Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
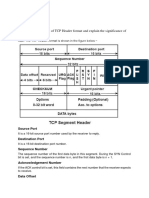
DNS, SMTP, Pop, FTP, HTTP
Hochgeladen von
Bapuji Valaboju0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
47 Ansichten9 SeitenOriginaltitel
Application layer
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
PPTX, PDF, TXT oder online auf Scribd lesen
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als PPTX, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
47 Ansichten9 SeitenDNS, SMTP, Pop, FTP, HTTP
Hochgeladen von
Bapuji ValabojuCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als PPTX, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
Sie sind auf Seite 1von 9
Application Layer Protocols
DNS, SMTP, POP, FTP, HTTP
Application Layer Protocols
DNS, SMTP, POP, FTP, HTTP
An application layer protocol defines how application
processes (clients and servers), running on different
end systems, pass messages to each other.
In particular, an application layer protocol defines:
The types of messages, e.g., request messages and
response messages.
• The syntax of the various message types, i.e., the
fields in the message and how the fields are
delineated.
• The semantics of the fields, i.e., the meaning of the
information that the field is supposed to contain;
• Rules for determining when and how a process
sends messages and responds to messages.
• To identify an entity, TCP/IP protocol uses the IP
address which uniquely identifies the connection of
a host to the Internet.
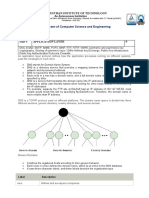
• DNS is a hierarchical system, based on a distributed
database, that uses a hierarchy of Name Servers to
resolve Internet host names into the corresponding
IP addresses required for packet routing by issuing a
DNS query to a name server.
• However, people refer to use names instead of
address. Therefore, we need a system that can map
a name to an address and conversely an address to
name.
• In TCP/IP, this is the domain name system.
• DNS in the Internet: DNS is protocol that can be
used in different platforms.
• Domain name space is divided into three categories.
• Generic Domain: The generic domain defines
registered hosts according, to their generic
behaviour. Each node in the tree defines a domain
which is an index to the domain name space
database.
•One of the most popular network service is electronic mail (e-
mail).
•The TCP/IP protocol that supports electronic mail on the Internet
is called Simple Mail Transfer Protocol (SMTP).
•SMTP transfers messages from senders' mail servers to the
recipients' mail servers using TCP connections.
•Users based on e-mail addresses.
•SMTP provides services for mail exchange between users on the
same or different computers.
•Following the client/server model:
SMTP has two sides: a client side which executes on a
sender's mail server, and server side which executes on
recipient's mail server.
Both the client and server sides of SMTP run on every mail
server.
When a mail server sends mail (to other mail servers), it acts
as an SMTP client.
When a mail server receives mail (from other mail servers) it
acts as an SMTP server.
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Chapter 09Dokument56 SeitenChapter 09maged abbass100% (2)
- WINSEM2020-21 CSE1004 ETH VL2020210504039 Reference Material I 20-May-2021 Application LayerDokument44 SeitenWINSEM2020-21 CSE1004 ETH VL2020210504039 Reference Material I 20-May-2021 Application LayerDivij BahlNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter - 10Dokument36 SeitenChapter - 10Sindhu official radhakrishnNoch keine Bewertungen
- CN UNIT-1 Application Layer ProtocolsDokument39 SeitenCN UNIT-1 Application Layer ProtocolsKowsalya GNoch keine Bewertungen
- 14 Application LayerDokument40 Seiten14 Application LayerRahul AryanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lesson 03 Rev Final PDFDokument9 SeitenLesson 03 Rev Final PDFThilan NawagamuwaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Application Layer: Prepared byDokument35 SeitenApplication Layer: Prepared byIhab AmerNoch keine Bewertungen
- CCN Unit 5Dokument47 SeitenCCN Unit 5sweethaa harinishriNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture 3Dokument32 SeitenLecture 3jasmhmyd205Noch keine Bewertungen
- Computer Networks (1) - 157-172Dokument16 SeitenComputer Networks (1) - 157-172Harini VelrajNoch keine Bewertungen
- Applications:Electronic Mail (SMTP, Pop, Imap, Mime) : Presented By-Tarun Lall Badrinath Sai Kumar PraveenDokument28 SeitenApplications:Electronic Mail (SMTP, Pop, Imap, Mime) : Presented By-Tarun Lall Badrinath Sai Kumar PraveenkdhanamjayNoch keine Bewertungen
- Computer Network Unit-5 NotesDokument44 SeitenComputer Network Unit-5 NotessuchitaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit V Application Layer Protocols (DNS, SMTP, POP, FTP, HTTP) Study NotesDokument5 SeitenUnit V Application Layer Protocols (DNS, SMTP, POP, FTP, HTTP) Study NotesSheba ParimalaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture12 Application LayerDokument33 SeitenLecture12 Application Layernguyenquanglinh01121999Noch keine Bewertungen
- Protocols & ApplicationDokument32 SeitenProtocols & ApplicationS M AkashNoch keine Bewertungen
- Application Layer ProtocolsDokument33 SeitenApplication Layer ProtocolsSarah AliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ty CN Sem 1Dokument89 SeitenTy CN Sem 1Saniya PathanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture 3Dokument42 SeitenLecture 3Hassan allaNoch keine Bewertungen
- CH 5Dokument91 SeitenCH 5avantikabakshiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit - 4: Source PortDokument13 SeitenUnit - 4: Source PortthirumalreddyNoch keine Bewertungen
- NetworkDokument9 SeitenNetworkrobigew824Noch keine Bewertungen
- UNIT V Application LayerDokument38 SeitenUNIT V Application Layerharsharewards1Noch keine Bewertungen
- CN 5th UnitDokument9 SeitenCN 5th Unitnishita patidarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Data Communication and NetworkingDokument4 SeitenData Communication and NetworkingUnwritten StoryNoch keine Bewertungen
- CN Unit V R18Dokument27 SeitenCN Unit V R18Sahithi Priya AttiliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Computer Networks UNIT 5Dokument21 SeitenComputer Networks UNIT 5thefamousbro123Noch keine Bewertungen
- Web TechnologyDokument37 SeitenWeb Technologybobiwis866Noch keine Bewertungen
- Unit-5 Computer NetworkDokument10 SeitenUnit-5 Computer NetworkShivansh tomarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Day 4.2 - Application Layer ProtocolDokument33 SeitenDay 4.2 - Application Layer ProtocolNabila NatashaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Application LayerDokument33 SeitenApplication Layerramna kNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cs8591 Computer Networks 1103969345 CN NotesDokument240 SeitenCs8591 Computer Networks 1103969345 CN Notesfirstandlastname1100Noch keine Bewertungen
- A (4 Files Merged)Dokument130 SeitenA (4 Files Merged)hussainbedsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Application Layer HellowDokument37 SeitenApplication Layer HellowMAYANK SANJAY SINGH StudentNoch keine Bewertungen
- TCP Ip StackDokument26 SeitenTCP Ip StackNikhil GaddamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 1: Introduction: Data CommunicationsDokument47 SeitenChapter 1: Introduction: Data CommunicationsYihune NegesseNoch keine Bewertungen
- Presentation LayerDokument18 SeitenPresentation LayerPriti PritiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Module 1Dokument36 SeitenModule 1PALLAVI RNoch keine Bewertungen
- Application LayerDokument2 SeitenApplication LayerNorielNoch keine Bewertungen
- CN Unit 5Dokument38 SeitenCN Unit 533 ABHISHEK WAGHNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture FourDokument25 SeitenLecture FourERICK LOUIS ADOKONoch keine Bewertungen
- Computer NetworksDokument22 SeitenComputer NetworksRISHINoch keine Bewertungen
- The Application Layer Includes The Following FunctionsDokument15 SeitenThe Application Layer Includes The Following FunctionsCaptain AmericaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 6Dokument26 SeitenChapter 6zelalemNoch keine Bewertungen
- Application ProtocolsDokument28 SeitenApplication Protocolsrez habloNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cse 405 7Dokument32 SeitenCse 405 7backbencher kiddoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Application Layer IntroductionDokument14 SeitenApplication Layer IntroductionVivek BhattNoch keine Bewertungen
- Traditional Applications - Electronic Mail (SMTP, POP3, IMAP, MIME) - HTTP - Web Services - DNS-SNMPDokument39 SeitenTraditional Applications - Electronic Mail (SMTP, POP3, IMAP, MIME) - HTTP - Web Services - DNS-SNMPanish.t.pNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit V: Introduction To: Session, Presentation and APPLICATION LayersDokument47 SeitenUnit V: Introduction To: Session, Presentation and APPLICATION LayersNiranjan AcharyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Application, Presentation, and SessionDokument2 SeitenApplication, Presentation, and SessionAku Cuma ikut-ikutanNoch keine Bewertungen
- COMP519: Web Programming Autumn 2013: The Slides Are Derivatives of Ones byDokument30 SeitenCOMP519: Web Programming Autumn 2013: The Slides Are Derivatives of Ones byrejincjNoch keine Bewertungen
- COMP519: Web Programming Autumn 2013: The Slides Are Derivatives of Ones byDokument30 SeitenCOMP519: Web Programming Autumn 2013: The Slides Are Derivatives of Ones byrejincjNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 5 CNDokument28 SeitenUnit 5 CNkumargpj7091Noch keine Bewertungen
- Unit II-finalDokument35 SeitenUnit II-finalSNEHANoch keine Bewertungen
- Computer Networks: Application LayerDokument64 SeitenComputer Networks: Application LayerkratiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Application Layer: Presented By: Sanskrati Upadhyay Roll Number: MT19CPS018Dokument29 SeitenApplication Layer: Presented By: Sanskrati Upadhyay Roll Number: MT19CPS018Vishal Raj (MT19CPS020)Noch keine Bewertungen
- ECEN 619 Slide 3Dokument17 SeitenECEN 619 Slide 3Sanjiti BhargavaNoch keine Bewertungen
- DNS (Domain Name Service) - TCP and Udp 53: The Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP)Dokument13 SeitenDNS (Domain Name Service) - TCP and Udp 53: The Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP)Suraj Singh RajputNoch keine Bewertungen
- CN Assignment On Self-Learning Topics: Name: Lavish Poddar Roll No: 637 PRN No: 40464920181124510038Dokument2 SeitenCN Assignment On Self-Learning Topics: Name: Lavish Poddar Roll No: 637 PRN No: 40464920181124510038Abrar NirbanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Advanced Computer Networks - CS716 Power Point Slides Lecture 42Dokument48 SeitenAdvanced Computer Networks - CS716 Power Point Slides Lecture 42Taran AulakhNoch keine Bewertungen
- Evaluation of Some SMTP Testing, Email Verification, Header Analysis, SSL Checkers, Email Delivery, Email Forwarding and WordPress Email ToolsVon EverandEvaluation of Some SMTP Testing, Email Verification, Header Analysis, SSL Checkers, Email Delivery, Email Forwarding and WordPress Email ToolsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Evaluation of Some SMTP Testing, SSL Checkers, Email Delivery, Email Forwarding and WP Email Tools: Evaluation of Some SMTP Testing, SSL Checkers, Email Delivery, Email Forwarding and WordPress Email ToolsVon EverandEvaluation of Some SMTP Testing, SSL Checkers, Email Delivery, Email Forwarding and WP Email Tools: Evaluation of Some SMTP Testing, SSL Checkers, Email Delivery, Email Forwarding and WordPress Email ToolsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Deadlock Prevention, Avoidance, and DetectionDokument29 SeitenDeadlock Prevention, Avoidance, and DetectionBapuji ValabojuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter4 ArithmeticDokument74 SeitenChapter4 ArithmeticBapuji ValabojuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 02Dokument35 SeitenChapter 02lghmshariNoch keine Bewertungen
- Deadlock Prevention, Avoidance, and DetectionDokument29 SeitenDeadlock Prevention, Avoidance, and DetectionBapuji ValabojuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Jawaharlal Nehru Engineering College: Laboratory ManualDokument28 SeitenJawaharlal Nehru Engineering College: Laboratory ManualBapuji ValabojuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Memory Management: Operating Systems: Internals and Design Principles, 6/EDokument42 SeitenMemory Management: Operating Systems: Internals and Design Principles, 6/ENancy Jerlin JosephNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 02Dokument35 SeitenChapter 02lghmshariNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Solar System - Its Origin and Early DevelopmentDokument68 SeitenThe Solar System - Its Origin and Early DevelopmentBapuji ValabojuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Part 6: The Application Layer Example: The World Wide WebDokument15 SeitenPart 6: The Application Layer Example: The World Wide WebBapuji ValabojuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Potato Battery ActivityDokument11 SeitenPotato Battery ActivityBapuji ValabojuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Inter-Process Communication: Message PassingDokument41 SeitenInter-Process Communication: Message Passingalwil1012Noch keine Bewertungen
- Deadlock Prevention, Avoidance, and DetectionDokument29 SeitenDeadlock Prevention, Avoidance, and DetectionBapuji ValabojuNoch keine Bewertungen
- R19MCASyllabus JNTUHDokument99 SeitenR19MCASyllabus JNTUHBapuji ValabojuNoch keine Bewertungen
- 14 Flip FlopsDokument19 Seiten14 Flip Flopsrajesh5500Noch keine Bewertungen
- A Quick Introduction To The Domain Name System: David ConradDokument74 SeitenA Quick Introduction To The Domain Name System: David ConradbatraswatiNoch keine Bewertungen
- DNS, SMTP, Pop, FTP, HTTPDokument9 SeitenDNS, SMTP, Pop, FTP, HTTPBapuji ValabojuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapters 7 & 8 Memory Management: Operating Systems: Internals and Design Principles, 6/EDokument96 SeitenChapters 7 & 8 Memory Management: Operating Systems: Internals and Design Principles, 6/EBapuji ValabojuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapters 7 & 8 Memory Management: Operating Systems: Internals and Design Principles, 6/EDokument96 SeitenChapters 7 & 8 Memory Management: Operating Systems: Internals and Design Principles, 6/EBapuji ValabojuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapters 7 & 8 Memory Management: Operating Systems: Internals and Design Principles, 6/EDokument96 SeitenChapters 7 & 8 Memory Management: Operating Systems: Internals and Design Principles, 6/EBapuji ValabojuNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Quick Introduction To The Domain Name System: David ConradDokument74 SeitenA Quick Introduction To The Domain Name System: David ConradbatraswatiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cross-Language Information Retrieval (CLIR) : Ananthakrishnan RDokument32 SeitenCross-Language Information Retrieval (CLIR) : Ananthakrishnan RBapuji ValabojuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cross-Language Information Retrieval (CLIR) : Ananthakrishnan RDokument32 SeitenCross-Language Information Retrieval (CLIR) : Ananthakrishnan RBapuji ValabojuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cross-Language Information Retrieval (CLIR) : Ananthakrishnan RDokument32 SeitenCross-Language Information Retrieval (CLIR) : Ananthakrishnan RBapuji ValabojuNoch keine Bewertungen
- 15 Vehicle AuthenticationDokument26 Seiten15 Vehicle AuthenticationBapuji ValabojuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Latches and Flip-Flops: 7.1 Bistable ElementDokument18 SeitenLatches and Flip-Flops: 7.1 Bistable ElementArnav GuptaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Win Runner NavigationDokument12 SeitenWin Runner NavigationBapuji ValabojuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Winrunner TutorialDokument193 SeitenWinrunner TutorialfaridkhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Act Vity DiaDokument1 SeiteAct Vity DiaBapuji ValabojuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Open Audit of - To Localhost From 1Dokument91 SeitenOpen Audit of - To Localhost From 1carillpowerNoch keine Bewertungen
- 05 Google Cloud and Hybrid Network ArchitectureDokument41 Seiten05 Google Cloud and Hybrid Network Architecturepourab bhattacharyyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lab Exercise - Lesson 7Dokument2 SeitenLab Exercise - Lesson 7Corrales Briyan JoyNoch keine Bewertungen
- 3HH-00057-2283-DFZZA-01P06-R4202v CFT WorkshopDokument25 Seiten3HH-00057-2283-DFZZA-01P06-R4202v CFT WorkshopStavros SotiriadisNoch keine Bewertungen
- SEL SEO Periodic Table 2019Dokument15 SeitenSEL SEO Periodic Table 2019KalpeshNoch keine Bewertungen
- 03 Information Security and Acceptable Use of ICT Policy v3 0Dokument16 Seiten03 Information Security and Acceptable Use of ICT Policy v3 0proftechitspecialistNoch keine Bewertungen
- Arquitectura EndPoint PDFDokument278 SeitenArquitectura EndPoint PDFgrivera_565843Noch keine Bewertungen
- Connector DefinitionsDokument21 SeitenConnector DefinitionsKhushboo KapurNoch keine Bewertungen
- Amazon Simple Storage Service: Getting Started GuideDokument17 SeitenAmazon Simple Storage Service: Getting Started GuideRahul KarthiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bonus 3 - The White Hat Hacks PDFDokument14 SeitenBonus 3 - The White Hat Hacks PDFSAranNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ijp 5 - Google SearchDokument2 SeitenIjp 5 - Google SearchHAMMAD SHAHNoch keine Bewertungen
- Zeus Botnet Defined Samuel Egiefameh Advisor: Dr. Willie Thompson IIDokument19 SeitenZeus Botnet Defined Samuel Egiefameh Advisor: Dr. Willie Thompson IIAsalia ZavalaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Information Technology: Technical Consultant PanelDokument4 SeitenInformation Technology: Technical Consultant PanelmjmacrohonNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Use of Computers in Security and PoliceDokument9 SeitenThe Use of Computers in Security and PoliceInna PugaciovaNoch keine Bewertungen
- SE0217 White PaperDokument6 SeitenSE0217 White PaperPaul WallNoch keine Bewertungen
- 3.5.5 Packet Tracer Configure VPN For Remote Access Answer KeyDokument6 Seiten3.5.5 Packet Tracer Configure VPN For Remote Access Answer Keymalaklmawt0000Noch keine Bewertungen
- Tigran Hamasyan - Vardavar - PDFDokument1 SeiteTigran Hamasyan - Vardavar - PDFafyrntgqsuoveqhocpNoch keine Bewertungen
- How To Upload From IBMi Using FTPS-20150831Dokument14 SeitenHow To Upload From IBMi Using FTPS-20150831Sandria MiguelNoch keine Bewertungen
- 4.2.2.4 Lab - Troubleshooting EtherChannelDokument2 Seiten4.2.2.4 Lab - Troubleshooting EtherChannelAndres RamosNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Teaching Office of The Church PDFDokument21 SeitenThe Teaching Office of The Church PDFPeter LindNoch keine Bewertungen
- Security Mechanisms:-: EnciphermentDokument64 SeitenSecurity Mechanisms:-: EnciphermentHeli ShahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ethics in Information Technology, Second Edition: Freedom of ExpressionDokument30 SeitenEthics in Information Technology, Second Edition: Freedom of ExpressionPauline Bogador MayordomoNoch keine Bewertungen
- NABARD CSF 06 Feb 2020Dokument19 SeitenNABARD CSF 06 Feb 2020Bijay Kumar SwainNoch keine Bewertungen
- CompTIA Security SY0 601Dokument6 SeitenCompTIA Security SY0 601RubenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Spoki Noki - Google SearchDokument1 SeiteSpoki Noki - Google SearchabdallaNoch keine Bewertungen
- China StudiesDokument8 SeitenChina StudiesSahadev PatraNoch keine Bewertungen
- SD-WAN and Routing Subscription FAQDokument22 SeitenSD-WAN and Routing Subscription FAQAdithyo DewanggaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Digital Marketing Affiliate Marketing Zalando Renault 4 12 2017 Marco Larocca Conoscente Cut 2017 12 04 14 36 14 PDFDokument53 SeitenDigital Marketing Affiliate Marketing Zalando Renault 4 12 2017 Marco Larocca Conoscente Cut 2017 12 04 14 36 14 PDFAfshan AbdullayevaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Study of Authentication and Authorization in Cloud ComputingDokument3 SeitenStudy of Authentication and Authorization in Cloud ComputingEditor IJRITCCNoch keine Bewertungen
- What Is Cpaas?: Communications Platform As A ServiceDokument25 SeitenWhat Is Cpaas?: Communications Platform As A ServiceShabir AhmedNoch keine Bewertungen