Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
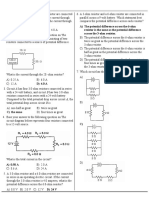
MCQ2-Sat Com
Hochgeladen von
Keilla Romabiles Leopando0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
42 Ansichten41 SeitenCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
PPTX, PDF, TXT oder online auf Scribd lesen
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als PPTX, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
42 Ansichten41 SeitenMCQ2-Sat Com
Hochgeladen von
Keilla Romabiles LeopandoCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als PPTX, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
Sie sind auf Seite 1von 41
MCQ: SATELLITE COMMUNICATIONS
Prepared by: Keilla Marie R. Leopando, ECE,
CCNA
Practice Questions
1. For real-time communication, LEO
systems require:
a. a constellation of satellites
b. tracking dish antennas
c. very high power
d. all of the above
Practice Questions
1. For real-time communication, LEO
systems require:
a. a constellation of satellites
b. tracking dish antennas
c. very high power
d. all of the above
Practice Questions
2. The maximum propagation delay of a
geostationary satellite is
A. 278 ms
B. 239 ms
C. 300 ms
D. 250 ms
Practice Questions
2. The maximum propagation delay of a
geostationary satellite is
A. 278 ms
B. 239 ms
C. 300 ms
D. 250 ms
Practice Questions
3 The frequency bands used by Ku-band
satellites are:
a. 4 GHz and 6 GHz
b. 12 GHz and 14 GHz
c. 20 GHz and 30 GHz
d. none of the above
Practice Questions
3. The frequency bands used by Ku-band
satellites are:
a. 4 GHz and 6 GHz
b. 12 GHz and 14 GHz
c. 20 GHz and 30 GHz
d. none of the above
Practice Questions
4. The transmitter-receiver combination in
the satellite is known as a _______
a) Relay
b) Repeater
c) Transponder
d) Duplexer
Practice Questions
4. The transmitter-receiver combination in
the satellite is known as a _______
a) Relay
b) Repeater
c) Transponder
d) Duplexer
Practice Questions
5. What is the reason for carrying multiple
transponders in a satellite?
a) More number of operating channel
b) Better reception
c) More gain
d) Redundancy
Practice Questions
5. What is the reason for carrying multiple
transponders in a satellite?
a) More number of operating channel
b) Better reception
c) More gain
d) Redundancy
Practice Questions
6. Why are VHF, UHF, and microwave
signals used in satellite communication?
a) More bandwidth
b) More spectrum space
c) Are not diffracted by the ionosphere
d) Economically viable
Practice Questions
6. Why are VHF, UHF, and microwave
signals used in satellite communication?
a) More bandwidth
b) More spectrum space
c) Are not diffracted by the ionosphere
d) Economically viable
Practice Questions
7. What is the reason for shifting from c
band to ku band in satellite communication?
a) Lesser attenuation
b) Less power requirements
c) More bandwidth
d) Overcrowding
Practice Questions
7. What is the reason for shifting from c
band to ku band in satellite communication?
a) Lesser attenuation
b) Less power requirements
c) More bandwidth
d) Overcrowding
Practice Questions
8. Why are techniques like frequency reuse
and spatial isolation carried out?
a) Reduce traffic load
b) More gain
c) High speed
d) Error detection
Practice Questions
8. Why are techniques like frequency reuse
and spatial isolation carried out?
a) Reduce traffic load
b) More gain
c) High speed
d) Error detection
Practice Questions
9. Rotation of a geosynchronous satellite
means its
A. drift from stationary position
B. wobbling
C. three-axis stabilization
D. three-dimensional stabilization
Practice Questions
9. Rotation of a geosynchronous satellite
means its
A. drift from stationary position
B. wobbling
C. three-axis stabilization
D. three-dimensional stabilization
Practice Questions
10. A satellite covers longitude of earth up to
A.110°
B.120°
C.150°
D. 180°
Practice Questions
10. A satellite covers longitude of earth up to
A.110°
B.120°
C.150°
D. 180°
Practice Questions
11. Whole world can be covered with
A.2 geo-stationary satellites
B.3 geo-stationary satellites
C.4 geo-stationary satellites
D. 5 geo-stationary satellites
Practice Questions
11. Whole world can be covered with
A.2 geo-stationary satellites
B.3 geo-stationary satellites
C.4 geo-stationary satellites
D. 5 geo-stationary satellites
Practice Questions
12. Descending pass for a satellite means a
pass from
A. North to South
B. South to North
C. East to West
D. West to East
Practice Questions
12. Descending pass for a satellite means a
pass from
A. North to South
B. South to North
C. East to West
D. West to East
Practice Questions
13. Satellite engine use
A. Liquid fuel
B. Jet propulsion
C. Ion propulsion system
D. Solar jet
Practice Questions
13. Satellite engine use
A. Liquid fuel
B. Jet propulsion
C. Ion propulsion system
D. Solar jet
Practice Questions
14. _______ detects the satellite signal
relayed from the feed and converts it to an
electric current, amplifies and lower its
frequency
A. feedhorn
B. Satellite dish
C. Satellite receiver
D. Low noise block downconverter
Practice Questions
14. _______ detects the satellite signal
relayed from the feed and converts it to an
electric current, amplifies and lower its
frequency
A. feedhorn
B. Satellite dish
C. Satellite receiver
D. Low noise block downconverter
Practice Questions
15. What kind of battery panels are used in
some advanced satellites?
A. Gallium arsenide solar panel
B. Germanium based panels
C. Silicon based panels
D. Gallium phosphate solar panel
Practice Questions
15. What kind of battery panels are used in
some advanced satellites?
A. Gallium arsenide solar panel
B. Germanium based panels
C. Silicon based panels
D. Gallium phosphate solar panel
Practice Questions
16.Galileo satellites are inclined at the
orbital planes of ____ with reference to the
equatorial plane.
A. 64 degrees
B. 17 degrees
C. 56 degrees
D. 34 degrees
Practice Questions
16. Galileo satellites are inclined at the
orbital planes of ____ with reference to the
equatorial plane.
A. 64 degrees
B. 17 degrees
C. 56 degrees
D. 34 degrees
Practice Questions
17. Satellite orbiting in the same direction as
earth’s rotation and at an angular velocity greater
than the earth is called prograde orbit; and a
satellite orbiting which is in the opposite direction
as Earth’s rotation or in the same direction but at
an angular velocity less than that of Earth is known
as
a. Haley’s orbit
b. Elliptical orbit
c. Equatorial orbit
d. Retrograde orbit
Practice Questions
17. Satellite orbiting in the same direction as
earth’s rotation and at an angular velocity greater
than the earth is called prograde orbit; and a
satellite orbiting which is in the opposite direction
as Earth’s rotation or in the same direction but at
an angular velocity less than that of Earth is known
as
a. Haley’s orbit
b. Elliptical orbit
c. Equatorial orbit
d. Retrograde orbit
Practice Questions
18. Which of the following is the most common
application of satellite?
A. Surveillance
B. Military application
C. Communications
D. Newscasting
Practice Questions
18. Which of the following is the most common
application of satellite?
A. Surveillance
B. Military application
C. Communications
D. Newscasting
Practice Questions
19. The smallest beam of a satellite antenna
radiation pattern
A. Zone beam
B. Hemispheric beam
C. Spot beam
D. Global beam
Practice Questions
19. The smallest beam of a satellite antenna
radiation pattern
A. Zone beam
B. Hemispheric beam
C. Spot beam
D. Global beam
Practice Questions
20. What is a device that detects both vertically
and horizontally polarized signals simultaneously?
A. Orthomode transducer
B. Crystal detector
C. Optoisolator
D. Isomode detector
Practice Questions
20. What is a device that detects both vertically
and horizontally polarized signals simultaneously?
A. Orthomode transducer
B. Crystal detector
C. Optoisolator
D. Isomode detector
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- PINOYBIX SATELLITE COMMUNICATION QuestionDokument47 SeitenPINOYBIX SATELLITE COMMUNICATION QuestionCamille VeaNoch keine Bewertungen
- MCQs - Satellite CommunicationDokument26 SeitenMCQs - Satellite Communicationshamsundar kulkarniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Satellite Comm MCQ PDFDokument20 SeitenSatellite Comm MCQ PDFdbircsNoch keine Bewertungen
- F.CN343 Seminar 4-MC Quistions Problems PDFDokument8 SeitenF.CN343 Seminar 4-MC Quistions Problems PDFTemuulen AsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Satellite Comms QuestionaresDokument74 SeitenSatellite Comms QuestionaresraymondNoch keine Bewertungen
- Microwave CommunicationsDokument221 SeitenMicrowave CommunicationscajaroNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mutiple Choice Question For Satellite CommunicationDokument4 SeitenMutiple Choice Question For Satellite CommunicationRaja Pirian67% (3)
- MCQ - SAtellite and CommunicationsDokument11 SeitenMCQ - SAtellite and CommunicationsTanyaGarg100% (1)
- Comms 4 Satcom AnswersDokument5 SeitenComms 4 Satcom AnswersjobelleNoch keine Bewertungen
- MCQs in Satellite Communications Part I - PinoyBIX - Engineering ReviewDokument9 SeitenMCQs in Satellite Communications Part I - PinoyBIX - Engineering ReviewKitacatesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Satellite Communication Objective PDFDokument81 SeitenSatellite Communication Objective PDFAnkit JhaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 08 SatcomDokument11 Seiten08 SatcomAchilles AldaveNoch keine Bewertungen
- Group Study - Satcom - QuestionnaireDokument9 SeitenGroup Study - Satcom - QuestionnaireJason Ismael TorresNoch keine Bewertungen
- Antenna McqsDokument7 SeitenAntenna McqsTalha KhalidNoch keine Bewertungen
- Group Study - Satcom Answer KeyDokument9 SeitenGroup Study - Satcom Answer KeySheehan Kayne De CardoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hypersat PDFDokument49 SeitenHypersat PDFjobelleNoch keine Bewertungen
- Important MCQ - Satellite CommunicationDokument8 SeitenImportant MCQ - Satellite CommunicationarijitlgspNoch keine Bewertungen
- Advanced Communication - MANU RAJU-APDokument78 SeitenAdvanced Communication - MANU RAJU-APshilpasusanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Satellite CommunicationDokument27 SeitenSatellite CommunicationJohn Arman ArcayaNoch keine Bewertungen
- MCQs in Microwave Communications Part IIIDokument10 SeitenMCQs in Microwave Communications Part IIIRaghu Veer KNoch keine Bewertungen
- Purple Hat App: Multiple Choice QuestionsDokument49 SeitenPurple Hat App: Multiple Choice QuestionsSharvesh ChopadeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sta. Ana Avenue. Corner Leon Garcia ST., Davao City Tel. No. (082) 303-3078, (082) 295-7219Dokument3 SeitenSta. Ana Avenue. Corner Leon Garcia ST., Davao City Tel. No. (082) 303-3078, (082) 295-7219Jhonel AlbarracinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Antenna Question and AnswerDokument5 SeitenAntenna Question and AnswerIsaiah Philip Alob MacamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Adu SatcomDokument1 SeiteAdu SatcomHannah Dizon ReinaresNoch keine Bewertungen
- MWC - 22533 - MCQ Set 3 - Winter 2020Dokument15 SeitenMWC - 22533 - MCQ Set 3 - Winter 2020KHEDEKAR HRUTUJA100% (1)
- Antenna and WaveguidesDokument5 SeitenAntenna and WaveguidesRenz Dave Attos SiyNoch keine Bewertungen
- SMC PDFDokument144 SeitenSMC PDFRahul TadeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Antennas and Radio Wave PropagationDokument7 SeitenAntennas and Radio Wave PropagationMike PuaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Satellite Communictions BitsDokument8 SeitenSatellite Communictions Bitsvasudev jellaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Technical Seminar BY: Saroj SahDokument28 SeitenTechnical Seminar BY: Saroj SahNurshuhaila SueNoch keine Bewertungen
- Communications Engineering Mastery Test 8 ECE Pre-BoardDokument35 SeitenCommunications Engineering Mastery Test 8 ECE Pre-BoardXyNoch keine Bewertungen
- MCQs in Microwave Communications Part IIDokument9 SeitenMCQs in Microwave Communications Part IIRaghu Veer KNoch keine Bewertungen
- Kennedy Q&ADokument9 SeitenKennedy Q&AKrit JimenezNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1 - 300Dokument48 Seiten1 - 300Jeff Michael GomezNoch keine Bewertungen
- EC 801C Question BankDokument12 SeitenEC 801C Question BankSatyaki PalNoch keine Bewertungen
- COMMS 2 - Antenna & RadiowaveANSWERSDokument4 SeitenCOMMS 2 - Antenna & RadiowaveANSWERSRovina LacunaNoch keine Bewertungen
- End Sem QuestionsDokument9 SeitenEnd Sem QuestionsAakansha SuchittaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1-fainle exam third 2019-2020- 1 نموذجDokument3 Seiten1-fainle exam third 2019-2020- 1 نموذجمهيمن الابراهيميNoch keine Bewertungen
- CS203 Switching Theory and Logic DesignDokument5 SeitenCS203 Switching Theory and Logic DesignsivaramkumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- E-II Satellite Communication - MCQ - Vijay ChakoleDokument179 SeitenE-II Satellite Communication - MCQ - Vijay ChakoleHarsh DaharwalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 5 3,4 1MDokument3 SeitenUnit 5 3,4 1Mchinnujan24Noch keine Bewertungen
- 101Dokument11 Seiten101Superb HMNoch keine Bewertungen
- Qwestion ExamDokument3 SeitenQwestion ExamKumbati SupertiksNoch keine Bewertungen
- Satellite Communication 2 Marks AnswersDokument6 SeitenSatellite Communication 2 Marks Answersvivek_ch87100% (5)
- ##Question Bank of WMC - REC-085Dokument50 Seiten##Question Bank of WMC - REC-085Kshitij PalNoch keine Bewertungen
- COMMS 2 - Antenna & RadiowaveDokument5 SeitenCOMMS 2 - Antenna & RadiowaveGretel Abella InesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Avionics Questions and AnswersDokument69 SeitenAvionics Questions and AnswersNiguse BerhanuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electro Magnetic Field: Answer: CDokument10 SeitenElectro Magnetic Field: Answer: CPrem RajNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 2 Satellite Subsystem Multiple Choice Question BankDokument3 SeitenChapter 2 Satellite Subsystem Multiple Choice Question BankABESIT College of Engineering100% (1)
- PSU MCQs On Satellite Communication and RadarDokument6 SeitenPSU MCQs On Satellite Communication and RadarMohan Devaraj67% (3)
- Ece LawsDokument4 SeitenEce LawsJam MagatNoch keine Bewertungen
- KennedyDokument4 SeitenKennedyMichael SalvahanNoch keine Bewertungen
- MCQs in Microwave Communications Part IDokument10 SeitenMCQs in Microwave Communications Part IRaghu Veer KNoch keine Bewertungen
- EST Microwave2 NotesDokument28 SeitenEST Microwave2 NotesElmarie RecorbaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 100 MCQDokument20 Seiten100 MCQJoseph Kerby J. NavaNoch keine Bewertungen
- MCQs Satellite 1 150 OnlyDokument6 SeitenMCQs Satellite 1 150 OnlyMoneth PerezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Satellite Communication (Pinoybix)Dokument31 SeitenSatellite Communication (Pinoybix)Jason MiralloNoch keine Bewertungen
- Uncertainties in GPS Positioning: A Mathematical DiscourseVon EverandUncertainties in GPS Positioning: A Mathematical DiscourseBewertung: 3 von 5 Sternen3/5 (2)
- Satellite Communications Systems Engineering: Atmospheric Effects, Satellite Link Design and System PerformanceVon EverandSatellite Communications Systems Engineering: Atmospheric Effects, Satellite Link Design and System PerformanceNoch keine Bewertungen
- Correlation & ConvolutionDokument17 SeitenCorrelation & ConvolutionKeilla Romabiles LeopandoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Phase-Locked Loop (PLL) : EE174 - SJSU Tan NguyenDokument40 SeitenPhase-Locked Loop (PLL) : EE174 - SJSU Tan NguyenriponkumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Controlling 4ECEDokument23 SeitenControlling 4ECEKeilla Romabiles LeopandoNoch keine Bewertungen
- DectobcdDokument2 SeitenDectobcdKeilla Romabiles LeopandoNoch keine Bewertungen
- MCQ1Dokument51 SeitenMCQ1Keilla Romabiles LeopandoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cpe083 Lecture2Dokument9 SeitenCpe083 Lecture2Keilla Romabiles LeopandoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assignment ADIDokument2 SeitenAssignment ADIKeilla Romabiles LeopandoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Integral&DerivativeDokument2 SeitenIntegral&DerivativeKeilla Romabiles LeopandoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electrical SafetyDokument15 SeitenElectrical SafetyKeilla Romabiles LeopandoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Emergency PreparednessDokument16 SeitenEmergency PreparednessKeilla Romabiles LeopandoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Emergency PreparednessDokument16 SeitenEmergency PreparednessKeilla Romabiles LeopandoNoch keine Bewertungen
- ProblemSet1 LeopandoDokument10 SeitenProblemSet1 LeopandoKeilla Romabiles LeopandoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Emergency PreparednessDokument16 SeitenEmergency PreparednessKeilla Romabiles LeopandoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chopper FormulaDokument1 SeiteChopper FormulaKeilla Romabiles LeopandoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Math 151 (WN10) CH 3 NotesDokument52 SeitenMath 151 (WN10) CH 3 NotesKeilla Romabiles LeopandoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Motion - 1&2DDokument2 SeitenMotion - 1&2DKeilla Romabiles LeopandoNoch keine Bewertungen
- xs01 PDFDokument3 Seitenxs01 PDFKeilla Romabiles LeopandoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Solution Quiz3 INME4045 2004 PDFDokument2 SeitenSolution Quiz3 INME4045 2004 PDFKeilla Romabiles LeopandoNoch keine Bewertungen
- PHYS 102 - Exam 1 - Spring 2015: Identify The Choice That Best Completes The Statement or Answers The QuestionDokument6 SeitenPHYS 102 - Exam 1 - Spring 2015: Identify The Choice That Best Completes The Statement or Answers The QuestionKeilla Romabiles LeopandoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Notes/Lect 4 MMTDokument19 SeitenNotes/Lect 4 MMTKeilla Romabiles LeopandoNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Second Law of Thermodynamics: MAE 320 - Chapter 6Dokument8 SeitenThe Second Law of Thermodynamics: MAE 320 - Chapter 6Keilla Romabiles LeopandoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture 1 Acoustic FundamentalsDokument50 SeitenLecture 1 Acoustic FundamentalsKeilla Romabiles LeopandoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Solution Quiz3 INME4045 2004Dokument2 SeitenSolution Quiz3 INME4045 2004Keilla Romabiles LeopandoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ass2 Broadcast FinalDokument2 SeitenAss2 Broadcast FinalKeilla Romabiles LeopandoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Circuits Practice Test KeyDokument6 SeitenCircuits Practice Test KeyKeilla Romabiles LeopandoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Circuits Practice Test KeyDokument6 SeitenCircuits Practice Test KeyKeilla Romabiles LeopandoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 14Dokument24 SeitenChapter 14Keilla Romabiles LeopandoNoch keine Bewertungen
- GATE EE 2002 Actual Paper PDFDokument24 SeitenGATE EE 2002 Actual Paper PDFKeilla Romabiles LeopandoNoch keine Bewertungen
- KBP Broadcast Code 2011Dokument52 SeitenKBP Broadcast Code 2011Jairdan BabacNoch keine Bewertungen
- 3 LoopDokument6 Seiten3 Loopbayman66Noch keine Bewertungen
- Wireless Data Encryption and Decryption Using Radio Frequence (FINAL YEAR PROJECT OF ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING)Dokument54 SeitenWireless Data Encryption and Decryption Using Radio Frequence (FINAL YEAR PROJECT OF ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING)syedfahadraza62785% (20)
- 3e0377 Install Note Io Expansion Interface - 2Dokument11 Seiten3e0377 Install Note Io Expansion Interface - 2bsdygswdywNoch keine Bewertungen
- Antenna Systems GuideDokument72 SeitenAntenna Systems GuidecvevasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Design Consideration of Microstrip Patch AntennaDokument11 SeitenDesign Consideration of Microstrip Patch AntennaNag ChallaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Department of Electronic Engineering: Final Year Project ReportDokument57 SeitenDepartment of Electronic Engineering: Final Year Project ReportMichael NzekiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Evolution of Gi-FiDokument18 SeitenEvolution of Gi-FiAmeeenaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Transmission Analysis of A Single Hop For Microwave Link-ADokument36 SeitenTransmission Analysis of A Single Hop For Microwave Link-Aeyasu abebe adoNoch keine Bewertungen
- t4502 Motorola RadioDokument64 Seitent4502 Motorola Radiopaulsniff6Noch keine Bewertungen
- A High-Capacity Transmission Technique Using A Wide Range of Frequencies, Which Enables A Large Number of Messages To Be Communicated SimultaneouslyDokument1 SeiteA High-Capacity Transmission Technique Using A Wide Range of Frequencies, Which Enables A Large Number of Messages To Be Communicated Simultaneouslymukhtar omerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Digital Com theory-Compiled-P.Nagaraju PDFDokument59 SeitenDigital Com theory-Compiled-P.Nagaraju PDFprashanth_02Noch keine Bewertungen
- Assignment 2: Communication TheoryDokument2 SeitenAssignment 2: Communication TheoryJahnavi RameshNoch keine Bewertungen
- User's Guide: Personal Am/Fm Stereo Compact Disc Player With 45 Second Digital Anti-Shock ProtectionDokument19 SeitenUser's Guide: Personal Am/Fm Stereo Compact Disc Player With 45 Second Digital Anti-Shock ProtectionmwuestNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture 5 - Digital ModulationDokument12 SeitenLecture 5 - Digital ModulationAbdulrahmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Department of Electronics & Telecommunication Engineering Teaching Plan (5 Sem ENTC) Name of The Teacher: Prof. BISHNU PRIYA SAMALDokument2 SeitenDepartment of Electronics & Telecommunication Engineering Teaching Plan (5 Sem ENTC) Name of The Teacher: Prof. BISHNU PRIYA SAMALAnanyaja DebadiptaNoch keine Bewertungen
- SRAN HW Wiring 4G OverlayDokument19 SeitenSRAN HW Wiring 4G OverlayAdin AlayubiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bss Additional Info On SDCCH Abis Fail Call c1075Dokument2 SeitenBss Additional Info On SDCCH Abis Fail Call c1075Pankaj KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Radio Over Fiber TechnologyDokument46 SeitenRadio Over Fiber TechnologySyed Shahzaib RazaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 7/8" CELLFLEX® Premium Attenuation Low-Loss Foam-Dielectric Coaxial CableDokument4 Seiten7/8" CELLFLEX® Premium Attenuation Low-Loss Foam-Dielectric Coaxial CableLuciano Silvério LeiteNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sample Project ReportDokument47 SeitenSample Project ReportRaman SvNoch keine Bewertungen
- Digital Video Camera Recorder: DCR-TRV230/TRV330/TRV530Dokument156 SeitenDigital Video Camera Recorder: DCR-TRV230/TRV330/TRV530maseloNoch keine Bewertungen
- Platinum Gateway ManualDokument8 SeitenPlatinum Gateway Manualjose luisNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unity Gain Base Station and Marine UHF Antenna: DescriptionDokument1 SeiteUnity Gain Base Station and Marine UHF Antenna: DescriptionMerdan HudaykuliyevNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ja-100 Catalogue enDokument32 SeitenJa-100 Catalogue ensarsmajorNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ge SSB HBDokument234 SeitenGe SSB HBwpettit_2Noch keine Bewertungen
- Build A Return Loss BridgeDokument6 SeitenBuild A Return Loss Bridgegrezmos100% (1)
- VoLTE Modelling in AtollDokument6 SeitenVoLTE Modelling in AtollthiepvtNoch keine Bewertungen
- A320 Emergency Location TransmitterDokument20 SeitenA320 Emergency Location TransmitterBernard XavierNoch keine Bewertungen
- JHCP BRUTE Literature PDFDokument2 SeitenJHCP BRUTE Literature PDFandreodeoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Datacard CD800 Card Printer User's Guide: Part No. 527443-001 Rev. ADokument114 SeitenDatacard CD800 Card Printer User's Guide: Part No. 527443-001 Rev. ADawson BanksNoch keine Bewertungen