Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Tense
Hochgeladen von
Abdul Mannan Khawaja0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
35 Ansichten14 SeitenCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
PPTX, PDF, TXT oder online auf Scribd lesen
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als PPTX, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
35 Ansichten14 SeitenTense
Hochgeladen von
Abdul Mannan KhawajaCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als PPTX, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
Sie sind auf Seite 1von 14
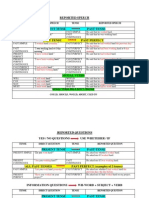
What is Tense?
The word “Tense” is derived from the Latin
word “Tempus” which means time. Based on
time frame, that is when the action is taking
place, we can divide or categorize tense into
three types:
• Present Tense
• Past Tense
• Future Tense
The present, past and future tenses have
been categorized into four types.
Indefinite Tense
Continuous Tense
Perfect Tense
Perfect Continuous Tense
Present Indefinite Tense
The tense which expresses a repeated
action or situation that exists only now. It
can also represent a timeless facts.
EXAMPLES:
The sun rises in the east. (Timeless Fact)
Spiders make webs. (Timeless Fact)
I brush my teeth twice a day. (Habitual)
I go to school daily. (Habitual)
Structure:
Simple sentence
S + Ist form of verb (-s or -es) + O.
Ex: He writes an essay.
He, she, it or any name= Singular noun = s, es
I, we, you, they=plural noun ( s, es are not used.)
Negative sentence
S + do/does +not+ Ist form of verb + O
Ex: He does not read the book.
He, she, it, any name (singular noun) does
I, we, you, they (plural noun) do
Interrogative Sentence
Do/does + S + Ist form of verb + O + ?
Ex: Does she pass the exams?
Present Continuous Tense
Actions happening at the moment of
speaking (now).
I am writing an email.
She is speaking to someone.
Actions that are scheduled in the future.
I’m going to meet Barbara tonight.
Structure
Simple Sentence
Subj + am/is/are + 1st form of verb +ing + Obj.
Negative Sentence
Subj + am/is/are + not + 1st form of verb +ing +
Obj.
Interrogative Sentence
Am/is/are + subj + 1st form of verb +ing + Obj?
Examples
I am working in bank.
He is not working in bank.
Are you working in bank?
Present Perfect Tense
To talk about a present situation that
started in the past and there is some
sort of completion in them.
Example:
They have visited many places.
I have written 16 books.
Structure
Simple Sentence
Subj + have/has +3rd form of verb + Obj.
Negative Sentence
Subj + have/has+ not + 3rd form of verb+ Obj
Interrogative Sentence
Have/has+ subj + 3rd form of verb + Obj?
Examples
He has bought a lot of new clothes.
He has not bought a lot of new clothes.
Has he bought a lot of new clothes?
Present Perfect Continuous
Actions that started in the past, continue
into the present, and may continue into
the future.
Examples:
The children have been playing since
morning.
My neighbour has been living next door
to me for two years.
Structure
Simple Sentence
Subj + have/has + been +1st form of verb + ing+ Obj+
since/for +time
Negative Sentence
Subj + have/has +not+ been +1st form of verb + ing+
Obj+ since/for +time
Interrogative Sentence
Have/has +subject+ been +1st form of verb + ing+
Obj+ since/for +time?
Examples
He has been living in this house since Wednesday.
He has not been living in this house since Wednesday.
Has he been living in this house since Wednesday?
Use of ‘for’ and ‘since’
For and Since – We use them with present
perfect to talk about the duration of a state or an
action which began in the past and which still
continues. They answer the question “How long...?
For: To talk about how long an action or state has
continued (period of time)
She has been working here for three months.
Since: To refer to the specific moment when a
state or an action began. (point of time)
She has been working here since last summer.
Difference b/w Perfect and Perfect
Continuous
The present perfect continuous tense is used to talk
about a continuous, but not necessarily finished
action or situation.
The present perfect tense is used to talk about a
finished action or situation.
Examples:
I have been gardening since morning. (Focus on
continuity)
I have planted several new saplings. (Focus on
completion)
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeVon EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (537)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeVon EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (5794)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceVon EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (895)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Von EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Bewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (98)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceVon EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (588)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingVon EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (400)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerVon EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (271)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItVon EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (838)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyVon EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (2259)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealVon EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (74)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureVon EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryVon EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnVon EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (234)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaVon EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (266)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersVon EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (345)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaVon EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (45)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreVon EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Von EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Bewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesVon EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (821)
- English 7 Module - Week 4Dokument10 SeitenEnglish 7 Module - Week 4Edna AcedillaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Skillful Listening Speaking Level 2 Unit 7 Fear PDFDokument10 SeitenSkillful Listening Speaking Level 2 Unit 7 Fear PDFJaniele F. Scarabelot100% (1)
- TOEFL Grammar Guide PDFDokument78 SeitenTOEFL Grammar Guide PDFMint Abdallahi90% (29)
- Forming Present Perfect: Irregular VerbsDokument3 SeitenForming Present Perfect: Irregular VerbsJavier Gutierrez100% (1)
- 6 TensesDokument51 Seiten6 TensesSyedWajahatAli100% (1)
- EnglishDokument76 SeitenEnglishArghyaNandiNoch keine Bewertungen
- English Verb PDFDokument13 SeitenEnglish Verb PDFXenia LysyukNoch keine Bewertungen
- English ConditionalsDokument4 SeitenEnglish ConditionalsAser MorganNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sample Pages CatalogueDokument24 SeitenSample Pages CatalogueShisha Gra0% (1)
- Present Perfect AdvancedDokument4 SeitenPresent Perfect Advanceddiala_aliNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2ESO Summer WorkDokument38 Seiten2ESO Summer WorkAnastasia GarcíaNoch keine Bewertungen
- English Grammar SummarynDokument86 SeitenEnglish Grammar SummarynAbdussalām Al-MuzāmbiqīNoch keine Bewertungen
- 16 Tenses Form (Strive, Sting)Dokument3 Seiten16 Tenses Form (Strive, Sting)Tia Novita BoestamiNoch keine Bewertungen
- 16 Narration E-BookDokument278 Seiten16 Narration E-BookSumit khanathia100% (2)
- PAST AND PERFECT TENSES Lesson G7Dokument1 SeitePAST AND PERFECT TENSES Lesson G7Joshua Lander Soquita CadayonaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Class 6 - VerbDokument28 SeitenClass 6 - VerbjoshuaNoch keine Bewertungen
- My Present Perfect vs. Simple PastDokument18 SeitenMy Present Perfect vs. Simple PastRosmery RiberaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Passive VoiceDokument6 SeitenPassive VoiceAriana CordovaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Aspect Tense 2021Dokument4 SeitenAspect Tense 2021Ola ŁabędźNoch keine Bewertungen
- English Perfect Tense ExerciseDokument6 SeitenEnglish Perfect Tense ExerciseHamerZanchezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Reported Speech - Rules To Change TensesDokument9 SeitenReported Speech - Rules To Change TensesAadil ShakulNoch keine Bewertungen
- Understanding Verb TenseDokument20 SeitenUnderstanding Verb TenseLewy Katrin S. Cortez100% (1)
- Nicoleta Medrea - English For Law and Public Administration.Dokument57 SeitenNicoleta Medrea - English For Law and Public Administration.gramadorin-10% (1)
- 15 Points 0Dokument28 Seiten15 Points 0zineb larouiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Reported Speech ChartDokument3 SeitenReported Speech ChartLeonidas Miranda100% (1)
- ''Constructional Morphology - The Georgian Version'' (Olga Gurevich, 2006)Dokument257 Seiten''Constructional Morphology - The Georgian Version'' (Olga Gurevich, 2006)ThriwNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 7 Narrative TensesDokument2 SeitenUnit 7 Narrative Tensescmooreruiz18Noch keine Bewertungen
- The Verb (Tenses)Dokument43 SeitenThe Verb (Tenses)Bianca DenisaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Micro LessonDokument31 SeitenMicro LessonMarcela Borges PradoNoch keine Bewertungen
- TEST PAPER Present PerfectDokument3 SeitenTEST PAPER Present PerfectIoana-Maria TodeaNoch keine Bewertungen