Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Lecture 10 - BCH-701 Enzymes Part 3
Hochgeladen von
Rana Furqan0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
11 Ansichten12 SeitenOriginaltitel
Lecture 10_BCH-701 Enzymes part 3
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
PPTX, PDF, TXT oder online auf Scribd lesen
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als PPTX, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
11 Ansichten12 SeitenLecture 10 - BCH-701 Enzymes Part 3
Hochgeladen von
Rana FurqanCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als PPTX, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
Sie sind auf Seite 1von 12
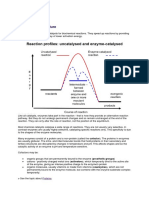
Regulation of enzyme activity
Mechanisms of regulating enzyme activity
1. Allosteric enzymes
• Enzymes whose activity can be changed by
molecules (effector molecules) other than
substrate.
• Allosteric means other site or other structure.
• The interaction of an inhibitor at an allosteric
site changes the structure of the enzyme so
that the active site is also changed.
Processes involving the allosteric enzyme
i. Negative allosterism
Effector binding sites alters the shape of the active site of the enzyme making
it to an inactive configuration
ii. Positive allosterism
Effector binding sites that alters the shape of inactive site of enzyme to an
active configuration. Therefore binding of the effector molecule regulates
enzyme activity by determining whether it will be active or not.
2. Feedback inhibition
• An enzyme regulation process in which formation of a product inhibits an
earlier reaction in the sequence. It controls the allosteric enzymes.
• This occurs when an end product of a pathway accumulates as the
metabolic demand for it declines.
• This end product in turn binds to the regulatory enzyme at the start of the
pathway and decreases its activity the greater the end product levels the
greater the inhibition of enzyme activity.
3. Proenzymes (Zymogen)
• The inactive form of enzyme which can be activated by removing
a small part on their polypeptide chain.
• Mostly are digestive enzymes and blood clotting enzymes
4. Protein Modification
• Another mechanism that can on and off the enzyme.
• This is a process in which a chemical group is covalently
added to or removed from the protein.
• The most common example is phosphorylation in which a
phosphate is transferred from an activated donor (usually
ATP) to an amino acid on the regulatory enzyme.
Enzyme Inhibitors
Non specific Specific
Denaturation Irreversible Reversible
Competitive Non competitive
Acids and bases Allosteric
Temperature feedback
Alcohol
Heavy metals
Reducing agents
Enzyme Inhibitors
Enzyme inhibitors are chemical that can bind to enzyme and either
eliminate or drastically reduce their catalytic ability
Classification
1.Reversibility
Deals whether the inhibition will eventually dissociate from the enzyme
releasing it in the active form.
2. Competition
Refers whether the inhibitor is a structural analog or look alike of the
substrate. If so the inhibitor and substrate will compete for the enzyme’s
active site
Enzyme inhibitors
1. Irreversible inhibitors
2. Reversible inhibitors
a. Competitive inhibitors
b. Uncompetitive inhibitors
c. Mixed inhibitors
d. Non competitive inhibitors
Irreversible inhibitors
• Usually covalently modify an enzyme and inhibition can therefore not be
reversed.
• Often contains highly reactive functional group such as aldehydes, alkenes ,
haloalkenes etc
Reversible inhibitors
• Bind to enzymes with non covalent interactions such as hydrogen bonds,
hydrophobic interactions and ionic bonds.
• Generally don not undergo chemical reactions when bound to the enzyme
and can be easily removed.
Competitive inhibitor
• They are molecules that resemble the structure and charge distribution of the
natural substrate for a particular enzyme.
• The inhibition is competitive because the inhibitor and substrate compete for
the binding to the enzymes active site.
Uncompetitive inhibition
The inhibitor binds only to the substrate–enzyme complex.
Mixed inhibition
• The inhibitor can bind to the enzyme at the same time as the enzymes
substrate. However the binding of the inhibitor affects the binding of
the substrata and vice versa.
• Although it is possible for mixed type inhibitors to bind in the active
site, this type of inhibition generally results from an allosteric effect
where the inhibitor binds to a different site on an enzyme.
Non competitive inhibitor
• Is a form of mixed inhibitor where the binding of the inhibitor to the
enzyme reduces its activity but does not affect the binding of substrate.
• Binds to R groups of amino acids or perhaps to the metal ion cofactor.
• Modifies the shape of the active site.
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- A-level Biology Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsVon EverandA-level Biology Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (5)
- Regulation of Enzyme ActivityDokument26 SeitenRegulation of Enzyme ActivityWeird WorldNoch keine Bewertungen
- Enzyme InhibitionDokument49 SeitenEnzyme InhibitionJaden StanislausNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 4 B Inhibition of Enzyme Activity 3rd Year Chemistry Dep'tDokument21 SeitenChapter 4 B Inhibition of Enzyme Activity 3rd Year Chemistry Dep'telsaNoch keine Bewertungen
- What Are Enzymes?Dokument11 SeitenWhat Are Enzymes?krishnarajagopal2011Noch keine Bewertungen
- ENZYMES Semester 1 (2)Dokument51 SeitenENZYMES Semester 1 (2)asadullah2315Noch keine Bewertungen
- EnzymesDokument18 SeitenEnzymesKim TanNoch keine Bewertungen
- L-3 Enzyme InhibitorsDokument4 SeitenL-3 Enzyme InhibitorsLiyakath AliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Botany J-Adhikary Enzymology 4Dokument9 SeitenBotany J-Adhikary Enzymology 4Dharmesh R.DNoch keine Bewertungen
- Enzymes: Efficient Catalysts for Biochemical ReactionsDokument7 SeitenEnzymes: Efficient Catalysts for Biochemical ReactionsLALITH SAI KNoch keine Bewertungen
- How Enzymes Speed Up Biochemical ReactionsDokument16 SeitenHow Enzymes Speed Up Biochemical ReactionsZEE zee100% (2)
- EnzymesDokument29 SeitenEnzymesClarenz Ken TatierraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gibbs Free Energy and Metabolism RegulationDokument29 SeitenGibbs Free Energy and Metabolism RegulationMaya AwadNoch keine Bewertungen
- EnzymesDokument9 SeitenEnzymesWaseem El-HelwNoch keine Bewertungen
- 14 Biochemistry Lecture - Enzymes 3Dokument60 Seiten14 Biochemistry Lecture - Enzymes 3AMIRA HELAYELNoch keine Bewertungen
- Enzymes: An SEO-Optimized Guide to Structure, Function and RegulationDokument9 SeitenEnzymes: An SEO-Optimized Guide to Structure, Function and RegulationMaria AnghelacheNoch keine Bewertungen
- 231 Lecture 15Dokument14 Seiten231 Lecture 15Rana AbdullahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Enzyme UpdatedDokument42 SeitenEnzyme UpdatedBukhari DiangkaNoch keine Bewertungen
- What Are Enzyme Inhibitors?: EnzymesDokument5 SeitenWhat Are Enzyme Inhibitors?: EnzymesRica NorcioNoch keine Bewertungen
- Enzymes: Biological Catalysts and RegulationDokument31 SeitenEnzymes: Biological Catalysts and RegulationdrhydrogenNoch keine Bewertungen
- EnzymesDokument44 SeitenEnzymesYumul, Jewel B.Noch keine Bewertungen
- Slide EnzymeDokument27 SeitenSlide EnzymeReni Fatmawati100% (1)
- Inhibition and RegulationDokument28 SeitenInhibition and RegulationRoyal MindNoch keine Bewertungen
- Enzymes:: "Helper" Protein MoleculesDokument26 SeitenEnzymes:: "Helper" Protein MoleculesAyesha JamilNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biochemistry: By: Angela Marie Ferrer BSN 2BDokument13 SeitenBiochemistry: By: Angela Marie Ferrer BSN 2BNoemi Martinez FerrerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Enzyme Inhibition MechanismsDokument8 SeitenEnzyme Inhibition MechanismsfayeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Enzymes: D. F. PalacioDokument31 SeitenEnzymes: D. F. PalacioCarlo AniagNoch keine Bewertungen
- Enzymes PPT BioDokument22 SeitenEnzymes PPT Biovoyav37617Noch keine Bewertungen
- Helper Protein Molecules Called EnzymesDokument7 SeitenHelper Protein Molecules Called EnzymesMuhammad Junaid IqbalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture On EnzymesDokument26 SeitenLecture On EnzymesDAVIE MATIASNoch keine Bewertungen
- Enzyme .Dokument36 SeitenEnzyme .Yudamalik Ibrahim1987Noch keine Bewertungen
- Week 6 EnzymessDokument49 SeitenWeek 6 EnzymessRechell Mae DaclesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Metabolism (HL)Dokument26 SeitenMetabolism (HL)Sapreen KaurNoch keine Bewertungen
- What Are Enzymes?: E E E EDokument15 SeitenWhat Are Enzymes?: E E E EFarhana MuradNoch keine Bewertungen
- Enzyme InhibitorsDokument27 SeitenEnzyme InhibitorsNAUSHEEN SULTANANoch keine Bewertungen
- C1 W14 EnzymesDokument49 SeitenC1 W14 EnzymesJasmine Kaye CuizonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Enzymes Speed Up ReactionsDokument24 SeitenEnzymes Speed Up ReactionsAmy PhamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biochemistry Chapter # 1 EnzymesDokument10 SeitenBiochemistry Chapter # 1 EnzymesUsman AhmadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Enzyme RegulationDokument16 SeitenEnzyme RegulationnadimbioinformaticsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Enzymes PresDokument34 SeitenEnzymes PresRasmia SalamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Enzymes: - Sucrase - Lactase - MaltaseDokument4 SeitenEnzymes: - Sucrase - Lactase - MaltaseKate Nicole EjercitoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 1 - EnzymesDokument84 SeitenChapter 1 - EnzymesNorsuzianaNoch keine Bewertungen
- EnzymesDokument5 SeitenEnzymeseyosiyas tekleweyinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Enzymes: Structure, Function and Factors Affecting ActivityDokument5 SeitenEnzymes: Structure, Function and Factors Affecting Activitytiyf mojaleedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Molecular Interactions in Cell Events: Advanced Higher BiologyDokument21 SeitenMolecular Interactions in Cell Events: Advanced Higher Biologyhina_hashmiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Module 11: EnzymesDokument3 SeitenModule 11: EnzymesMariam EskandariNoch keine Bewertungen
- Protein Denaturation: EnzymesDokument7 SeitenProtein Denaturation: EnzymescharlesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Enzymes: Function, Structure, and Factors Affecting ActivityDokument5 SeitenEnzymes: Function, Structure, and Factors Affecting ActivitySameer ButtNoch keine Bewertungen
- c1.1 EnzymesDokument36 Seitenc1.1 Enzymeshwqhd asjdhuaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Enzymes catalyze biological reactionsDokument3 SeitenEnzymes catalyze biological reactionsDavid PetalcurinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture 5 - Regulation of Enzyme Activity. Isoenzymes. Localization of Enzymes and PlasmaDokument26 SeitenLecture 5 - Regulation of Enzyme Activity. Isoenzymes. Localization of Enzymes and PlasmaEiad SamyNoch keine Bewertungen
- BIO 203 Biochemistry I by Seyhun YURDUGÜL, PH.D.: Enzyme InhibitionDokument59 SeitenBIO 203 Biochemistry I by Seyhun YURDUGÜL, PH.D.: Enzyme InhibitionYasin Çağrı KılıçerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Enzymes - Part IIDokument71 SeitenEnzymes - Part IIBarış KaplanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Enzyme Inhibition Types and MechanismsDokument29 SeitenEnzyme Inhibition Types and MechanismsDarshan DSSNoch keine Bewertungen
- All of Those Enzymes Up and Metabolize As Fast As Possible! As It TurnsDokument11 SeitenAll of Those Enzymes Up and Metabolize As Fast As Possible! As It TurnsshahzebNoch keine Bewertungen
- Enzyme InhibitionDokument19 SeitenEnzyme InhibitionM Aimal KhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Enzyme CatalysisDokument35 SeitenEnzyme CatalysisMihir IyerNoch keine Bewertungen
- BIOCHEMISTRY II- INTERMEDIARY METABOLISM ENZYMESDokument61 SeitenBIOCHEMISTRY II- INTERMEDIARY METABOLISM ENZYMESNaiomiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Basic Enzyme and Digestive Enzyme AnggelDokument24 SeitenBasic Enzyme and Digestive Enzyme AnggelLia AuliantiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture 9 - BCH-701 Enzymes Part 2Dokument16 SeitenLecture 9 - BCH-701 Enzymes Part 2Rana FurqanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture 9 - BCH-701 Enzymes Part 2Dokument16 SeitenLecture 9 - BCH-701 Enzymes Part 2Rana FurqanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Peptides and PolypeptidesDokument19 SeitenPeptides and PolypeptidesRana FurqanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture 6 - BCH-701Dokument13 SeitenLecture 6 - BCH-701Rana FurqanNoch keine Bewertungen
- The 3D structures and functions of proteinsDokument14 SeitenThe 3D structures and functions of proteinsRana FurqanNoch keine Bewertungen
- The 20 building blocks of proteinsDokument23 SeitenThe 20 building blocks of proteinsRana FurqanNoch keine Bewertungen
- The 20 building blocks of proteinsDokument23 SeitenThe 20 building blocks of proteinsRana FurqanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture 6 - BCH-701Dokument13 SeitenLecture 6 - BCH-701Rana FurqanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Epithelium Surface SpecializationsDokument41 SeitenEpithelium Surface SpecializationsMitzel SapaloNoch keine Bewertungen
- Describe RNA Structure and Function.: Video: DNA Vs RNADokument4 SeitenDescribe RNA Structure and Function.: Video: DNA Vs RNAMark Christian Dimson GalangNoch keine Bewertungen
- TANCET 2016 Syllabus BiotechnologyDokument1 SeiteTANCET 2016 Syllabus Biotechnologysrinivasa karthesan sankaranNoch keine Bewertungen
- L17 L18 Lipids 2013 14Dokument23 SeitenL17 L18 Lipids 2013 14Pejvak KHorram DinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dna Model Rubric: Level of ProficiencyDokument1 SeiteDna Model Rubric: Level of ProficiencyMichelle BaguioNoch keine Bewertungen
- IPMB Practical Training ManualDokument50 SeitenIPMB Practical Training ManualAhmed 75Noch keine Bewertungen
- Revision Notes For Class 12 CBSE Chemistry, Biomolecules - TopperlearningDokument14 SeitenRevision Notes For Class 12 CBSE Chemistry, Biomolecules - TopperlearningRishabh Bhandari100% (2)
- Human Physiology An Integrated Approach 7th Edition Silverthorn Solutions ManualDokument17 SeitenHuman Physiology An Integrated Approach 7th Edition Silverthorn Solutions ManualLarryPiercenofdx100% (13)
- In Silico in Drug Discovery TechniquesDokument21 SeitenIn Silico in Drug Discovery Techniquesvershaparcha100% (1)
- A Comprehensive Guide To Managing AutismDokument89 SeitenA Comprehensive Guide To Managing Autismapi-3696876100% (4)
- DNA Found in FoodDokument22 SeitenDNA Found in Foodemmanuel333100% (1)
- Cambridge International AS & A Level: BIOLOGY 9700/04Dokument26 SeitenCambridge International AS & A Level: BIOLOGY 9700/04Raphael JosephNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bagong AlamatDokument11 SeitenBagong Alamatmax delvalleNoch keine Bewertungen
- Additional Notes - Light Transmission Aggregometry NotesDokument7 SeitenAdditional Notes - Light Transmission Aggregometry NotesAndrej TerzicNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biological Activity Analysis of Native and Recombinant StreptokinaseDokument16 SeitenBiological Activity Analysis of Native and Recombinant Streptokinasesaeedazadi1352100% (1)
- KIT CD117 A Review On Expression in Normal and Neoplastic TissuesDokument16 SeitenKIT CD117 A Review On Expression in Normal and Neoplastic TissuesVlado VladNoch keine Bewertungen
- Immunology and Serology Quiz 1 1Dokument19 SeitenImmunology and Serology Quiz 1 1Kaius KawaseNoch keine Bewertungen
- He367t R1 RCDokument2 SeitenHe367t R1 RCSedighe VafaieNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mitochondria & Ageing: Extracted From The Presentation by Lee Know, NDDokument4 SeitenMitochondria & Ageing: Extracted From The Presentation by Lee Know, NDDavid100% (1)
- HumulinDokument14 SeitenHumulin18014556010 ANNU KHASANoch keine Bewertungen
- Exocytosis and Endocytosis: © 2012 Pearson Education, IncDokument49 SeitenExocytosis and Endocytosis: © 2012 Pearson Education, IncGlein CenizaNoch keine Bewertungen
- BIOCHEM DigestionDokument53 SeitenBIOCHEM DigestionAngelika Perez CunanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Human Cell AnatomyDokument56 SeitenHuman Cell Anatomysanthiyasandy100% (3)
- Di truyền cơ sở-Ch8 (10) -From DNA to Proteins p1-IUHDokument26 SeitenDi truyền cơ sở-Ch8 (10) -From DNA to Proteins p1-IUHNam NguyenHoangNoch keine Bewertungen
- Regulation of Osteoclast Function and Bone Mass by Receptor For Advanced Glycation End Products (RAGE)Dokument14 SeitenRegulation of Osteoclast Function and Bone Mass by Receptor For Advanced Glycation End Products (RAGE)dumboo21Noch keine Bewertungen
- Lesson Plan in Chemistry - PasaDokument6 SeitenLesson Plan in Chemistry - PasaPenelope Soria EjadaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Liver Pathology and AlcoholDokument621 SeitenLiver Pathology and AlcoholKazoAAUNoch keine Bewertungen
- Comprehensive Genomic Profiling at IlluminaDokument23 SeitenComprehensive Genomic Profiling at IlluminaSaulius BarauskasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lab 4 Enzymes and The Catalase LabDokument18 SeitenLab 4 Enzymes and The Catalase LabAmy Hollingsworth100% (1)
- IB Biology Revision Notes FULLDokument3 SeitenIB Biology Revision Notes FULLAtulya BharadwajNoch keine Bewertungen