 SeitenTurnbull CV Onlineapi-294951257Noch keine Bewertungen
- CO 101 Introductory Computing CO 102 Computing LabDokument17 SeitenCO 101 Introductory Computing CO 102 Computing Labadityabaid4Noch keine Bewertungen
- Ebook Stackoverflow For ItextDokument336 SeitenEbook Stackoverflow For ItextAnonymous cZTeTlkag9Noch keine Bewertungen