Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Antiprotozoal and Antihelminthic Drugs - Handout
Hochgeladen von
donzOriginalbeschreibung:
Originaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Antiprotozoal and Antihelminthic Drugs - Handout
Hochgeladen von
donzCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
` ` ` ` ` `
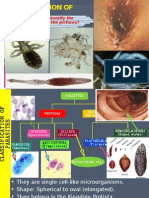
Malaria Amoebiasis Trypanosomiasis Leishmaniasis Giardiasis Trichomoniasis
` ` ` `
Caused by the plasmodium protozoa Four different plasmodium species Vector: female Anopheles mosquito Transmitted via blood transfusion, congenitally, or via infected needles by drug abusers.
Life Cycle of the plasmodium: Sexual in the mosquito Asexual in human
EXOERYTHROCYTIC PHASE outside RBC ERYTHROCYTIC PHASE inside RBC
Erythrocytic:
CHLOROQUINE, MEFLOQUINE, QUININE, HYDROXYCHLOROQUINE
Exoerythrocytic:
PRIMAQUINE (prevents relapse)
Chloroquine-resistant strains
QUININE SULFADOXINE+PYRIMETHAMINE (Fansidar)
Multi-drug resistant strains
Artemesin-lumerfrantine
CHLOROQUINE, MEFLOQUINE, QUININE, HYDROXYCHLOROQUINE
4-aminoquinoline derivatives Bind to parasite nucleoproteins and interfere with protein synthesis and alter pH of parasite Chloroquine prophylactic drug Chloroquine & Hydroxychloroquine have antiinflammatory effects
SIDE EFFECTS: N/V, D, anorexia, abd pain, dizziness, headache ` Quinine: N/V, tinnitus, vertigo
CINCHONISM SYNDROME
ADVERSE EFFECTS: ` Hepatotoxicity ` Dermatological changes (rashes, alopecia) ` Hemolytic anemia (chloroquine) ` Permanent eye damage/blindness (chloroquine) ` Nephrotoxicity (quinine) ` Steven Johnson Syndrome (Fansidar)
1.
2.
3.
4.
Screen the client for any contraindications (liver dysfunction, alcoholism, psoriasis, retinal disease, pregnancy & lactation) Arrange for appropriate culture and sensitivity tests before beginning therapy Administer the complete course of the drug. Mark a calendar for prophylactic doses. Monitor hepatic function and ophthalmologic examination before and periodically during treatment
5. 6.
7.
8.
9.
Provide comfort and safety measures Maintain nutrition and address diarrheal problems Advise clients traveling to malaria-infested countries to receive prophylactic doses of antimalarial drug before leaving, during visit and upon return. Instruct client to take oral antimalarial drugs with food or at mealtime Warn client about consuming large quantities of alochol
` `
Amoebiasis Leishmaniasis
Skin, mucuous membrane infection
Trypanosomiasis
African sleeping sickness, Chagas disease
Trichomoniasis
Vaginal infection
Giardiasis
Intestinal infection, travelers diarrhea
PCP/ Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia
ARC (lung)
METRONIDAZOLE (Flagyl)
Bactericidal (H. pylori, anaerobic bacterial infection), Trichonacidal (trichomoniasis) & Protozoacidal/Amoebicidal (amoebiasis) Prophylaxis in colorectal surgery Has METALLIC TASTE;
Side Effects/Adverse Effects:
x x x x N/V, D, headache, dizziness Neurotoxicity numbness, vertigo, ataxia Hepatotoxic DISULFIRAM-LIKE EFFECT
` `
` `
Assess for hepatic function and CNS disease Instruct client to avoid alcohol-containing products during & 48 hours after tx completion. Client should complete the course of medication even if symptoms disappear Maintain nutrition & hydration Patient may take the medication with meals if GI upset occurs; inform of the drugs metallic taste Inform patient that his/her urine may turn red-brown in color (high doses) CNS effects/ safety precautions
Atovaquone
PCP
`
Paramomycin
Intestinal amoebiasis
Pentamidine
Trypanosomiasis Leishmaniasis PCP
`
Pyrimethamine
Toxoplasmosis
Yinodazole
Trichomoniasis, Giardiasis & amoebiasis
Nematodes
Elongated round worms
Cestodes
True tapeworms
Trematodes
Flukes, flat-shaped flatworms
Intestinal parasitism Tissue-invading worm infections:
TRICHINOSIS FILARIASIS SCHISTOSOMIASIS
Mebendazole (Antiox)
Drug of choice: ` Whipworm, Pinworm, Hookworm, Roundworm Action: binds & interferes the synthesis of parasites microtublules and decreases glucose uptake ` Parasites are expelled in the feces Side effects: Abd pain, diarrhea
Pyrantel pamoate (Combatrin) Uses: Pinworm, Hookworm, Roundworm
Action: paralyzes the worm by depolarizing neuromucsular receptor of parasites ` Parasites are expelled in the feces Side effects: N/V, D
Albendazole (Albenza)
Dog tapeworm and pork tapeworm TERATOGENIC
Thiabendazole (Minthezol)
Uses: strongyloidiasis, trichinosis Action: microtubular aggregation Side effects: Steven-Johnson Syndrome
Niclosamide
Use: Cestodes
Common side effects: GI upset, dizziness, headache, drowsiness
Praziquantel (Biltricide)
Use: Schistosomiasis
1. 2. 3. 4.
5. 6. 7.
Collect stool specimen Obtain history of food intake & how the food was prepared Administer antihelminthics after meals or with food to reduce gastric upset Explain the importance of handwashing and proper hygiene; daily change & laundering of underwear, towels and bed linens, disinfection of toilet facilities Maintain nutrition Emphasize importance of taking prescribed drug at designated times and keeping HCP appointments Safety precautions
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Lecture6 Intro, Classification of ParasitesDokument38 SeitenLecture6 Intro, Classification of ParasitesJumar Villegas100% (1)
- Antiprotozoal AgentsDokument4 SeitenAntiprotozoal AgentsReem NurNoch keine Bewertungen
- Malaria Case Management Training Manual For Health Professionals in Ethiopia Participants ManualDokument200 SeitenMalaria Case Management Training Manual For Health Professionals in Ethiopia Participants ManualEleni HagosNoch keine Bewertungen
- DysenteryDokument9 SeitenDysenteryRifki HerdaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- PROTOZOADokument3 SeitenPROTOZOAMaria Jevica Barandon SolimanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Malaria FalciparumDokument35 SeitenMalaria FalciparumAboubakar Moalim Mahad moh'dNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fever with Chills and Rigors: A Case of MalariaDokument19 SeitenFever with Chills and Rigors: A Case of MalariaREETHUNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 12 Drugs, Microbes, The Elements of Chemotherapy: Building Your KnowledgeDokument12 SeitenChapter 12 Drugs, Microbes, The Elements of Chemotherapy: Building Your Knowledgemalenya1100% (1)
- Vaginitis: - Trichomoniasis - Vulvovaginal Candidiasis (VVC) - Bacterial Vaginosis (BV)Dokument94 SeitenVaginitis: - Trichomoniasis - Vulvovaginal Candidiasis (VVC) - Bacterial Vaginosis (BV)AileenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Malaria Drug PharmacologyDokument37 SeitenMalaria Drug PharmacologyShashidharan MenonNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Who Treatment Protocol For MalariaDokument18 SeitenThe Who Treatment Protocol For MalariatabletvodaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hiv Treatment: IC2 Haemato-Lymphoid and Tropical Medicine HLTM Dr. Eoghan de Barra 2014Dokument55 SeitenHiv Treatment: IC2 Haemato-Lymphoid and Tropical Medicine HLTM Dr. Eoghan de Barra 2014Faiq Syukri Bin SaparudinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Clinical Guidelines Diagnosis and Treatment Manual PDFDokument324 SeitenClinical Guidelines Diagnosis and Treatment Manual PDFBaba IsubNoch keine Bewertungen
- Antiprotozoal Drugs Classification and Mechanism of ActionDokument21 SeitenAntiprotozoal Drugs Classification and Mechanism of ActionCurex QANoch keine Bewertungen
- Infectious DiseaseDokument151 SeitenInfectious Diseasebolt boltNoch keine Bewertungen
- DR Romila Chimoriya Lecturer Department of Pediatrics: Acute Rheumatic FeverDokument27 SeitenDR Romila Chimoriya Lecturer Department of Pediatrics: Acute Rheumatic FeverDhiraj PantNoch keine Bewertungen
- AntiMalarial PharmDokument3 SeitenAntiMalarial PharmKartik ReddyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Antiprotozoal Agents 6Dokument29 SeitenAntiprotozoal Agents 6EinsteenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Magacyada Cudurada Iyo Waxa English Lagu Yiraahdo: Home Wararka Baargaal Maqaalo About Baargaal Nala Soo XiriirDokument6 SeitenMagacyada Cudurada Iyo Waxa English Lagu Yiraahdo: Home Wararka Baargaal Maqaalo About Baargaal Nala Soo Xiriircankawaab100% (1)
- Presented By:dr - Anita Chaudhari Roll No: 2Dokument22 SeitenPresented By:dr - Anita Chaudhari Roll No: 2younismushtaq100% (1)
- Vaginal Discharge Causes and TreatmentDokument47 SeitenVaginal Discharge Causes and TreatmentGladstone AsadNoch keine Bewertungen
- AscariasisDokument50 SeitenAscariasisAnaleah MalayaoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ventilator Associated Pneumonia (Vap)Dokument11 SeitenVentilator Associated Pneumonia (Vap)Suresh KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- K46 Pharmacology of Anthelminthics, Antiprotozoal, & Antimalaria (Farmakologi)Dokument78 SeitenK46 Pharmacology of Anthelminthics, Antiprotozoal, & Antimalaria (Farmakologi)ayapillaiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Findings of Fact & Conclusions of Law in Faber DecisionDokument184 SeitenFindings of Fact & Conclusions of Law in Faber DecisionLeslie RubinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Blood Tissue and FlagellatesDokument15 SeitenBlood Tissue and FlagellatesHughNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1.intro of EpidemiologyDokument30 Seiten1.intro of EpidemiologyMuhammad AsifNoch keine Bewertungen
- Phylum Platyhelminthes (Flatworms) : Important InformationDokument26 SeitenPhylum Platyhelminthes (Flatworms) : Important InformationYoussef EmadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Infectious Diseases in Pregnancy - 2005 Vol.32 Issues 3Dokument290 SeitenInfectious Diseases in Pregnancy - 2005 Vol.32 Issues 3Rickky Kurniawan,MDNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tropical Infectious Diseases PDFDokument1.788 SeitenTropical Infectious Diseases PDFMax Izarra Almonacid0% (1)
- Hiv Infection and AidsDokument51 SeitenHiv Infection and Aidspokhara gharipatanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Anne Gershon (Editor), Peter Hotez (Editor), Samuel Katz (Editor) - Krugman's Infectious Diseases of Children-Mosby, in PDFDokument2.854 SeitenAnne Gershon (Editor), Peter Hotez (Editor), Samuel Katz (Editor) - Krugman's Infectious Diseases of Children-Mosby, in PDFyudhoNoch keine Bewertungen
- MDR GNR PreventionDokument45 SeitenMDR GNR Preventiondjdiek100% (1)
- East Timor Antibiotic Guidelines Jan17 PRINT v3Dokument114 SeitenEast Timor Antibiotic Guidelines Jan17 PRINT v3Yoan Manuel Ruiz ArencibiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Entamoeba histolytica (True PathogenDokument112 SeitenEntamoeba histolytica (True PathogenMiaQuiambaoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cestoda: Dr. Hendra (Tropmed) Parasitology Department Medical Faculty of UnpriDokument42 SeitenCestoda: Dr. Hendra (Tropmed) Parasitology Department Medical Faculty of UnpriElvy ShaluNoch keine Bewertungen
- Vulvovaginal Candidiasis and Bacterial VaginosisDokument16 SeitenVulvovaginal Candidiasis and Bacterial VaginosisAdnanda Maulan100% (1)
- DVT Diagnostics ACCPDokument2 SeitenDVT Diagnostics ACCPKholil ElsirajNoch keine Bewertungen
- Managing Tuberculosis in PregnancyDokument1 SeiteManaging Tuberculosis in PregnancyAndi Tenri Ola Oddang IINoch keine Bewertungen
- UTIs Caused by Common PathogensDokument63 SeitenUTIs Caused by Common PathogensdeasyahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Emerging Infectious DiseasesDokument175 SeitenEmerging Infectious Diseasesmani100% (2)
- Hepatitis C: Immunology Lab ResearchDokument21 SeitenHepatitis C: Immunology Lab ResearchLeon LevyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Brucellosis: A Highly Contagious Zoonotic DiseaseDokument55 SeitenBrucellosis: A Highly Contagious Zoonotic Diseasesana shakeelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Carcinoma Rectum - Janak - NEWDokument74 SeitenCarcinoma Rectum - Janak - NEWTowhidulIslamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Scrub TyphusDokument2 SeitenScrub TyphusitsankurzNoch keine Bewertungen
- Scrub Typhus.Dokument27 SeitenScrub Typhus.tummalapalli venkateswara raoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Emetics and Antiemetics 2012 PDFDokument36 SeitenEmetics and Antiemetics 2012 PDFJamaluddin Ahmad A.M100% (2)
- Malaria 25 03 09Dokument131 SeitenMalaria 25 03 09Dr.Jagadish Nuchina100% (5)
- Antibiotic Stewardship PDFDokument11 SeitenAntibiotic Stewardship PDFujangNoch keine Bewertungen
- Prac PracDokument16 SeitenPrac PracIdkNoch keine Bewertungen
- Guildelines For Hiv Testing NacoDokument165 SeitenGuildelines For Hiv Testing NacoNagendra Singh BeniwalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hiv PPDokument37 SeitenHiv PPJitendra YadavNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pharmacogenomics: From Discovery to Clinical ImplementationVon EverandPharmacogenomics: From Discovery to Clinical ImplementationShowkat Ahmad GanieNoch keine Bewertungen
- Therapeutic Hypothermia - Principles, Indications, Practical ApplicationVon EverandTherapeutic Hypothermia - Principles, Indications, Practical ApplicationNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pathogenesis, Treatment and Prevention of LeishmaniasisVon EverandPathogenesis, Treatment and Prevention of LeishmaniasisMukesh SamantNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter - Iii Antimalarial, Antiprotozoal and Anthelmintic DrugsDokument28 SeitenChapter - Iii Antimalarial, Antiprotozoal and Anthelmintic DrugsNEHA DIXITNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pcol 2 Reporting Antiprotozoal DrugsDokument131 SeitenPcol 2 Reporting Antiprotozoal DrugsKIM PRIELANoch keine Bewertungen
- Farmakologi AntiprotozoaDokument32 SeitenFarmakologi AntiprotozoatriyantiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Antimalarial Drug CologyDokument15 SeitenAntimalarial Drug CologyManthan ChauhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Classification and Mechanism of Macrolides, Tetracyclines and FluoroquinolonesDokument28 SeitenClassification and Mechanism of Macrolides, Tetracyclines and FluoroquinolonesH.M. PiashNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nonfarmakologi Behaviour ManagementDokument23 SeitenNonfarmakologi Behaviour ManagementSilviana AzhariNoch keine Bewertungen
- Administration of Enema TechniquesDokument34 SeitenAdministration of Enema TechniquesVishalni Menon Returnz100% (2)
- A Case Study On Mrs Ec With Diabetes Mellitus 1615Dokument4 SeitenA Case Study On Mrs Ec With Diabetes Mellitus 1615Dauda Muize AdewaleNoch keine Bewertungen
- Suctioning The TracheostomyDokument16 SeitenSuctioning The TracheostomyJaily Mariano100% (1)
- HijamaDokument10 SeitenHijamaGendale Am-isNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 58 - Drugs Affecting Gastrointestinal MotilityDokument12 SeitenChapter 58 - Drugs Affecting Gastrointestinal MotilityJonathonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fpsyt 13 1049476Dokument12 SeitenFpsyt 13 1049476putriNoch keine Bewertungen
- 3 2.Msds Shell GTL Sarawax Sx50v1915072016gbDokument18 Seiten3 2.Msds Shell GTL Sarawax Sx50v1915072016gbArturo BLANCAS MARTINEZNoch keine Bewertungen
- Parkinson DiseaseDokument9 SeitenParkinson DiseaseMarco GunawanNoch keine Bewertungen
- AMC Recalls 2014Dokument99 SeitenAMC Recalls 2014saleema1175% (4)
- Epididymal CystDokument6 SeitenEpididymal CystShree Kumar MishraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Principles in Trauma ManagementDokument34 SeitenPrinciples in Trauma Managementvirz23Noch keine Bewertungen
- FOI Research On AcupunctureDokument118 SeitenFOI Research On AcupunctureDilutionsUKNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cartilage GraftsDokument30 SeitenCartilage GraftsDr.Zahida AkhtarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Vital SignsDokument8 SeitenVital SignsKenneth DayritNoch keine Bewertungen
- NAVLE Question of The DayDokument3 SeitenNAVLE Question of The DayJuneyoung Lee100% (2)
- Curriculum Vitae - Tripura KashyapDokument13 SeitenCurriculum Vitae - Tripura Kashyapdanceandmovement63Noch keine Bewertungen
- The Role of Physiotherapy in The Management of Functional Neurological Disorder in Children and AdolescentsDokument13 SeitenThe Role of Physiotherapy in The Management of Functional Neurological Disorder in Children and AdolescentsLIZETH MUnOZ SOLARTENoch keine Bewertungen
- Disease Prevention Primary Secondary TertiaryDokument1 SeiteDisease Prevention Primary Secondary TertiaryprogramgrabberNoch keine Bewertungen
- Stugeron® TabletsDokument3 SeitenStugeron® TabletsmahgadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biomechanical PrinciplesDokument84 SeitenBiomechanical PrinciplesbhongskirnNoch keine Bewertungen
- Abordaje Linfadenopatia PerifericaDokument13 SeitenAbordaje Linfadenopatia PerifericaTony Gomez Luna LeyvaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Treatment of Pregnancy-Related Lumbar and Pelvic Girdle Pain by The Yoga Method: A Randomized Controlled StudyDokument8 SeitenTreatment of Pregnancy-Related Lumbar and Pelvic Girdle Pain by The Yoga Method: A Randomized Controlled StudyJosephineeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ganga Action PlanDokument18 SeitenGanga Action PlanAjithEdathootNoch keine Bewertungen
- Potts DiseaseDokument8 SeitenPotts Diseaseaimeeros0% (2)
- KetamineDokument12 SeitenKetamineLuis Herbst100% (1)
- Sample Practicum InternPlanDokument5 SeitenSample Practicum InternPlanNadz GimeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Contoh Proposal Klinik Fisioterapi Di Puskesmas Jombatan JombangDokument4 SeitenContoh Proposal Klinik Fisioterapi Di Puskesmas Jombatan JombangLuqmanul HakimNoch keine Bewertungen
- Safety Data SheetDokument7 SeitenSafety Data SheettienNoch keine Bewertungen
- Adlerian Therapy Written ReportDokument3 SeitenAdlerian Therapy Written ReportEl Jhonna Duyag-MamaNoch keine Bewertungen