Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
ECG (Electrocardiogram)
Hochgeladen von
Monica Angelique Salayo0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
18 Ansichten13 SeitenCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
PPTX, PDF, TXT oder online auf Scribd lesen
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als PPTX, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
18 Ansichten13 SeitenECG (Electrocardiogram)
Hochgeladen von
Monica Angelique SalayoCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als PPTX, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
Sie sind auf Seite 1von 13
ECG (Electrocardiogram)
Prepared by: Monica Angelique P. Salayo
WHAT IS ECG?
• An ECG is a method of measuring, displaying and
recording the electrical activity of a heart
• Interpretation of these details allows diagnosis of a
wide range of heart conditions. These conditions
can vary from minor to life threatening
Reasons for an ECG
• Patients who complain of chest pain or shortness of
breath
• To help determine if there is an acute myocardial
infarction or heart attack present
• Can help decide whether the pain is due to angina or
narrowing of blood vessels to the heart muscle
• To determine the status of the heart prior to procedures
such as surgery and/or after treatment for conditions
such as a heart attack (myocardial infarction, or MI),
endocarditis (inflammation or infection of one or more
of the heart valves), or after procedures such as heart
surgery or cardiac catheterization
Anatomy and Function of the
Heart's Electrical System
• The heart's pumping action
is regulated by an electrical
conduction system that
coordinates the contraction
of the various chambers of
the heart.
Nursing Considerations
• Always verify doctor’s order
• Explain the procedure to the patient and offer
opportunity to ask any questions about the
procedure.
• Generally, fasting is not required before the test.
• Ask the patient about all medications ( prescribed
and OTC drugs and herbal supplements.
• An ECG can be performed almost anywhere, as
the equipment is very compact and portable. Thus,
you may undergo an ECG in:
• physician's office,
• ECG department of the hospital or clinic,
• procedure or testing area,
• emergency department,
• hospital room or bed.
• An ECG normally takes approximately five to 10
minutes, including attaching and detaching
electrodes.
•
The area (s) where the electrodes are to be placed
may be shaves. If the chest, arms, or legs are very
hairy, it may be clip/shave small patches of hair, as
needed, so that the electrodes will stick closely to the
skin.
• Ask patient if he/she have pacemaker.
• Ask to remove any jewelry or other objects that may
interfere with the procedure.
• Have patient to lie flat in the center of a table or bed for
the procedure with his/ her arms at his/her sides.
• Make sure that the patient’s feet are not touching
the bed board.
• Ask the patient to relax to minimize muscle
trembling. It will be important for patient to lie still
and not talk during the procedure, so as not to
interfere with the tracing.
• Select flat, fleshy areas to place the electrode.
Avoid muscular and bony areas.
• If the patient has an amputated limb, choose a
site in the stump.
ELECTRODES PLACEMENT
LIMB LEADS COLOR
Right arm Red
(RA)
Left arm Yellow
(LA)
Right foot Black
(RF/ground
)
Left foot Green
(LF)
ELECTRODES PLACEMENT
PRECORDIAL POSITION COLOR
LEADS
V1 4th ICS at the Red
right sternal
border
V2 4TH ICS at the Yellow
left sternal
border
V3 Halfway Green
between V2
and V4 (left)
V4 5th ICS at the Brown
left mid
clavicular line
V5 5th ICS at the Black
anterior axillary
V6 5th ICS at left Purple
mid-axillary line
ECG Paper
ECG Paper
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryVon EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (231)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Von EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Bewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (119)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItVon EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (838)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaVon EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (265)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingVon EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (399)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceVon EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (587)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyVon EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (2219)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeVon EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (5794)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnVon EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (234)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeVon EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (537)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerVon EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (271)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreVon EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1090)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesVon EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (821)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersVon EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (344)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceVon EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (890)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureVon EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (474)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaVon EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (45)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Von EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Bewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (98)
- Intro - New Covenant TheologyDokument15 SeitenIntro - New Covenant TheologyDavid SalazarNoch keine Bewertungen
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealVon EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (73)
- VajroliDokument3 SeitenVajroliJithu BayiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biosimilars: Pros and Cons in Current Practice: MBBS, MRCP (Uk), FRCP (Edin), FamsDokument51 SeitenBiosimilars: Pros and Cons in Current Practice: MBBS, MRCP (Uk), FRCP (Edin), FamshoneyworksNoch keine Bewertungen
- Counseling techniques for special populationsDokument67 SeitenCounseling techniques for special populationsSittie Nabila Panandigan100% (2)
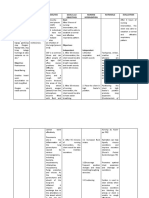
- Cues Nursing Diagnosis Analysis GOALS and Objectives Nursing Intervention Rationale Evaluation Subjective: GoalDokument4 SeitenCues Nursing Diagnosis Analysis GOALS and Objectives Nursing Intervention Rationale Evaluation Subjective: GoalMonica Angelique SalayoNoch keine Bewertungen
- José Rizal: The Life of The National HeroDokument9 SeitenJosé Rizal: The Life of The National HeroMark Harry Olivier P. VanguardiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Commercial Bank of Africa Market ResearchDokument27 SeitenCommercial Bank of Africa Market Researchprince185Noch keine Bewertungen
- Epd-Lca Meranti Plywood-Final ReportDokument29 SeitenEpd-Lca Meranti Plywood-Final ReporttangNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Anatomy and Physiology of The Respiratory SystemDokument26 SeitenThe Anatomy and Physiology of The Respiratory SystemMonica Angelique SalayoNoch keine Bewertungen
- ACS MedsDokument5 SeitenACS MedsMonica Angelique SalayoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Stroke DefDokument11 SeitenStroke DefMonica Angelique SalayoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Genito-Urinary AssessmentDokument52 SeitenGenito-Urinary AssessmentMonica Angelique SalayoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Abdominal Neurological AssessmentDokument4 SeitenAbdominal Neurological AssessmentMonica Angelique SalayoNoch keine Bewertungen
- FINAL Snake Bite Case PresDokument48 SeitenFINAL Snake Bite Case PresMonica Angelique SalayoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drug Classification Indication Mechanism of ActionDokument9 SeitenDrug Classification Indication Mechanism of ActionMonica Angelique SalayoNoch keine Bewertungen
- ACS MedsDokument5 SeitenACS MedsMonica Angelique SalayoNoch keine Bewertungen
- CVADokument8 SeitenCVAMonica Angelique SalayoNoch keine Bewertungen
- CVADokument8 SeitenCVAMonica Angelique SalayoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Abdominal Neurological AssessmentDokument4 SeitenAbdominal Neurological AssessmentMonica Angelique SalayoNoch keine Bewertungen
- CVADokument8 SeitenCVAMonica Angelique SalayoNoch keine Bewertungen
- TO B.inggris Dzakiy Bag 2Dokument21 SeitenTO B.inggris Dzakiy Bag 2Ayu RatnaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Kinematic Viscosity, Units & DimensionDokument7 SeitenKinematic Viscosity, Units & DimensionPrithwish Kr SutradharNoch keine Bewertungen
- MedicineDokument19 SeitenMedicineSarah100% (1)
- Sources of Coherent RadiationDokument7 SeitenSources of Coherent RadiationSubhash DhungelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fraud under Indian Contract Act - Essentials and Exceptions to Mere SilenceDokument6 SeitenFraud under Indian Contract Act - Essentials and Exceptions to Mere SilenceabhilashNoch keine Bewertungen
- CHAP 1: STATS & SCIENTIFIC METHODDokument9 SeitenCHAP 1: STATS & SCIENTIFIC METHODJesheryll ReasNoch keine Bewertungen
- PrisonerDokument10 SeitenPrisonerAbdi ShakourNoch keine Bewertungen
- 9851 BCG Vaccine Professional HCWDokument4 Seiten9851 BCG Vaccine Professional HCWIuliana PanaitNoch keine Bewertungen
- CS201 Midterm Solved MCQs With ReferenceDokument4 SeitenCS201 Midterm Solved MCQs With Referencegenome companyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Demand for Money Theory ExplainedDokument31 SeitenDemand for Money Theory Explainedrichard kapimpaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chauvin Arnoux 8220Dokument43 SeitenChauvin Arnoux 8220Danilo MuñozNoch keine Bewertungen
- Reactions of Hydrocarbons and HaloalkanesDokument6 SeitenReactions of Hydrocarbons and HaloalkanesGwynethAdrienneLeighVillapandoNoch keine Bewertungen
- MT 06Dokument2 SeitenMT 06Glen Rey BrunNoch keine Bewertungen
- Affidavit of DesistanceDokument6 SeitenAffidavit of Desistancesalasvictor319Noch keine Bewertungen
- English - Method BobathDokument4 SeitenEnglish - Method Bobathje_corektNoch keine Bewertungen
- B1 Mod 01 MathsDokument152 SeitenB1 Mod 01 MathsTharrmaselan VmanimaranNoch keine Bewertungen
- PROJECT REPORT Personal Selling PDFDokument19 SeitenPROJECT REPORT Personal Selling PDFHimaja GharaiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sugar Cane White FlyDokument13 SeitenSugar Cane White Flyvishnu0751Noch keine Bewertungen
- What Is Link AdaptationDokument4 SeitenWhat Is Link AdaptationAshutosh SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- English Proficiency Test (EPT) Reviewer With Answers - Part 1 - Online E LearnDokument4 SeitenEnglish Proficiency Test (EPT) Reviewer With Answers - Part 1 - Online E LearnMary Joy OlitoquitNoch keine Bewertungen
- About Nysc Ict CD in Imo StateDokument9 SeitenAbout Nysc Ict CD in Imo StateIsoft PexNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter04 PDFDokument36 SeitenChapter04 PDFBabuM ACC FIN ECONoch keine Bewertungen
- GATE Instrumentation Engineering Solved 2013Dokument22 SeitenGATE Instrumentation Engineering Solved 2013Meghraj ChiniyaNoch keine Bewertungen