Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Neisseria: Dr. NG Woei Kean
Hochgeladen von
Wong Shuan0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
24 Ansichten19 SeitenNeisseria is a genus of bacteria that includes the human pathogens N. meningitidis (meningococcus) and N. gonorrhoeae (gonococcus). These bacteria are Gram-negative diplococci that can cause meningitis and sexually transmitted infections, respectively. They have various virulence factors that allow invasion and resistance to immune responses, such as pili, porins and lipooligosaccharide. Diagnosis involves culturing samples from sites of infection on selective media and identifying bacterial antigens.
Originalbeschreibung:
Originaltitel
3.7 Neisseria
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
PPTX, PDF, TXT oder online auf Scribd lesen
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenNeisseria is a genus of bacteria that includes the human pathogens N. meningitidis (meningococcus) and N. gonorrhoeae (gonococcus). These bacteria are Gram-negative diplococci that can cause meningitis and sexually transmitted infections, respectively. They have various virulence factors that allow invasion and resistance to immune responses, such as pili, porins and lipooligosaccharide. Diagnosis involves culturing samples from sites of infection on selective media and identifying bacterial antigens.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als PPTX, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
24 Ansichten19 SeitenNeisseria: Dr. NG Woei Kean
Hochgeladen von
Wong ShuanNeisseria is a genus of bacteria that includes the human pathogens N. meningitidis (meningococcus) and N. gonorrhoeae (gonococcus). These bacteria are Gram-negative diplococci that can cause meningitis and sexually transmitted infections, respectively. They have various virulence factors that allow invasion and resistance to immune responses, such as pili, porins and lipooligosaccharide. Diagnosis involves culturing samples from sites of infection on selective media and identifying bacterial antigens.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als PPTX, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
Sie sind auf Seite 1von 19
Neisseria
Dr. Ng Woei Kean
Ph.D. (Molecular Medicine)
Classification
• Neisseria is one of the four genera under the
family Neisseriaceae.
Neisseriaceae
Neisseria
Moraxella
Kingella
Acinetobacter
• There are 8 species under Neisseria, only N.
gonorrhea (gonococcus) and N.
meningitidis (meningococcus) are known
primary human pathogens.
• Other species of Neisseria are nonpathogenic or
commensal flora in human host and may be
opportunistic pathogen.
• Other species of Neisseria are extracellular to
polymorphonuclear (PMN) cells.
General Characteristics
• Neisseria are gram negative cocci and arranged
in pairs.
• They are oxidase positive.
• Grows better in increased CO2 concentration.
• They are found intracellular to PMN.
• Moraxella, Acinetobacter and Veillonela
resembles Neisseria morphologically.
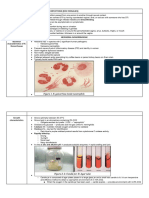
Neisseria gonorrhoeae present in a Gram stain of a patient with
gonococcal urethritis. The N. gonorrhoeae are the intracellular
gram- negative diplococci within the cytoplasm of the
polymorphonuclear (PMN) cell.
Characteristics of N.
meningitidis and N. gonorrhea
• Obligate human pathogen.
• Does not grow at 22°C compared to other
neisseria.
• They are highly autolytic.
• They need enriched media to grow.
• They are pilated when isolated.
• Transformation occurs in pilated form.
How to differentiate N meningitidis from N gonorrhea?
Sugar utilization - Pattern of acid production from sugars e.g.
glucose, maltose, sucrose and lactose identify Neisseria and related
species.
Diseases Caused by
Meningococcus
• Asymptomatic carrier rate is 5-10% in nasopharynx
• Meningococcemia
• Meningitis
• Waterhouse-Friderichsen syndrome
• Rarely pneumonia
Host factors which predisposes meningococcal diseases
1. Absence of bactericidal antibodies
2. Production of blocking Antibodies
3. C6, C7 & C8 deficiency
4. Deficiency of Mannose Binding Protein (MBP)
Diseases Caused by
Gonococcus
• Men: urethritis, epididymitis.
• Women: cervicitis (ascending infection of uterine
cavity, fallopian tubes leading to complications).
• Pharyngitis
• Conjunctivitis in neonates
• Disseminated gonococcal infection:
arthritis, endocarditis, meningitis - 1%
Host factors which predisposes gonococcal diseases
1. Production of blocking Antibodies - production of IgG
blocking Antibodies blocking anti-LOS IgM (LOS-
lipooligosaccharide)
2. C6, C7 & C8 deficiency
Virulence Factors
Capsule
N. meningitidis N. gonorrhea
• Capsule is acidic • Unknown
polysaccharides.
• Most capsule composed of
sialic acid.
• There are 13 sero groups
based on capsule: A, B, C, H,
I, K, L, M, Y, X, Z, E-29 & W-
135.
• It is anti-phagocyte and anti-
complement, confers serum
resistance.
Major surface proteins - Pili
N. meningitidis N. gonorrhea
• Pili promotes attachment • Pili mediates attachment
to epithelial cells, to columnar epithelial
endothelial cells and cell
RBC • Necessary for DNA
• Necessary for DNA uptake
uptake • Anti-phagocytic
• Undergo antigenic
variation
Major surface proteins - Porins
N. meningitidis N. gonorrhea
• Class 1, 2,3 - Used for • Por A and PorB (formerly
serotyping. PIA and PIB - used for
Serotyping and for entry of
nutrient.
• Class 4 - Target for blocking • Rmp (reduction modifiable
IgA that protects protein) antigen for
meningococcus from IgG production of IgG that block
and complement-mediated killing by IgM and
killing. complements.
• Class 5 OMP: promotes • Opacity protein Or Opa (PII):
adherence to host cell and Promotes adherence to
WBC. mucosa and PMN. 6-8
different antigenic types;
confers opaque colony.
Major Surface Structure - Lipooligosaccharide (LOS)
N. meningitidis N. gonorrhea
• 13 serotypes. • Six antigenically distinct
• Causes cytokine release, serotypes.
septic shock and DIC • LOS damages cells.
(disseminated • It exhibits antigenic
intravascular coagulation variation.
syndrome). • Target of IgM.
• Sialylation of LOS and
become serum resistant
by inactivation of
complements and
preventing deposition of
C3b
• Both produces IgA proteases and contain Iron binding
protein
Virulence factors of meningococcus
Mechanism of Invasion of
Epithelial Cells
• Neisseria adheres to mucous secreting non-
ciliated cells by pili and Opa proteins.
• LOS and PDG causes ciliostasis.
• Endocytosis is directed by porins.
• Endocytosed bacteria is egested into basement
membrane leading to inflammation.
• Ciliated and non-ciliated cells are destroyed.
• Organisms resist killing by antibodies and
complements.
• Attachment to endothelial cells and
dissemination through blood.
Diagnosis of Meningococcus
Specimens to isolate N. meningitidis depends on
the stage or type of infection:
• Nasopharynx is cultured to determine carrier
state.
• Blood during meningo-coccemia.
• Skin lesions from petechial rash if present.
• Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) for meningitis.
• Synovial fluid in cases of suspected septic
arthritis.
Types of test
• Gram stain
• Culture
• Bacterial antigen detection in CSF
* CSF should be centrifuged at 1500 X g for 15
minutes. The supernatant fluid removed and used
for direct detection of soluble antigens. The
sediment should be cultured on chocolate agar
and thioglycollate broth.
Diagnosis of Gonococcus
• Swabs for N. gonorrhea should be collected and
transported in Amies modifies transport media
Types of test
• Gram stain
• Culture: in Thayer-Martin selective media.
• Molecular methods: The non-amplified DNA
probe assay is used for direct detection of
gonococcal ribosomal RNA (rRNA) in genital
and conjuctival specimens.
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- ImmunologyDokument92 SeitenImmunology[161]Shuaib AktherNoch keine Bewertungen
- Manufacturing Finance With SAP ERP Financials: Subbu RamakrishnanDokument33 SeitenManufacturing Finance With SAP ERP Financials: Subbu RamakrishnanKhalifa Hassan100% (1)
- Edoc - Pub Grade 10 Science DLL q3 Week 3Dokument5 SeitenEdoc - Pub Grade 10 Science DLL q3 Week 3Geraldine Pascua CardenasNoch keine Bewertungen
- University of Cape Coasst: Mls303A: Microbiology IiiDokument31 SeitenUniversity of Cape Coasst: Mls303A: Microbiology IiiErnest KyereNoch keine Bewertungen
- Terraform AWSDokument1.531 SeitenTerraform AWSTilted Mowa100% (1)
- PURL Questions and AnswersDokument3 SeitenPURL Questions and AnswersSHAHAN VS100% (5)
- Gram Negative Bacteria of Medical Importance - PPTX, MONDAYDokument113 SeitenGram Negative Bacteria of Medical Importance - PPTX, MONDAYGeorge C. KasondaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Agents of Respiratory DiseaseDokument25 SeitenAgents of Respiratory DiseaseAbid AliNoch keine Bewertungen
- NeisseriaDokument32 SeitenNeisseriaKeshant SamarooNoch keine Bewertungen
- Air Defence Systems: Export CatalogueDokument105 SeitenAir Defence Systems: Export CatalogueserrorysNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lab7 - Gram Negative CocciDokument116 SeitenLab7 - Gram Negative Cocciนุชนรี ศรีวิเชียรNoch keine Bewertungen
- Family NeisseriaDokument38 SeitenFamily NeisseriakavyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gram Negative CocciDokument21 SeitenGram Negative Cocciprecious mubangaNoch keine Bewertungen
- General Xtics. Neisseria Meningitidis (Meningococcus) : Gram-Negative CocciDokument19 SeitenGeneral Xtics. Neisseria Meningitidis (Meningococcus) : Gram-Negative CocciMoses Tamba MomohNoch keine Bewertungen
- New Chapter 3 Medical Microbiology (1) 2Dokument130 SeitenNew Chapter 3 Medical Microbiology (1) 2Rani Faed SabraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Neisseria, Diph, AnthraxDokument53 SeitenNeisseria, Diph, AnthraxAyat MostafaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gram Negative CocciDokument21 SeitenGram Negative CocciAyeshaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Neisseria Meningitidis PDFDokument8 SeitenNeisseria Meningitidis PDFmulyadiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Microbiology Chapter 1Dokument14 SeitenMicrobiology Chapter 1Milad MovahediNoch keine Bewertungen
- Neisseria 160915072903Dokument26 SeitenNeisseria 160915072903HARSH BAGDINoch keine Bewertungen
- Prepared by Honorable GAKWAYA: Gram NegativeDokument19 SeitenPrepared by Honorable GAKWAYA: Gram NegativeNyakubahwa HonoreNoch keine Bewertungen
- Micro GramNegCocci MD2021Dokument5 SeitenMicro GramNegCocci MD2021Patricia Mae de JesusNoch keine Bewertungen
- Immunity To MicrobesDokument25 SeitenImmunity To MicrobestimcarasNoch keine Bewertungen
- 9 Unit 7 - Virology HODokument90 Seiten9 Unit 7 - Virology HOThirdy PinedaNoch keine Bewertungen
- N MeningitidisDokument3 SeitenN MeningitidisSajjad Hossain ShuvoNoch keine Bewertungen
- CHAPTER IV Pathogenic Gram Negative CocciDokument23 SeitenCHAPTER IV Pathogenic Gram Negative Cocciyosef awokeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter44 With Comments - Mycoplasma and UreaplasmaDokument17 SeitenChapter44 With Comments - Mycoplasma and UreaplasmaGordon JamesonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 20Dokument81 SeitenChapter 20songezo mbutyeNoch keine Bewertungen
- ImmunologyDokument91 SeitenImmunologyNicole FigueroaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Neisseria Spp.Dokument22 SeitenNeisseria Spp.sajad abasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Module 9.4 + Microbio + Study GuideDokument33 SeitenModule 9.4 + Microbio + Study GuideMikhail LamayoNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2021 - l4 Medical Bacteriology - Gram Negative Bacteria (I)Dokument52 Seiten2021 - l4 Medical Bacteriology - Gram Negative Bacteria (I)Tonny YuliantoNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1 - GP Pyogenic Cocci - Staph, Strept - Feb 2022Dokument183 Seiten1 - GP Pyogenic Cocci - Staph, Strept - Feb 2022Redwan KedirNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pathogenesis-Bacterial Virulence FactorsDokument34 SeitenPathogenesis-Bacterial Virulence FactorsTayyaba QamarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sexually Transmitted Infections 19-21Dokument4 SeitenSexually Transmitted Infections 19-21Ashar AhmadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Resource B: The Immune System: Innate Defenses and Adaptive DefensesDokument10 SeitenResource B: The Immune System: Innate Defenses and Adaptive DefensesLorraine FeyreNoch keine Bewertungen
- Airborne Bacterial Infection 6-10Dokument10 SeitenAirborne Bacterial Infection 6-10Ashar AhmadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bac NotesDokument22 SeitenBac NotesK PrashasthaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Theme: Gramnegative Cocci (Gonococci, Meningococci)Dokument52 SeitenTheme: Gramnegative Cocci (Gonococci, Meningococci)Mann SarwanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pyogenic Microorganisms: Roy, Nova, Jessie, Szechia, and ShangyoungDokument34 SeitenPyogenic Microorganisms: Roy, Nova, Jessie, Szechia, and ShangyoungMitra NofembriNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gram Negative Bacteria - 18Dokument58 SeitenGram Negative Bacteria - 18Julia MartinezNoch keine Bewertungen
- IMMUNOLOGYDokument47 SeitenIMMUNOLOGYHarsh NimavatNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bacte03 NEISSERIA AND MORAXELLADokument11 SeitenBacte03 NEISSERIA AND MORAXELLAAngelic AngelesNoch keine Bewertungen
- CryptococcusDokument57 SeitenCryptococcusማላያላም ማላያላምNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1.0pathogenesis of Fungal Diseases (Mycoses)Dokument48 Seiten1.0pathogenesis of Fungal Diseases (Mycoses)Jiya MuhammadNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1 - GP Pyogenic Cocci - Staph, StreptDokument183 Seiten1 - GP Pyogenic Cocci - Staph, StreptkamaluNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pathogenic Gram Negative CocciiDokument31 SeitenPathogenic Gram Negative Cocciitemesgensemahegn55Noch keine Bewertungen
- Neisseria MeningitidisDokument53 SeitenNeisseria MeningitidisPratibha AgarwalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Streptococcus: Mrs. Jincy Ealias M.Sc. (N) Asst. Professor Mr. Binu Babu MBA, M.Sc. (N) Asst. ProfessorDokument30 SeitenStreptococcus: Mrs. Jincy Ealias M.Sc. (N) Asst. Professor Mr. Binu Babu MBA, M.Sc. (N) Asst. ProfessorNimatul MurtafiahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Clinical Immunology in Practise 2013 - 6th Years - Vula - 17mayDokument72 SeitenClinical Immunology in Practise 2013 - 6th Years - Vula - 17mayPhaimNoch keine Bewertungen
- 5 NeisseriaceaeDokument6 Seiten5 NeisseriaceaeRosevelle AlayonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lab Diagnosis and TreatmentDokument22 SeitenLab Diagnosis and TreatmentDavid lufafaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Neisseria MeningitidisDokument28 SeitenNeisseria MeningitidisAshar AhmadNoch keine Bewertungen
- MicrobiologyDokument334 SeitenMicrobiologyaucukagapeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture 9. Neisseria GonorrhoeaeDokument81 SeitenLecture 9. Neisseria GonorrhoeaeHadiqa ArshadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction of Mycoses-2021Dokument20 SeitenIntroduction of Mycoses-2021Fajar AnshoriNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gram Positive RodsDokument74 SeitenGram Positive RodsSophia E. BucarileNoch keine Bewertungen
- Streptococcocus BacteriaDokument37 SeitenStreptococcocus Bacteriaprecious mubangaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Leprosy 2023Dokument55 SeitenLeprosy 2023Obatoye SeyiNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2) BacteriologyDokument94 Seiten2) BacteriologyMadhulikaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Immunological Aspects of Parasitic Diseases in Immunocompromised IndividualsDokument34 SeitenImmunological Aspects of Parasitic Diseases in Immunocompromised IndividualsKade SilabanNoch keine Bewertungen
- SYPHILIS (103 To 108) PPT - PPTX - 20230906 - 161225 - 0000Dokument15 SeitenSYPHILIS (103 To 108) PPT - PPTX - 20230906 - 161225 - 0000Aaditya GadhviNoch keine Bewertungen
- Microbial Aspect of GABHSDokument13 SeitenMicrobial Aspect of GABHSAdelia Maharani DNoch keine Bewertungen
- Progress in Immunology: First International Congress of ImmunologyVon EverandProgress in Immunology: First International Congress of ImmunologyBernard AmosNoch keine Bewertungen
- Volume of Naoh Added (ML) PH: Titration Curve of A Weak Acid With Strong BaseDokument6 SeitenVolume of Naoh Added (ML) PH: Titration Curve of A Weak Acid With Strong BaseWong ShuanNoch keine Bewertungen
- 5.2 Antimicrobial Resistance EditDokument23 Seiten5.2 Antimicrobial Resistance EditWong ShuanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Btgroup5 - Planning Proposal - Mar 2020Dokument18 SeitenBtgroup5 - Planning Proposal - Mar 2020Wong ShuanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Such As Arsenic (As), Which Is Poisonous For HumansDokument2 SeitenSuch As Arsenic (As), Which Is Poisonous For HumansWong ShuanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Proposal Problem: Acid Mine Drainage 1. Chemical Compounds:: 4fes + 15O + 14H O - 4fe (Oh) + 8H SoDokument2 SeitenProposal Problem: Acid Mine Drainage 1. Chemical Compounds:: 4fes + 15O + 14H O - 4fe (Oh) + 8H SoWong ShuanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Vibrio: Dr. NG Woei KeanDokument13 SeitenVibrio: Dr. NG Woei KeanWong ShuanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mycobacterium: Dr. NG Woei KeanDokument28 SeitenMycobacterium: Dr. NG Woei KeanWong ShuanNoch keine Bewertungen
- 5.1 Antimicrobial AgentsDokument22 Seiten5.1 Antimicrobial AgentsWong ShuanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Enterobacteriaceae: Dr. NG Woei KeanDokument53 SeitenEnterobacteriaceae: Dr. NG Woei KeanWong ShuanNoch keine Bewertungen
- 3.4 Helicobacter PyloriDokument25 Seiten3.4 Helicobacter PyloriWong ShuanNoch keine Bewertungen
- L7.4 Aromatic CompoundsDokument54 SeitenL7.4 Aromatic CompoundsWong ShuanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assignment 2 PDFDokument1 SeiteAssignment 2 PDFWong ShuanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Streptococci: Dr. NG Woei KeanDokument30 SeitenStreptococci: Dr. NG Woei KeanWong ShuanNoch keine Bewertungen
- 3.1 Staphylococci PDFDokument36 Seiten3.1 Staphylococci PDFWong ShuanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Magazine Genre: Travel Masthead: Traverse, Venture Magazine Cover SampleDokument1 SeiteMagazine Genre: Travel Masthead: Traverse, Venture Magazine Cover SampleWong ShuanNoch keine Bewertungen
- 44Dokument2 Seiten44menakadevieceNoch keine Bewertungen
- Data StreamDokument256 SeitenData Streamy suresh babuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Brochure Mastertile TilingDokument48 SeitenBrochure Mastertile TilingMaha Mufleh100% (1)
- Fatty AcidsDokument13 SeitenFatty AcidsRaviraj MalaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Normal DistributionDokument9 SeitenThe Normal DistributionElfren BulongNoch keine Bewertungen
- 34P S4hana1909 BPD en UsDokument18 Seiten34P S4hana1909 BPD en UsBiji RoyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sacramento County Compensation Survey Board of SupervisorsDokument13 SeitenSacramento County Compensation Survey Board of SupervisorsCBS13Noch keine Bewertungen
- NPN Silicon: Semiconductor Technical DataDokument8 SeitenNPN Silicon: Semiconductor Technical DataMinh Hà QuangNoch keine Bewertungen
- Specification For Neoprene Coating On The Riser CasingDokument17 SeitenSpecification For Neoprene Coating On The Riser CasingLambang AsmaraNoch keine Bewertungen
- AWP 4A Syllabus Fall 2021 (Misinformation)Dokument11 SeitenAWP 4A Syllabus Fall 2021 (Misinformation)camNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cultures of The West A History, Volume 1 To 1750 3rd PDFDokument720 SeitenCultures of The West A History, Volume 1 To 1750 3rd PDFtonnyNoch keine Bewertungen
- LGDokument36 SeitenLGNanchavisNoch keine Bewertungen
- Zielinski AnArcheology For AnArchivesDokument10 SeitenZielinski AnArcheology For AnArchivesPEDRO JOSENoch keine Bewertungen
- 2022+ACCF+111+Class+test+2 Moderated+versionDokument8 Seiten2022+ACCF+111+Class+test+2 Moderated+versionLucas LuluNoch keine Bewertungen
- Essay Writing TipsDokument4 SeitenEssay Writing TipsSubhasish MitraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Namma Kalvi 10th English Pta Model Question Papers 217163Dokument36 SeitenNamma Kalvi 10th English Pta Model Question Papers 217163609001Noch keine Bewertungen
- 2008 IASS SLTE 2008 Chi Pauletti PDFDokument10 Seiten2008 IASS SLTE 2008 Chi Pauletti PDFammarNoch keine Bewertungen
- The History of The Photocopy MachineDokument2 SeitenThe History of The Photocopy MachineAndy WijayaNoch keine Bewertungen
- RCD - SEF (Liquidating)Dokument40 SeitenRCD - SEF (Liquidating)Chie NemzNoch keine Bewertungen
- BronchiolitisDokument5 SeitenBronchiolitisreshianeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lesson 3 - Practical ResearchDokument17 SeitenLesson 3 - Practical ResearchBenNoch keine Bewertungen
- InflammationDokument44 SeitenInflammationramsiyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- ECE3073 P4 Bus Interfacing Answers PDFDokument3 SeitenECE3073 P4 Bus Interfacing Answers PDFkewancamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Exercise On Coordination and ResponseDokument8 SeitenExercise On Coordination and ResponseNorliyana AliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter - 1 - Digital - Systems - and - Binary - Numbers EE228 15-16Dokument81 SeitenChapter - 1 - Digital - Systems - and - Binary - Numbers EE228 15-16mohamed hemdanNoch keine Bewertungen