Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Power Point Lectures To Accompany: Tomorrow's Technology and You, 9e
Hochgeladen von
Firdaus AzizeeOriginalbeschreibung:
Originaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Power Point Lectures To Accompany: Tomorrow's Technology and You, 9e
Hochgeladen von
Firdaus AzizeeCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Power Point
Lectures to
accompany
Tomorrow’s
Technology and
You, 9e
Copyright © 2009 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall
Slide 1
All rights reserved. No part of this publication may be
reproduced, stored in a retrieval system, or
transmitted, in any form or by any means, electronic,
mechanical, photocopying, recording, or otherwise,
without the prior written permission of the publisher.
Printed in the United States of America.
Copyright © 2009 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall Slide 2
Tomorrow’s
Technology
and You 9/e
Chapter 1
Our Digital Planet
Copyright © 2009 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall Slide 3
Tomorrow’s Technology and You 9/e
Chapter 1
Objectives
Describe several ways digital technology plays a critical role
in modern life
Discuss several key trends in the evolution of computers and
digital technology
Describe the major types of computers and their principle
uses
Explain how the explosive growth and evolution of the
Internet is changing the way people use information
technology
Copyright © 2009 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall Slide 4
Tomorrow’s Technology and You 9/e
Chapter 1
Objectives (cont.)
Explain how our information age differs from any time that
came before
Discuss the social and ethical impact of information
technology on our society
Copyright © 2009 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall Slide 5
Tomorrow’s Technology and You 9/e
Chapter 1
Creating Communities on the Living Web
MySpace creates an online community
experience for young people. Tom
Anderson and Chris DeWolfe
are the founders
Flickr creates a community for
people to share their pictures.
Copyright © 2009 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall Slide 6
Tomorrow’s Technology and You 9/e
Chapter 1
Living in a Nondigital World
Computers are no longer a luxury but rather a
commodity.
Computers and their applications are involved in all
aspects of our daily life.
Copyright © 2009 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall Slide 7
Tomorrow’s Technology and You 9/e
Chapter 1
Computers in Perspective
Every computer in use today follows the basic plan laid out
by Charles Babbage and Lady Lovelace.
Copyright © 2009 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall Slide 8
Tomorrow’s Technology and You 9/e
Chapter 1
Computers in Perspective
The first real computers:
1939: Konrad Zuse completed the first programmable,
general-purpose digital computer.
About the same time, the British government was
assembling a top-secret team of mathematicians and
engineers to crack Nazi military codes.
1943: The team led by mathematician Alan Turing and
others completed Colossus, considered by many to be
the first electronic digital computer.
Copyright © 2009 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall Slide 9
Tomorrow’s Technology and You 9/e
Chapter 1
Computers in Perspective
The first real computers (cont.):
1939: Iowa State University professor John Atanasoff
developed what could have been the first electronic digital
computer, the Atanasoff-Berry Computer (ABC).
The first real computers (cont.):
1944: Thanks to a one million dollar grant from IBM,
Harvard professor Howard Aiken developed the Mark I.
Copyright © 2009 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall Slide 10
Tomorrow’s Technology and You 9/e
Chapter 1
Computers in Perspective
The first real computers (cont.):
John Mauchly and J. Presper Eckert
helped the U.S. effort in World War II
by constructing a machine to calculate
trajectory tables for new guns.
ENIAC (Electronic Numerical Integrator and
Computer)
After the war, Mauchly and Eckert
started a private company called Sperry
and created UNIVAC I, the first
general-purpose commercial computer.
Copyright © 2009 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall Slide 11
Tomorrow’s Technology and You 9/e
Chapter 1
Computers in Perspective
Vacuum tubes were used in early computers.
Transistors replaced vacuum tubes starting in 1956.
By the mid-1960s transistors were replaced by integrated
circuits.
Copyright © 2009 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall Slide 12
Tomorrow’s Technology and You 9/e
Chapter 1
Computers in Perspective
Integrated circuits brought:
Increased reliability
Smaller size
Higher speed
Higher efficiency
Lower cost
Copyright © 2009 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall Slide 13
Tomorrow’s Technology and You 9/e
Chapter 1
Computers in Perspective
1971: The first microprocessor was invented by Intel
engineers.
The PC (personal computer) revolution began in
1970:
Apple
Commodore
Tandy
Moore’s law–Gordon Moore predicted that the number of
transistors that can be packed into a silicon chip of the same
price would roughly double every two years.
Copyright © 2009 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall Slide 14
Tomorrow’s Technology and You 9/e
Chapter 1
Computers Today: A Brief Taxonomy
Desktop computers haven’t completely replaced big computers,
which have also evolved.
Embedded computers
Special-purpose computer: Dedicated
computers that perform specific tasks.
Controlling the temperature and humidity
Monitoring your heart rate
Monitoring your house security system
The program is etched on silicon so it
cannot be altered. This is called firmware.
Copyright © 2009 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall Slide 15
Tomorrow’s Technology and You 9/e
Chapter 1
Computers Today: A Brief Taxonomy
Personal computers and workstations
PCs serve a single user at a time
PCs are a tool for:
Enhancing productivity
Creativity
Communication
PCs can be classified as:
Desktop
Workstation
Laptop
Copyright © 2009 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall Slide 16
Tomorrow’s Technology and You 9/e
Chapter 1
Computers Today: A Brief Taxonomy
Personal computers and workstations
(cont.)
Desktop computer
A PC designed to sit on a desk or
table for extended periods of time
Common components:
• Tower with internal key
components
• Monitor
• Keyboard
• Mouse
• Speakers
Has one or more power cables
connecting it to an electrical outlet
Copyright © 2009 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall Slide 17
Tomorrow’s Technology and You 9/e
Chapter 1
Computers Today: A Brief Taxonomy
Personal computers and workstations (cont.)
Workstations
High-end desktop computers with massive
computing power used for high-end interactive
applications
As workstations become less
expensive and desktops become
more powerful, the line that
separates them is becoming as
much a marketing distinction
as a technical one.
Copyright © 2009 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall Slide 18
Tomorrow’s Technology and You 9/e
Chapter 1
Computers Today: A Brief Taxonomy
Personal computers and
workstations (cont.)
Laptop, or notebook,
computers are personal
computers designed with
portability in mind.
Some components are
left off to help keep
size and weight down.
Copyright © 2009 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall Slide 19
Tomorrow’s Technology and You 9/e
Chapter 1
Computers Today: A Brief Taxonomy
Handheld devices
Handheld devices are small enough to
tuck into pockets and serve the needs
of users who value mobility over a full-
sized keyboard and screen.
PDA (personal digital assistant)
• Palm
• Pocket PC
Smart phones
• iPhone
Copyright © 2009 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall Slide 20
Tomorrow’s Technology and You 9/e
Chapter 1
Computers Today: A Brief Taxonomy
Servers
Computers designed to provide
software and other resources to
other computers over a network.
Copyright © 2009 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall Slide 21
Tomorrow’s Technology and You 9/e
Chapter 1
Computers Today: A Brief Taxonomy
Mainframes and supercomputers
Mainframes
Used by large organizations, such as banks
and airlines, for big computing jobs
Communicate with mainframe
through terminals
Multiple communications
at one time through process
of timesharing
Copyright © 2009 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall Slide 22
Tomorrow’s Technology and You 9/e
Chapter 1
Computers Today: A Brief Taxonomy
Mainframes and supercomputers (cont.)
Supercomputers
For power users who need access to the
fastest, most powerful computers made
Copyright © 2009 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall Slide 23
Tomorrow’s Technology and You 9/e
Chapter 1
Computer Connections: The Internet Revolution
Networks
Connect devices together
1960s: Internet developed with backing of the U.S.
government
Copyright © 2009 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall Slide 24
Tomorrow’s Technology and You 9/e
Chapter 1
Computer Connections: The Internet Revolution
The Internet explosion–over a billion people with Internet access by
the end of 2005
Electronic mail
E-mail software
World Wide Web
Led the Internet’s transformation from a text-only
environment into a multimedia landscape incorporating
pictures, animation, sounds, and video
Copyright © 2009 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall Slide 25
Tomorrow’s Technology and You 9/e
Chapter 1
Computer Connections: The Internet Revolution
The Internet explosion–over a billion people with Internet access by
the end of 2005 (cont.)
Web browsers
Programs that in effect, serve as navigable windows into
the Web
Hypertext links
Tie together millions of Web pages created by diverse
authors
Internet supports varied activities
eBay used to make international transactions
Real-time multiplayer games
Copyright © 2009 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall Slide 26
Tomorrow’s Technology and You 9/e
Chapter 1
Into the Information Age
In the history of our society we have had:
An agricultural age
An industrial age
Now we are in a new age, the information age:
More and more people earn their living working with
words, numbers, and ideas.
Copyright © 2009 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall Slide 27
Tomorrow’s Technology and You 9/e
Chapter 1
Into the Information Age
Living with digital technology
Explanations: clarifying technology
Computer literacy is already improving our day-to-
day lives and careers.
Applications: digital technology in action
Applications enable you to use a computer for
specific purposes.
Copyright © 2009 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall Slide 28
Tomorrow’s Technology and You 9/e
Chapter 1
Living with Digital Technology
Implications: social and ethical issues
The threat to personal privacy posed by large databases and
computer networks
The hazards of high-tech crime and the difficulty of keeping
data secure
The difficulty of defining and protecting intellectual property in
an all-digital age
Copyright © 2009 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall Slide 30
Tomorrow’s Technology and You 9/e
Chapter 1
Living with Digital Technology
Implications: social and ethical issues (cont.)
The threat of automation and the dehumanization of work
The abuse of information as a tool of political and economic
power
The emergence of biodigital technology
The dangers of dependence on
complex technology
Copyright © 2009 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall Slide 31
Tomorrow’s Technology and You 9/e
Chapter 1
Into the Information Age
Working the Web
Web search strategies
Get to know your search engines
Be specific when you search
Know your plusses and minuses
Be selective
Triangulate
Beware of urban legends
Organize your favorites
Protect your privacy
Be conscious of cookies and bugs
Remember that online shopping isn’t always better
Shop with care
Copyright © 2009 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall Slide 32
Tomorrow’s Technology and You 9/e
Chapter 1
Into the Information Age
Computer ethics
ACM (Association for Computing Machinery)
Guidelines for deciding how to “do the right thing:”
Know the rules and the law
Don’t assume that it’s OK if it’s legal
Think scenarios
When it doubt, talk it out
Make yourself proud
Remember the golden rule: Do unto others as you would have
them do unto you
Take the long view
Do your part
Copyright © 2009 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall Slide 33
Tomorrow’s Technology and You 9/e
Chapter 1
Lesson Summary
Computers have evolved at an
incredible pace since Charles
Babbage’s plan for an Analytical
Engine.
Computers today come in all
shapes and sizes, with specific
types being well-suited for
particular jobs.
Connecting to a network
enhances the value and power of
a computer:
Internet
WWW
Copyright © 2009 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall Slide 34
Tomorrow’s Technology and You 9/e
Chapter 1
Lesson Summary (cont.)
Computers and information
technology have changed
the world rapidly and
irreversibly.
Emerging technologies, such
as artificial intelligence, offer
promise for future
applications.
Computers threaten our
privacy, our security, and
perhaps our way of life.
Information technology is
here to stay.
Copyright © 2009 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall Slide 35
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeVon EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (537)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Von EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Bewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (98)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeVon EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (5794)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingVon EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (400)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceVon EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (588)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureVon EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryVon EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (231)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceVon EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (895)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnVon EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (234)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItVon EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (838)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerVon EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (271)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaVon EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (266)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealVon EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaVon EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (45)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersVon EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (345)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyVon EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (2259)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreVon EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Von EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Bewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesVon EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (821)
- M32R-FPU: Software ManualDokument192 SeitenM32R-FPU: Software ManualВ'ячеслав ІльчукNoch keine Bewertungen
- High Bay 200w LedDokument3 SeitenHigh Bay 200w LedEdizon Ramos OrtizNoch keine Bewertungen
- LT230T Transfer Box Overhaul ManualDokument82 SeitenLT230T Transfer Box Overhaul ManualjunglemistNoch keine Bewertungen
- Life-365 - v2.2.3 - Users - Manual (1) - 26-53Dokument28 SeitenLife-365 - v2.2.3 - Users - Manual (1) - 26-53Fernando RosalesNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Amstrad TimesDokument32 SeitenThe Amstrad Timesavinash palNoch keine Bewertungen
- Eizo CS240 ManualDokument77 SeitenEizo CS240 ManualreadalotbutnowisdomyetNoch keine Bewertungen
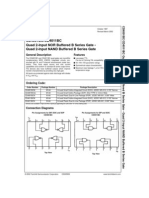
- CD4011BCDokument10 SeitenCD4011BCKike DavilaNoch keine Bewertungen
- My Cloud DL4100 PDFDokument7 SeitenMy Cloud DL4100 PDFdaveo80Noch keine Bewertungen
- Ansys Workbench 13: Theory - Applications - Case StudiesDokument4 SeitenAnsys Workbench 13: Theory - Applications - Case StudiesamodpanthiNoch keine Bewertungen
- MikroTik Load Balancing Over Multiple GatewaysDokument6 SeitenMikroTik Load Balancing Over Multiple GatewaysAndy Ndreu100% (1)
- Standardized FastenersDokument30 SeitenStandardized FastenersJas SumNoch keine Bewertungen
- 5500 HI Installation Guide (20111031)Dokument65 Seiten5500 HI Installation Guide (20111031)yocabezaNoch keine Bewertungen
- FangLing Shape Cutting Control System Operation and Installation Manual V2.2 - KTS MALLDokument162 SeitenFangLing Shape Cutting Control System Operation and Installation Manual V2.2 - KTS MALLkevin fernandez100% (1)
- Best Hacking Site: XP Tricks LL Some Call It HackDokument13 SeitenBest Hacking Site: XP Tricks LL Some Call It HackkarthithebossNoch keine Bewertungen
- Android - Intel® Atom™ x86 Image For Android - 4Dokument3 SeitenAndroid - Intel® Atom™ x86 Image For Android - 4VINAYNoch keine Bewertungen
- Human Fall Detection System: Department of Information TechnologyDokument17 SeitenHuman Fall Detection System: Department of Information Technologyrushabh lalwaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- NOS110 Study GuideDokument122 SeitenNOS110 Study GuideMax Potent100% (1)
- E&M Voice Card For LOOP-AM3440-A/B/C User'S ManualDokument32 SeitenE&M Voice Card For LOOP-AM3440-A/B/C User'S Manualarya_85Noch keine Bewertungen
- SPL 3200i 291075 DEDokument341 SeitenSPL 3200i 291075 DEArthur DivinoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Adv 7125Dokument16 SeitenAdv 7125georg1985Noch keine Bewertungen
- ObjectiveDokument3 SeitenObjectiveAshok GadhwalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Circular Saw Grinding Machines Complete RangeDokument24 SeitenCircular Saw Grinding Machines Complete RangeAttila PolacsekNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bat Detector Information Pack Sept 2011Dokument8 SeitenBat Detector Information Pack Sept 2011jijil1Noch keine Bewertungen
- Canon Ip2770 Driver - ReadmeDokument2 SeitenCanon Ip2770 Driver - ReadmeMicheal RinggitNoch keine Bewertungen
- 8051 Microcontroller and Its Interfacings: CourseDokument3 Seiten8051 Microcontroller and Its Interfacings: CourseAbhijeet RedekarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit2 Ass1 NewDokument3 SeitenUnit2 Ass1 Newmaurice007Noch keine Bewertungen
- Restart NastranDokument35 SeitenRestart NastranJacob Verghese100% (2)
- Fr-Connecttechno MTR 2013Dokument31 SeitenFr-Connecttechno MTR 2013Enrique MurgiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- NEWLOGODokument9 SeitenNEWLOGOgnohmNoch keine Bewertungen
- Laptop Condition ReportDokument3 SeitenLaptop Condition ReportAshok Kamath100% (1)