Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Drying: by Dr. Thomas A. Conteh
Hochgeladen von
Solomon D Fatorma0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
9 Ansichten26 SeitenOriginaltitel
drying-1
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
PPTX, PDF, TXT oder online auf Scribd lesen
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als PPTX, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
9 Ansichten26 SeitenDrying: by Dr. Thomas A. Conteh
Hochgeladen von
Solomon D FatormaCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als PPTX, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
Sie sind auf Seite 1von 26
Drying
By
Dr. Thomas A. Conteh
8/11/2020 Pharmaceutics Dept. COMAHS-USL
Contents:
1. Definition of drying
2. Importance of drying
3. Difference between drying and evaporation
4. Drying Equipments
5. Classification of dryers
6. Application of drying
7. Parameters to consider in selecting drying
equipment
8. Factors affecting drying
8/11/2020 Pharmaceutics Dept. COMAHS-USL
9. Mechanism of drying
8/11/2020 Pharmaceutics Dept. COMAHS-USL
Definition of drying
Drying is commonly the last stage in a
manufacturing process.
Drying is the final removal of water from
material (usually by heat)
Drying can take place without heat (Non-
thermal drying). Examples; a) Squeezing
wetted sponge. b) Adsorption by desiccant
(desiccation) c) Extraction.
8/11/2020 Pharmaceutics Dept. COMAHS-USL
Importance of drying
In pharmaceutical technology, drying is carried
out for one or more of the following reasons:
To avoid or eliminate moisture which may lead
to corrosion and decrease the product or drug
stability.
To improve or keep the good properties of a
material, e.g. Followability, compressibility.
To reduce the cost of transportation of large
volume materials ( liquids).
8/11/2020 Pharmaceutics Dept. COMAHS-USL
Importance of drying cont.….
In pharmaceutical technology, drying is carried
out for one or more of the following reasons:
cont.…
To make the material easy or more suitable for
handling.
Preservative.
The final step in Evaporation, Filtration,
Crystallization.
8/11/2020 Pharmaceutics Dept. COMAHS-USL
Difference between drying and evaporation
No Drying Evaporation
1 In drying processes, the main In evaporation processes, the main
operation usually carried out operation usually carried out on liquid
on solid materials, e.g. materials, e.g. solution, or products
powders, or products
2 Drying in most of the cases Evaporation include the removal of
means the removal of large amounts of water from
relatively small amounts of solutions.
water from solids
3 In most cases, drying involves Whereas evaporation means the
the removal of water at removal of water by boiling a solution.
temperatures below its boiling
point
8/11/2020 Pharmaceutics Dept. COMAHS-USL
Difference between drying and evaporation cont.….
No Drying Evaporation
4 In drying , water is usually While in evaporation , water is
removed by circulating air over removed from the material as pure
the material in order to carry water vapour mixed with other gases.
away the water vapour
8/11/2020 Pharmaceutics Dept. COMAHS-USL
Drying Equipments
Drum dryer (Film drying)
Spray dryer
Freeze Dryer
Tray drier
Fluidized Bed Dryer
Vacuum Dryer
8/11/2020 Pharmaceutics Dept. COMAHS-USL
Drum Dryer (Film Drying)
It consists of a drum of about 0.75-1.5 m in diameter
and 2-4 m in length, heated internally, usually by
steam and rotated on its longitudinal axis.
Operation: The liquid is applied to the surface and
spread to a film, this may be done in various ways,
but the simplest method is where the drum dips into
a feed pan. Drying rate is controlled by using a
suitable speed of rotation and the drum
temperature. The product is scraped from the
surface of the drum by means of a doctor knife.
8/11/2020 Pharmaceutics Dept. COMAHS-USL
Spray Dryer
The spray dryer provides a large surface area for
heat and mass transfer by atomizing the liquid to
small droplets.
These are sprayed into a stream of hot air, so that
each droplet dries to a solid particle.
The drying chamber resembles the cyclone
ensuring good circulation of air, to facilitate heat
and mass transfer, and that dried particles are
separated by the centrifugal action.
Spray dryer can be operated efficiently at various
feed rates.
8/11/2020 Pharmaceutics Dept. COMAHS-USL
Freeze Dryer
o Freeze drying is a process used to dry extremely heat
sensitive materials. It allows the drying , without
excessive damage, of proteins, blood products and
even microorganisms, which retain a small but
significant viability.
o In this process the initial liquid solution or suspension
is frozen, the pressure above the frozen state is
reduced and the water removed by sublimation.
o Thus a liquid-to-vapour transition takes place, but
here three states of matter involved: liquid to solid,
then solid to vapour.
8/11/2020 Pharmaceutics Dept. COMAHS-USL
Tray drier
Air flows in direction of the arrows over each
shelf in turn.
The wet material is spread on shallow trays
resting on the shelves.
Electrical elements or steam-heated pipes are
positioned so that the air is periodically
reheated after it has cooled by passage over
the wet material on one shelf before it passes
on the next.
8/11/2020 Pharmaceutics Dept. COMAHS-USL
Fluidized Bed Dryer
Fluidized’ means something that behaves like liquid.
In the fluidized bed dryer, the mixture of solids and
gas behave like a liquid and solid are called fluidized.
It provides good contact between hot air and
particles to obtain efficient drying.
The hot air is passed through a mesh, which
supports the conical vessel with a porous base.
This vessel is filled with powder to be dried.
It has wheels and can be clipped to the central plate
by means of a rapid acting ring closure.
8/11/2020 Pharmaceutics Dept. COMAHS-USL
Vacuum Dryer
• This equipment is a good example of conduction
drier. The vacuum oven consists of a jacketed
vessel to withstand vacuum within the oven.
• There are supports for the shelves giving a larger
area for conduction heat transfer. The oven can
be closed by a door.
• The oven is connected through a condenser and
liquid receiver to a vacuum pump.
• Operating pressure can be as low as 0.03-0.03
bar, at which pressures water boils at 25-35 0C.
8/11/2020 Pharmaceutics Dept. COMAHS-USL
Classification of Dryers
1. Adiabatic or Direct Dryers: Dryers that expose
the solids to a hot gas (usually air) are called
Adiabatic or Direct Dryers.
2. Non-Adiabatic or Indirect Dryers :Dryers in
which heat is transferred from an external
medium are known as non-adiabatic or
Indirect Dryers
8/11/2020 Pharmaceutics Dept. COMAHS-USL
In Adiabatic Dryers solids are exposed to the gas
in the following ways.
1. Cross-Circulation Drying: Gas is blown across the
surface of a bed or slab of solids.
2. Through Circulation Drying: Gas is blown through a bed
of coarse granular solids that are supported on a screen
3. Solids are showered downward through a slowly
moving gas stream in a rotary dryers
4. Gas passes through the solids at a velocity sufficient to
fluidize the bed
5. Solids are all entrained in a hi velocity gas stream and
are pneumatically conveyed from a mixing device to a
mechanical separator.
8/11/2020 Pharmaceutics Dept. COMAHS-USL
In Non-Adiabatic Dryers solids are exposed to
the hot surface or other source of heat in the
following ways.
Solids are spread over a stationary or slowly
moving horizontal surface and cooked until dry.
Surface may be heated
1) Electrically
2) Heat transfer fluid stream or hot water
3) Radiant heater.
8/11/2020 Pharmaceutics Dept. COMAHS-USL
Application of Drying
In the pharmaceutical industries, it is used as a
unit process in the manufacture of granules which
can be dispensed in bulk or converted into tablets
or capsules.
Drying can also be used to reduce the bulk and
weight of the material, thereby lowering the cost
of transportation and storage.
It helps in the preservation of crude drugs of plant
from mould growth, which occurs due to
presence of moisture.
8/11/2020 Pharmaceutics Dept. COMAHS-USL
It helps in the size reduction of crude drugs.
The presence of moisture in the crude drug
does not allow it to get powdered easily.
8/11/2020 Pharmaceutics Dept. COMAHS-USL
Parameters to consider in selecting drying equipment
Physical/chemical properties of the product.
Production capacity (Kg/hr)
Energy consumption must be minimized
Pollution must be controlled
Operating and maintenance costs must be
excessive.
8/11/2020 Pharmaceutics Dept. COMAHS-USL
Factors affecting drying
Temperature
Relative humidity and moisture
Temperature of material being dried
Surface area
Tray load
Size of the product
Nature of the material
8/11/2020 Pharmaceutics Dept. COMAHS-USL
Mechanism of Drying
Liquid diffusion: If the wet solid is at a
temperature below the boiling point of the liquid.
Vapour diffusion: If the liquid vapourises within
the material.
Condensation diffusion: If drying takes place at
very low temperature and pressure e.g. in freeze
drying.
8/11/2020 Pharmaceutics Dept. COMAHS-USL
Mechanism of Drying cont.…
Surface diffusion: Not proven but possible.
Hydrostatic pressure: It occurs when internal
vaporization rates exceed the rate of vapour
transport through the solid to the liquid to the
surrounding.
Heat transfer: It takes place from the heating
medium to solid, except in dielectric or high
frequency electric drying, where heat is generated
within the solid and flows to exterior surface.
8/11/2020 Pharmaceutics Dept. COMAHS-USL
Mass transfer: It involves movement of the
moisture to the surface of the solid and its
subsequent evaporation from the surface. The
transfer of vapours from the surface to the
surrounding medium is affected by external
conditions like temperature, humidity, air flow
rate, pressure and evaporating surface exposed.
NB: Heat transfer is categorized into; 1.)Direct
(convection) 2.) Radiant(radiation) 3.)Dielectric
or microwave (radiofrequency) 4.) Indirect or
contact (conduction).
8/11/2020 Pharmaceutics Dept. COMAHS-USL
THANK YOU
8/11/2020 Pharmaceutics Dept. COMAHS-USL
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Dryers and Drying ProcessesDokument24 SeitenDryers and Drying ProcessesKristine Joy MataroNoch keine Bewertungen
- Types of Industrial Dryers and Their Selection PDFDokument20 SeitenTypes of Industrial Dryers and Their Selection PDFHari KishoreNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drying EquipmentDokument9 SeitenDrying EquipmentHIT- MANNoch keine Bewertungen
- AbhiiiiDokument21 SeitenAbhiiiisreenuNoch keine Bewertungen
- 90pharmaceutical Unit Operations - PDF DryingDokument18 Seiten90pharmaceutical Unit Operations - PDF DryingGS SandhuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tray DryerDokument22 SeitenTray DryerjuaxxoNoch keine Bewertungen
- DryingDokument8 SeitenDryingAjaya Kumar MohapatraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drying PDFDokument48 SeitenDrying PDFuzzal ahmedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dryers and Drying Processes (Module 4)Dokument25 SeitenDryers and Drying Processes (Module 4)Gold BlandoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fot Assin 1Dokument10 SeitenFot Assin 1RishavNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dryers and Drying ProcessesDokument92 SeitenDryers and Drying ProcessesRoem Esmerna100% (3)
- Diseño de SecadoresDokument39 SeitenDiseño de SecadoresJosé Helí Vallejos CoronadoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Upload: Login SignupDokument16 SeitenUpload: Login SignupSeid AragawNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tray Dryer ExperimentDokument13 SeitenTray Dryer Experimentgeek311295% (37)
- Drying EquipmentsDokument18 SeitenDrying EquipmentsCeazar Justine FuluganNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fundamentals of DryingDokument14 SeitenFundamentals of DryingAlisha AnchearyNoch keine Bewertungen
- How Choose Vacuum DryerDokument4 SeitenHow Choose Vacuum DryerGomatheeswariNoch keine Bewertungen
- Spray DryingDokument8 SeitenSpray DryingcymyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drying 4Dokument48 SeitenDrying 4『ABN』NARUTO أبن ناروتو (Gamer)Noch keine Bewertungen
- Dryers Used in Food IndustryDokument9 SeitenDryers Used in Food Industry9567592146Noch keine Bewertungen
- Naseach Ko Lang KaninaDokument64 SeitenNaseach Ko Lang KaninaJonelou CusipagNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rotary EvaporatorDokument3 SeitenRotary EvaporatorDaryl ChianNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mass Transfer Project 1 PDFDokument25 SeitenMass Transfer Project 1 PDFwasie kebire0% (1)
- Design of DryersDokument39 SeitenDesign of DryersAnara Alam100% (1)
- Dryer DesignDokument39 SeitenDryer DesignPrashanth Chidambaram75% (4)
- Drying: - Removal of Relatively Small Amount of Water or Organic Liquids - Final Processing Step Before PackagingDokument124 SeitenDrying: - Removal of Relatively Small Amount of Water or Organic Liquids - Final Processing Step Before PackagingMiscrit Man100% (1)
- DryingDokument124 SeitenDryingNemesi De L'amourNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sourcebook Chapter6 PDFDokument7 SeitenSourcebook Chapter6 PDFtapanshahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dairy and Food EngineeringDokument45 SeitenDairy and Food EngineeringMouryakanth Reddy GangireddyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drying 2020Dokument26 SeitenDrying 2020Samir PatelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drying Notes FinalDokument34 SeitenDrying Notes FinalKeith OmwoyoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drying Is A Mass Transfer Process Consisting of The Removal of Water orDokument8 SeitenDrying Is A Mass Transfer Process Consisting of The Removal of Water orAbdelrhman AboodaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Types of Dryers and Their ApplicationsDokument8 SeitenTypes of Dryers and Their ApplicationsMa. Mikhaela ApuradoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Units Ops 2 Midterm ProjDokument7 SeitenUnits Ops 2 Midterm ProjmarielNoch keine Bewertungen
- Units Ops 2 Midterm ProjDokument7 SeitenUnits Ops 2 Midterm ProjmarielNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drying of Food: Pintu ChoudharyDokument52 SeitenDrying of Food: Pintu ChoudharyMahesh LandgeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Separation III: Chapter 2: DryingDokument98 SeitenSeparation III: Chapter 2: DryingSaranya DeviNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drying: Assoc - Prof.Jomjai Peerapattana Faculty of Pharmaceutical Sciences Khon Kaen UniversityDokument13 SeitenDrying: Assoc - Prof.Jomjai Peerapattana Faculty of Pharmaceutical Sciences Khon Kaen UniversityCalm Phurit SenachaiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drying Processes and MethodDokument21 SeitenDrying Processes and Methodmirobel455kezaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Spray Drying Is A Method of Producing A Dry Powder From A Liquid or SlurryDokument3 SeitenSpray Drying Is A Method of Producing A Dry Powder From A Liquid or SlurryMikoToh ItoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Principle, Construction, Working, Uses, Merits and Demerits of Freeze Dryer - PharmaguidelineDokument4 SeitenPrinciple, Construction, Working, Uses, Merits and Demerits of Freeze Dryer - PharmaguidelineKaren Pachchigar 1Noch keine Bewertungen
- Drying of Processes MaterialsDokument25 SeitenDrying of Processes MaterialsAlif Aikal Che HatNoch keine Bewertungen
- Application of DryingDokument31 SeitenApplication of Dryinguzzal ahmedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drying, and Drying Equipments 2Dokument37 SeitenDrying, and Drying Equipments 2Adheep DasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Vacuum Dryer: Aim: To Find Time of Constant Rate Period and Constant Fall Period Using ADokument6 SeitenVacuum Dryer: Aim: To Find Time of Constant Rate Period and Constant Fall Period Using Aanjan_srihari0% (1)
- Methods of DryingDokument2 SeitenMethods of Dryingvijay kumar honnaliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 11Dokument13 SeitenChapter 11zekariyas kuneNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1 Autoclave: Can Be Sterilized in An AutoclaveDokument4 Seiten1 Autoclave: Can Be Sterilized in An Autoclaveabdelrhman aboodaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit-3 Drying &humidification3Dokument46 SeitenUnit-3 Drying &humidification3chinna eranna100% (1)
- Bhople Et Al (2019)Dokument3 SeitenBhople Et Al (2019)amelia arum ramadhaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dryer DesignDokument18 SeitenDryer DesignCamille Guya50% (2)
- A Presentaion On DryingDokument40 SeitenA Presentaion On DryingMd. Abu Bakar Siddique TayefNoch keine Bewertungen
- Continuous Tunnel Dryer 2014Dokument22 SeitenContinuous Tunnel Dryer 2014ValeeMendezPadillaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Freeze Drying Literature FreviewDokument8 SeitenFreeze Drying Literature Freviewasad balochNoch keine Bewertungen
- KhanDokument4 SeitenKhanirfan hilmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Scribed 2Dokument51 SeitenScribed 2Hafiz Muhammad AzamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Temperature and Humidity Independent Control (THIC) of Air-conditioning SystemVon EverandTemperature and Humidity Independent Control (THIC) of Air-conditioning SystemNoch keine Bewertungen
- Handbook of Water and Wastewater Treatment TechnologiesVon EverandHandbook of Water and Wastewater Treatment TechnologiesBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (11)
- 0.1.clinical PharmacokineticsDokument60 Seiten0.1.clinical PharmacokineticsSolomon D FatormaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mircro Biology Assignmen Lectural: Doc Nuhu Bah ID NO: 975 Q1. List of DNA and RNA VirusesDokument2 SeitenMircro Biology Assignmen Lectural: Doc Nuhu Bah ID NO: 975 Q1. List of DNA and RNA VirusesSolomon D FatormaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Glycogen McqsDokument4 SeitenGlycogen McqsSolomon D Fatorma100% (4)
- Questions and Answers What Is The Name of The Heteropolysaccharides in The Basement Membrane?Dokument6 SeitenQuestions and Answers What Is The Name of The Heteropolysaccharides in The Basement Membrane?Solomon D FatormaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Quizziz April 28 2021Dokument1 SeiteQuizziz April 28 2021Angel GonzalesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Task: Apply The Principles of Circuit Theory To A Circuit With Constant Sources To Explain The Operation of That Circuits As Mentioned in The Below Task. 1. (A)Dokument18 SeitenTask: Apply The Principles of Circuit Theory To A Circuit With Constant Sources To Explain The Operation of That Circuits As Mentioned in The Below Task. 1. (A)Rohan KhareNoch keine Bewertungen
- Monographie BIPM-5 Tables Vdffdfol5Dokument256 SeitenMonographie BIPM-5 Tables Vdffdfol5arengifoipenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Transducer: Controller (Control Theory)Dokument5 SeitenTransducer: Controller (Control Theory)Farrukh JamilNoch keine Bewertungen
- Report Fluid MechanicsDokument6 SeitenReport Fluid Mechanicszatulsyera19Noch keine Bewertungen
- Techo GeneratorDokument18 SeitenTecho GeneratorBhola KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ferro SchneiderDokument30 SeitenFerro Schneidervoravuth srisomboonsuk100% (1)
- Centre of MassDokument32 SeitenCentre of MassR.Yashwanth Raj XBNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Anatomy of The EyeDokument3 SeitenThe Anatomy of The EyeChezcaDionisioNoch keine Bewertungen
- Plasma ParametersDokument6 SeitenPlasma ParametersSherzod HaydarovNoch keine Bewertungen
- Weather InstrumentsDokument6 SeitenWeather InstrumentskirkemmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Limit State Definitions of The Connection Design Calculations SDS2 V7331Dokument110 SeitenLimit State Definitions of The Connection Design Calculations SDS2 V7331fzhouNoch keine Bewertungen
- Design of Elastomeric Bearing System and AnalysisDokument11 SeitenDesign of Elastomeric Bearing System and Analysisabdelrahman emadNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1Dokument6 Seiten1Vanjared OcampoNoch keine Bewertungen
- CAMBER Calculations 100814Dokument6 SeitenCAMBER Calculations 100814tonaalaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gourley DeclarationDokument36 SeitenGourley DeclarationTechCrunchNoch keine Bewertungen
- What Is Short Transmission Line - Its Phasor Diagram & ABCD Parameters - Circuit GlobeDokument19 SeitenWhat Is Short Transmission Line - Its Phasor Diagram & ABCD Parameters - Circuit GlobeHumayun ArshadNoch keine Bewertungen
- 07 3DElasticity CompleteDokument45 Seiten07 3DElasticity CompleteSüleyman TüreNoch keine Bewertungen
- Solution Manual Principles of ElectronicDokument26 SeitenSolution Manual Principles of Electronic謝亮瑩Noch keine Bewertungen
- SIMPLE Algorithm: - by Rajat WaliaDokument25 SeitenSIMPLE Algorithm: - by Rajat WaliaMyNguyenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Refraction of Light (01!11!2023)Dokument5 SeitenRefraction of Light (01!11!2023)navrosepreetsingh8a4hhps14Noch keine Bewertungen
- 06 Chapter 7 - Lateral Earth Pressure-M PDFDokument62 Seiten06 Chapter 7 - Lateral Earth Pressure-M PDFogeboy sangcopanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Aapm 64Dokument43 SeitenAapm 64AnjihartsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Week4 Reservoir Temperatures and PressuresDokument28 SeitenWeek4 Reservoir Temperatures and PressuresTrevor100% (1)
- Diagnosing and Preventing Tray Damage in Distillation ColumnsDokument6 SeitenDiagnosing and Preventing Tray Damage in Distillation ColumnsdoufethiNoch keine Bewertungen
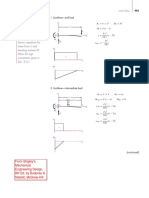
- Useful Beam EquationsDokument8 SeitenUseful Beam EquationsAXCNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ex03 05 WorksheetDokument4 SeitenEx03 05 Worksheetdrag600Noch keine Bewertungen
- Vector Group Test of TransformerDokument4 SeitenVector Group Test of TransformerHamayoun Murtaza100% (2)
- Problemas Resueltos Del Reichl - TMPDokument141 SeitenProblemas Resueltos Del Reichl - TMPLuis Alberto Aliaga VásquezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Presentation On LaserDokument19 SeitenPresentation On LaserBhargavNoch keine Bewertungen