Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Internet 08
Hochgeladen von
Jen Rhae Lim0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
17 Ansichten17 SeitenCopyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Verfügbare Formate
PPT, PDF, TXT oder online auf Scribd lesen
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Verfügbare Formate
Als PPT, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
17 Ansichten17 SeitenInternet 08
Hochgeladen von
Jen Rhae LimCopyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Verfügbare Formate
Als PPT, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
Sie sind auf Seite 1von 17
Computers:
Tools for an Information Age
Chapter 8
The Internet at Home and in the Workplace
Copyright © 2003 by Prentice Hall
Objectives
Briefly describe the history of the Internet
Describe what is needed to get on the
Internet
Describe generally what an Internet
service provider does
Describe the rudimentary functions of a
browser
Describe how to search the Internet
Copyright © 2003 by Prentice Hall 2
Objectives
List and describe the non-Web services of
the Internet
Describe the various types of e-commerce
Discuss e-commerce payments and taxes
Describe how advertising is done on the
Internet
Describe what an intranet is and how a
business uses it
Copyright © 2003 by Prentice Hall 3
Growth of Internet
Growth in host computers
72 million in 2000
162 million in 2002
Growth in users worldwide
567 million in 2002
780 million projected in 2003
Copyright © 2003 by Prentice Hall 4
A Quick Timeline
ARPANET developed in 1969
Designed to connect computers at four
locations
Designed to be resistant to disruption
E-mail capability added in 1972
National Science Foundation connected its
large network, NSFnet to ARPANET in
1986
Resulting network became known as the
Internet
Copyright © 2003 by Prentice Hall 5
Key People
Tim Berners-Lee
Marc Andreessen
Copyright © 2003 by Prentice Hall 6
Getting Started
The technology
The Internet service provider and the
browser
Browser functions and features
Copyright © 2003 by Prentice Hall 11
Searching the Internet
Search Engine – lets a user
specify search terms
Search engine builds database of
sites that match those terms
Uses spider software to build
database
Metasearch – searches search
engines and builds
comprehensive list
Internet directory – database is
developed by human
researchers rather than spider
Copyright © 2003 by Prentice Hall 20
Non-Web Services of the Internet
Newsgroups
FTP
Telnet
Copyright © 2003 by Prentice Hall 21
The World of E-Commerce
Electronic commerce - buying and selling
over the Internet
Three forms
Business-to-consumer (B2C)
Business-to-business (B2B)
Consumer-to-consumer (C2C)
Copyright © 2003 by Prentice Hall 28
Payments and Taxes
E-commerce payments
Some people are leery of submitting credit card
information online
Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) protocol provides a
secure way to make online payments
E-commerce taxes
Internet Tax Freedom Act provides tax relief on
Internet commerce
Commission studies the effects of taxation of Internet
commerce
Act set to expire in 2005
Copyright © 2003 by Prentice Hall 36
Internet Portals
Your first stop on the Internet
Provide personalization to users
Site is customized based on
information you provide
Encourages you to visit the site
often
Provide referrals to other
businesses
Site contains links to affiliate
sites
If you click on an affiliate site and
make a purchase, the portal
receives a percentage of the sale
Copyright © 2003 by Prentice Hall 37
Internet Advertising
Many advertisements on Web
sites are banner ads
Originally in the shape of a long
rectangle
Require the user to leave the
current site
Other ad types
Pop-over ads open a new
window on top of your current
window
Pop-under ads open a new
window underneath your current
window
Copyright © 2003 by Prentice Hall 38
Intranets
A private Internet-like network
Internal to a certain company
Extranets allow selected customers and suppliers
to have access to a company’s intranet
Easy to set up
Offer many potential uses
Can be linked to the Internet
Copyright © 2003 by Prentice Hall 39
Setting up an Intranet
Easy to set up
Most organizations already have a local area
network
Hardware requirements
Software requirements
Copyright © 2003 by Prentice Hall 40
Uses of Intranets
Users can
Retrieve information such as benefits
information and job openings
Submit vacation requests, applications for
open positions, etc.
Employers can post employee handbooks,
corporate policies, and other information in
a central location
Copyright © 2003 by Prentice Hall 43
Virtual Private Network
Technology that uses the Internet as a
channel for private data communication
Uses tunneling technology
Offers many benefits over a private
network
Much cheaper than dedicated lines
Data is secure
Turns remote network administration over to
ISP
Copyright © 2003 by Prentice Hall 44
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeVon EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (5794)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreVon EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1090)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItVon EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (838)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceVon EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (895)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceVon EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (588)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeVon EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (537)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersVon EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (345)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureVon EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesVon EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (821)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Von EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Bewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (121)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerVon EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingVon EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (400)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyVon EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Von EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Bewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaVon EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryVon EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnVon EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealVon EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaVon EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (45)
- Linky Map Linky MapDokument14 SeitenLinky Map Linky MapDavor BudimirNoch keine Bewertungen
- Browserstack Test PDFDokument2 SeitenBrowserstack Test PDFnavinkumargNoch keine Bewertungen
- Case Studies TB NCM Training ToolsDokument110 SeitenCase Studies TB NCM Training ToolsJen Rhae LimNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ethical Problems in Nursing ManagementDokument4 SeitenEthical Problems in Nursing ManagementJen Rhae LimNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bullying Among Nursing Staff 01Dokument10 SeitenBullying Among Nursing Staff 01Jen Rhae LimNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ethical Decisions ProcessDokument1 SeiteEthical Decisions ProcessJen Rhae LimNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCP For CTTDokument1 SeiteNCP For CTTJen Rhae LimNoch keine Bewertungen
- Postpartum ComplicationsDokument30 SeitenPostpartum ComplicationsJen Rhae LimNoch keine Bewertungen
- Active Versus Passive DevicesDokument6 SeitenActive Versus Passive DevicesSneha BandhaviNoch keine Bewertungen
- AVR: Which Microcontroller To Choose: PIC VsDokument17 SeitenAVR: Which Microcontroller To Choose: PIC VsMuhammad Zawar100% (1)
- Write About Global Catalog. How To View Replication Properties For AD PropertiesDokument19 SeitenWrite About Global Catalog. How To View Replication Properties For AD PropertiesChandan KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pune Institute of Computer Technology PUNE - 411043 Department of Electronics & TelecommunicationDokument12 SeitenPune Institute of Computer Technology PUNE - 411043 Department of Electronics & TelecommunicationNakul SharmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Peter Manning Electronic Music and CompuDokument570 SeitenPeter Manning Electronic Music and CompuEmptyRoom Alejandro Bello100% (1)
- CH 21 Hull OFOD9 TH EditionDokument40 SeitenCH 21 Hull OFOD9 TH Editionseanwu95Noch keine Bewertungen
- Annual Exam COMPUTER SC Class XIDokument8 SeitenAnnual Exam COMPUTER SC Class XIST JOSEPH'S SCHOOLNoch keine Bewertungen
- Getting Started With Satellite 6Dokument54 SeitenGetting Started With Satellite 6Sudheer KhanduriNoch keine Bewertungen
- Release Notes - READDokument3 SeitenRelease Notes - READHari KurniadiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Asml 20110808 Careers Brochure ASML NLDokument12 SeitenAsml 20110808 Careers Brochure ASML NLerkin1989Noch keine Bewertungen
- CaFSET (Antigua) Office Workbook - Sixth Edition - Programming Concepts Sample PagesDokument4 SeitenCaFSET (Antigua) Office Workbook - Sixth Edition - Programming Concepts Sample PagescafsetNoch keine Bewertungen
- Computer Logic Design Lab 213371Dokument24 SeitenComputer Logic Design Lab 213371Habib Ur rehmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Threat Analysis ReportDokument18 SeitenThreat Analysis Reporttodo nothingNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Business Case For SAP GIS IntegrationDokument7 SeitenA Business Case For SAP GIS IntegrationCharles AshmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Minhash PDFDokument2 SeitenMinhash PDFYiboNoch keine Bewertungen
- Science Technology and SocietyDokument18 SeitenScience Technology and SocietyRowena HinumlaNoch keine Bewertungen
- WoodwardCatalog PDFDokument48 SeitenWoodwardCatalog PDFJul Cesar100% (1)
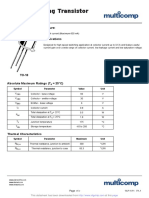
- PNP Switching Transistor: FeatureDokument2 SeitenPNP Switching Transistor: FeatureismailinesNoch keine Bewertungen
- FortiOS v4.0 MR3 Patch Release 11 Release NotesDokument31 SeitenFortiOS v4.0 MR3 Patch Release 11 Release NotesmonsieurkozoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lab 1Dokument8 SeitenLab 1Masud SarkerNoch keine Bewertungen
- SHA MAN 0052 Ver4 WebDokument96 SeitenSHA MAN 0052 Ver4 WebGreed CssNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hipaa Information and Consent FormDokument1 SeiteHipaa Information and Consent FormJake HennemanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nadir Qaiser Zong ProjectDokument42 SeitenNadir Qaiser Zong Projectloverboy_q_s80% (5)
- DirectionalEQManual PDFDokument2 SeitenDirectionalEQManual PDFdorutNoch keine Bewertungen
- DSLC™ Digital Synchronizer and Load Control: Installation and Operation ManualDokument114 SeitenDSLC™ Digital Synchronizer and Load Control: Installation and Operation ManualEdy TonelNoch keine Bewertungen
- BLCC610I Solution 6000 Installation Manual FTR2.6Dokument190 SeitenBLCC610I Solution 6000 Installation Manual FTR2.6ammy17643Noch keine Bewertungen
- Installation Instructions Avramis River MT4Dokument7 SeitenInstallation Instructions Avramis River MT4Muhammad HamzaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Excel ExerciseDokument296 SeitenExcel ExerciseshubhamNoch keine Bewertungen