Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Writing Engineering Abstracts
Hochgeladen von
柯泰德 (Ted Knoy)Originaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Writing Engineering Abstracts
Hochgeladen von
柯泰德 (Ted Knoy)Copyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Writing Engineering Abstracts(43)
http://www.chineseowl.idv.tw
:
(+)
(1 of 2)
(+) Our working group has become
increasingly intrigued with the current trend in contractual disputes that
often lead to time schedule delays.
A strictly adhered to time schedule is of priority concern in civil
engineering, with company owners and contractors often struggling to
reach a consensus on deadlines and constraints, requiring that
regulations, construction practices and schedule are clearly agreed
upon in the contract. While the time schedule outlined in a contract is
defined according to calendar dates, working days and project phases,
actual construction tasks are often complex and fail to comply with
antiquated time schedules. Therefore, this work describes an
enhanced contract time schedule that incorporates calendar dates,
working days and project phases. As duration of a contract includes
many circumstances, using only one time framework to determine the
entire project schedule time is an unreliable approach that will create
friction between the company owner and contractor. All foreseeable
circumstances must be integrated into the contract schedule.
(2 of 2)
The scope of the projects activities is determined. A time
schedule for each work task is then confirmed. Next, weather
conditions during the project are also forecasted. Additionally, the role
of al ternati ve desi gn and administrati ve assi gnments duri ng
implementation of the contract is evaluated. Moreover, other ways in
which the contractor influences this contracted work are assessed.
Finally, the above influences on this contract are considered to
determine the actual project schedule time. Analysis
results indicate that the proposed contract time schedule determines
more accurately the time constraints in a construction project than
conventional methods can. In addition to achieving a more accurate
budget than the originally forecasted one, the proposed schedule
ensures a higher quality than previous ones. In
addition to accurately predicting project completion, the proposed
schedule can determine budgetary constraints precisely.
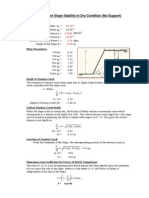
(1 of 2)
(+) Slope mitigation efforts in
many countries, including Taiwan, have focused on rainfall
induced, shallow type landslides of lateretic soil. Although
saturated soil mechanics is conventionally adopted to
analyze slope stability, many slopes remain unsaturated
dur i ng ordi nar y weat her and st or my condi t i ons.
Convent i onal l y adopt ed sat urated soi l mechani cs
procedures are limited in slope analyses owing to the
inability not only to explain why the slope remains stable
under a sharp slope angle during the dry season, but also
to predict accurately the failure time of the slope during
stormy conditions. Therefore, this study investigates
rainfall induced shallow type landslides in Taiwan by
adopting the theory of unsaturated soil mechanics. Capable
of determining the shear strength of soil during dry and
rainy seasons, the proposed method can estimate the
safety factor of the slope under various conditions.
(2 of 2)
The rainfall intensity and infiltration rate of the slope surface
are simulated using SEEP/W. The distribution of water pressure
soil slope under various conditions is then determined via
SEEP/W. Finally, results of SEEP/W are used as an input to the
SLOPE/W in order to determine the slope stability under various
conditions. Analytical results indicate that,
based on the unsaturated soil theory, the proposed method
evaluates the failure mechanism and failure time of a natural soil
slope precisely. Additionally, the method explains why the slope
can maintain a sharp slope angle during the dry season.
Importantly, the proposed method increases the
accuracy of slope stability analyses. The failure mechanism and
mitigation methods for the shallow type landslides are more
reliable for future applications.
Further details can be found at
http://www.chineseowl.idv.tw
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeVon EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (5794)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreVon EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1090)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItVon EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (838)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceVon EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (895)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceVon EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (588)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeVon EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (537)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersVon EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (344)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureVon EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesVon EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (821)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Von EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Bewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (121)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerVon EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingVon EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (400)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyVon EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Von EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Bewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaVon EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryVon EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnVon EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealVon EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaVon EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (45)
- Analysis of Earth Retaining Structures Using Finite Element and Finite Difference ApproachDokument20 SeitenAnalysis of Earth Retaining Structures Using Finite Element and Finite Difference ApproachSenthooran Mahendran100% (1)
- Vietnam 2: Giấy chứng nhận ESL của truyền thông kỹ thuậtDokument12 SeitenVietnam 2: Giấy chứng nhận ESL của truyền thông kỹ thuật柯泰德 (Ted Knoy)Noch keine Bewertungen
- Vietnam 2.61:Tổ chức lớp viết báo khoa học Y khoa đăng trên tạp chí quốc tếDokument19 SeitenVietnam 2.61:Tổ chức lớp viết báo khoa học Y khoa đăng trên tạp chí quốc tế柯泰德 (Ted Knoy)Noch keine Bewertungen
- Vietnam 6.9:Thư giới thiệu việc làmDokument15 SeitenVietnam 6.9:Thư giới thiệu việc làm柯泰德 (Ted Knoy)Noch keine Bewertungen
- Vietnam 6.8: Thư ứng dụng đào tạo (Thư xin việc)Dokument12 SeitenVietnam 6.8: Thư ứng dụng đào tạo (Thư xin việc)柯泰德 (Ted Knoy)Noch keine Bewertungen
- Vietnam 2.62:Tổ chức lớp viết báo khoa học Y khoa đăng trên tạp chí quốc tếDokument20 SeitenVietnam 2.62:Tổ chức lớp viết báo khoa học Y khoa đăng trên tạp chí quốc tế柯泰德 (Ted Knoy)Noch keine Bewertungen
- Vietnam 2.59:Tổ chức lớp viết báo khoa học Y khoa đăng trên tạp chí quốc tếDokument16 SeitenVietnam 2.59:Tổ chức lớp viết báo khoa học Y khoa đăng trên tạp chí quốc tế柯泰德 (Ted Knoy)Noch keine Bewertungen
- Vietnam 2.64:Tổ chức lớp viết báo khoa học Y khoa đăng trên tạp chí quốc tếDokument23 SeitenVietnam 2.64:Tổ chức lớp viết báo khoa học Y khoa đăng trên tạp chí quốc tế柯泰德 (Ted Knoy)Noch keine Bewertungen
- Vietnam 2.63:Tổ chức lớp viết báo khoa học Y khoa đăng trên tạp chí quốc tếDokument18 SeitenVietnam 2.63:Tổ chức lớp viết báo khoa học Y khoa đăng trên tạp chí quốc tế柯泰德 (Ted Knoy)Noch keine Bewertungen
- Vietnam 2.45:Tổ chức lớp viết báo khoa học đăng trên tạp chí quốc tếDokument14 SeitenVietnam 2.45:Tổ chức lớp viết báo khoa học đăng trên tạp chí quốc tế柯泰德 (Ted Knoy)Noch keine Bewertungen
- Vietnam 2.57:Tổ chức lớp viết báo khoa học Y khoa đăng trên tạp chí quốc tếDokument15 SeitenVietnam 2.57:Tổ chức lớp viết báo khoa học Y khoa đăng trên tạp chí quốc tế柯泰德 (Ted Knoy)Noch keine Bewertungen
- Vietnam 2.58:Tổ chức lớp viết báo khoa học Y khoa đăng trên tạp chí quốc tếDokument18 SeitenVietnam 2.58:Tổ chức lớp viết báo khoa học Y khoa đăng trên tạp chí quốc tế柯泰德 (Ted Knoy)Noch keine Bewertungen
- Vietnam 2.60:Tổ chức lớp viết báo khoa học Y khoa đăng trên tạp chí quốc tếDokument16 SeitenVietnam 2.60:Tổ chức lớp viết báo khoa học Y khoa đăng trên tạp chí quốc tế柯泰德 (Ted Knoy)Noch keine Bewertungen
- Vietnam 2.43:Tổ chức lớp viết báo khoa học đăng trên tạp chí quốc tếDokument14 SeitenVietnam 2.43:Tổ chức lớp viết báo khoa học đăng trên tạp chí quốc tế柯泰德 (Ted Knoy)Noch keine Bewertungen
- Vietnam 2.44:Tổ chức lớp viết báo khoa học đăng trên tạp chí quốc tếDokument16 SeitenVietnam 2.44:Tổ chức lớp viết báo khoa học đăng trên tạp chí quốc tế柯泰德 (Ted Knoy)Noch keine Bewertungen
- Vietnam 2.53:Tổ chức lớp viết báo khoa học Y khoa đăng trên tạp chí quốc tếDokument15 SeitenVietnam 2.53:Tổ chức lớp viết báo khoa học Y khoa đăng trên tạp chí quốc tế柯泰德 (Ted Knoy)Noch keine Bewertungen
- Vietnam 2.51:Tổ chức lớp viết báo khoa học Y khoa đăng trên tạp chí quốc tếDokument17 SeitenVietnam 2.51:Tổ chức lớp viết báo khoa học Y khoa đăng trên tạp chí quốc tế柯泰德 (Ted Knoy)Noch keine Bewertungen
- Vietnam 2.55:Cấu trúc bài báo nghiên cứuDokument20 SeitenVietnam 2.55:Cấu trúc bài báo nghiên cứu柯泰德 (Ted Knoy)Noch keine Bewertungen
- Vietnam 2.42:Tổ chức lớp viết báo khoa học đăng trên tạp chí quốc tếDokument17 SeitenVietnam 2.42:Tổ chức lớp viết báo khoa học đăng trên tạp chí quốc tế柯泰德 (Ted Knoy)Noch keine Bewertungen
- Vietnam 2.41:Tổ chức lớp viết báo khoa học thương mại đăng trên tạp chí quốc tếDokument24 SeitenVietnam 2.41:Tổ chức lớp viết báo khoa học thương mại đăng trên tạp chí quốc tế柯泰德 (Ted Knoy)Noch keine Bewertungen
- Vietnam 2.52:Tổ chức lớp viết báo khoa học Y khoa đăng trên tạp chí quốc tếDokument15 SeitenVietnam 2.52:Tổ chức lớp viết báo khoa học Y khoa đăng trên tạp chí quốc tế柯泰德 (Ted Knoy)Noch keine Bewertungen
- Vietnam 2.48:Tổ chức lớp viết báo khoa học Y khoa đăng trên tạp chí quốc tếDokument17 SeitenVietnam 2.48:Tổ chức lớp viết báo khoa học Y khoa đăng trên tạp chí quốc tế柯泰德 (Ted Knoy)Noch keine Bewertungen
- Vietnam 2.54:Tổ chức lớp viết báo khoa học Y khoa đăng trên tạp chí quốc tếDokument14 SeitenVietnam 2.54:Tổ chức lớp viết báo khoa học Y khoa đăng trên tạp chí quốc tế柯泰德 (Ted Knoy)Noch keine Bewertungen
- Vietnam 2.50:Tổ chức lớp viết báo khoa học Y khoa đăng trên tạp chí quốc tếDokument16 SeitenVietnam 2.50:Tổ chức lớp viết báo khoa học Y khoa đăng trên tạp chí quốc tế柯泰德 (Ted Knoy)Noch keine Bewertungen
- Vietnam 2.46:Tổ chức lớp viết báo khoa học đăng trên tạp chí quốc tếDokument19 SeitenVietnam 2.46:Tổ chức lớp viết báo khoa học đăng trên tạp chí quốc tế柯泰德 (Ted Knoy)Noch keine Bewertungen
- Vietnam 2.38:Tổ chức lớp viết báo khoa học thương mại đăng trên tạp chí quốc tếDokument18 SeitenVietnam 2.38:Tổ chức lớp viết báo khoa học thương mại đăng trên tạp chí quốc tế柯泰德 (Ted Knoy)Noch keine Bewertungen
- Vietnam 2.49:Tổ chức lớp viết báo khoa học Y khoa đăng trên tạp chí quốc tếDokument15 SeitenVietnam 2.49:Tổ chức lớp viết báo khoa học Y khoa đăng trên tạp chí quốc tế柯泰德 (Ted Knoy)Noch keine Bewertungen
- Vietnam 2.36:Tổ chức lớp viết báo khoa học thương mại đăng trên tạp chí quốc tếDokument21 SeitenVietnam 2.36:Tổ chức lớp viết báo khoa học thương mại đăng trên tạp chí quốc tế柯泰德 (Ted Knoy)Noch keine Bewertungen
- Vietnam 2.39:Tổ chức lớp viết báo khoa học thương mại đăng trên tạp chí quốc tếDokument18 SeitenVietnam 2.39:Tổ chức lớp viết báo khoa học thương mại đăng trên tạp chí quốc tế柯泰德 (Ted Knoy)Noch keine Bewertungen
- Vietnam 2.37:Tổ chức lớp viết báo khoa học thương mại đăng trên tạp chí quốc tếDokument17 SeitenVietnam 2.37:Tổ chức lớp viết báo khoa học thương mại đăng trên tạp chí quốc tế柯泰德 (Ted Knoy)Noch keine Bewertungen
- Vietnam 2.40:Tổ chức lớp viết báo khoa học thương mại đăng trên tạp chí quốc tếDokument19 SeitenVietnam 2.40:Tổ chức lớp viết báo khoa học thương mại đăng trên tạp chí quốc tế柯泰德 (Ted Knoy)Noch keine Bewertungen
- International Journal of Rock Mechanics and Mining Sciences & Geomechanics Abstracts Volume 21 Issue 5 1984 [Doi 10.1016%2F0148-9062%2884%2992985-1] -- Reinforced Retaining Walls- The Use of Old Motor Tyres (in French) - Long, N T;Dokument2 SeitenInternational Journal of Rock Mechanics and Mining Sciences & Geomechanics Abstracts Volume 21 Issue 5 1984 [Doi 10.1016%2F0148-9062%2884%2992985-1] -- Reinforced Retaining Walls- The Use of Old Motor Tyres (in French) - Long, N T;Dženana SmajićNoch keine Bewertungen
- PublicationDokument41 SeitenPublicationGerald Tan100% (1)
- Advanced Course in Slope Seepage and Foundation AnalysisDokument3 SeitenAdvanced Course in Slope Seepage and Foundation AnalysisReginald HammahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Theory of Structures-HandbookDokument25 SeitenTheory of Structures-HandbookDanica Rose SalangadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Soil Nails Loose Fill SlopesDokument98 SeitenSoil Nails Loose Fill Slopesisaych33zeNoch keine Bewertungen
- 3 - 2007-Determination of Slope Mass Rating PDFDokument9 Seiten3 - 2007-Determination of Slope Mass Rating PDFJampani HymavathiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Analysis of Earth DamDokument8 SeitenAnalysis of Earth DamMojtaba Mohebinia100% (2)
- AUTODYN - 2010 - Miller - An Explicit Numerical Model For The Study of Snow's Response To Explosive Air BlastDokument9 SeitenAUTODYN - 2010 - Miller - An Explicit Numerical Model For The Study of Snow's Response To Explosive Air BlastrzsoltNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rapid Drawdown With Simple Effective StressesDokument5 SeitenRapid Drawdown With Simple Effective StressesHiago MonteiroNoch keine Bewertungen
- Everything About GateDokument44 SeitenEverything About GatetigersayoojNoch keine Bewertungen
- EarthquakeLoading Example1Dokument35 SeitenEarthquakeLoading Example1jeanNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2 Slope Deflection Method For Statically Indeterminate Portal FrameDokument31 Seiten2 Slope Deflection Method For Statically Indeterminate Portal Framezulizwxn100% (1)
- GDM Ch-12 EmbankmentsDokument118 SeitenGDM Ch-12 EmbankmentstonaalaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Servicios en Control de Estabilidad de TaludesDokument5 SeitenServicios en Control de Estabilidad de TaludesAlvaro AlveoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Geology Lab 4Dokument9 SeitenGeology Lab 4Irana Swila0% (1)
- 4 Failure Analysis of Railwy EmbnkDokument4 Seiten4 Failure Analysis of Railwy EmbnkB Divya jyothiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Estabilización de Taludes - Usme PDFDokument70 SeitenEstabilización de Taludes - Usme PDFJuan Manuel Quintero100% (1)
- Hoek-Brown A Mohr-CoulombDokument7 SeitenHoek-Brown A Mohr-CoulombUriel Vélez OrejuelaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Proyecto Final Utilizando El Software Midas Gts para Estabilidad de TaludesDokument42 SeitenProyecto Final Utilizando El Software Midas Gts para Estabilidad de TaludesHeydy TrejosNoch keine Bewertungen
- GeoGuide1 RetainingWallDokument259 SeitenGeoGuide1 RetainingWallClaireNgok100% (1)
- CIE-GE Track Geo-Engineering (GE) ENDokument47 SeitenCIE-GE Track Geo-Engineering (GE) ENZar MaghustNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Q-Slope Method For Rock Slope EngineeringDokument17 SeitenThe Q-Slope Method For Rock Slope EngineeringmehdiNoch keine Bewertungen
- ChecklistDokument42 SeitenChecklistOsvaldo C. Nogueira100% (1)
- CDOT Drainage Design Manual Bank ProtectionDokument77 SeitenCDOT Drainage Design Manual Bank Protectionpablopadawan1Noch keine Bewertungen
- Rock Slope StabilityDokument7 SeitenRock Slope Stabilitysarvannn100% (1)
- Gege PaperDokument15 SeitenGege PaperAliNoch keine Bewertungen
- PHD0130 - Saurabh Rawat - 126602 - Ce - 2017Dokument313 SeitenPHD0130 - Saurabh Rawat - 126602 - Ce - 2017Nadeesh PriyashanNoch keine Bewertungen
- FHWA Soils and Foundations Excerpt PDFDokument110 SeitenFHWA Soils and Foundations Excerpt PDFVincent GacadNoch keine Bewertungen








































































![International Journal of Rock Mechanics and Mining Sciences & Geomechanics Abstracts Volume 21 Issue 5 1984 [Doi 10.1016%2F0148-9062%2884%2992985-1] -- Reinforced Retaining Walls- The Use of Old Motor Tyres (in French) - Long, N T;](https://imgv2-2-f.scribdassets.com/img/document/217209537/149x198/6c1c18cb7d/1397040855?v=1)