Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Accounting For Management
Hochgeladen von
Garima ThakurOriginalbeschreibung:
Originaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Accounting For Management
Hochgeladen von
Garima ThakurCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Amity Business School
Preparation of Final Accounts
Amity Business School
Final Accounts of a Company
A company needs to prepare its final accounts to ascertain the profit earned or loss suffered during the year and also the financial position of a business at the end of the year. For this purpose the company is preparing Final Accounts which is also known as Financial Statements. These include the following: 1. Trading Account 2. Profit and loss Account 3. Balance Sheet Trading Account: Trading Account is prepared to know the gross profit or gross loss arising or incurred as a result of the trading activities of a business. In other words, it is prepared to show the result of buying and selling of goods. The Trading Account shows the results of buying and selling of goods. In preparing this account, the general establishment charges are ignored and only the transactions in goods are included
Amity Business School
Need and Importance of Trading Account: It provides information about Gross Profit and Loss It provides information about the direct expenses Comparison of closing stock with those of previous year It provide safety against possible losses Preparation of Trading Account: Items written on the Dr. Side of Trading Account: Opening Stock Purchases and Purchases Return Direct Expenses, which includes Wages, Carriage inwards, Manufacturing expenses, Dock Charges, Import Duty, Excise Duty, Octroi, Royalty Items written on the Cr. Side of Trading Account: Sales and Sales Return Closing Stock
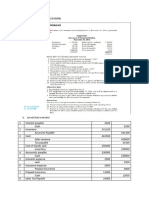
Form of Trading Account Trading A/c (For the year ended..) Particulars To Opening Stock To Purchases Less Purchase Return To wages To Wages & Salaries To Direct Expenses To Carriage To Carriage inwards To Gas, Fuel, and Power To Freight, Octroi and Cartage To Manufacturing Expenses To Factory Expenses To Dock Charges To Import Duty To Excise Duty To Royalty To Gross Profit (Transferred to P&L A/c) (Balancing Figure) Amount Particulars
Amity Business School
Amount
By Sales Less: Sales Return By Closing Stock By Gross Loss (Transferred to P&L A/c) (Balancing Figure)
Amity Business School
Prepare a Trading Account for the year ended 31 Dec 1993 from the following Balances:
Opening Stock Purchases Sales Freight and Octroi Wages Factory Lighting Coal, Gas and Water Purchase Return Sales Return Carriage on Purchase Carriage on Sales Factory Rent Office Rent Import Duty Closing Stock is valued at Rs. 60, 000 40, 000 2, 00, 000 5, 00, 000 6, 500 30, 000 10, 800 2, 200 12, 000 20, 000 8, 000 10, 000 12, 000 7, 500 32, 000
Amity Business School
Profit and Loss Account:
Trading account only discloses the gross profit earned as a result of buying and selling the goods. However, a businessman has to incur a number of expenses which are not taken to trading account. Hence a businessman is more interested in knowing the net profit earned or net loss incurred during the year. As such, a profit or loss account is prepared which contains all the items of losses and gains pertaining to the accounting period.
Form of Profit and Loss Account Profit and loss A/c (For the year ended..) Particulars To Gross Loss b/d (Transferred from Trading A/c) Office Expenses: To Salaries To Salaries and Wages To Rent, Rates & Taxes To Printing and Stationery To Postage & Telegram To Lighting To Insurance Premium To Telephone Charges To Legal Charges, Audit Fees To Traveling, Establishment Exp Selling and Distribution Exp. To Carriage Outwards To Advertisement, commission To Brokerage, Bad-Debts TO Export Duty, Packing Charges Miscellaneous Expenses: To Discount, Sales tax To Repairs, Depreciation, interest Exp To Bank Charges, Entertainment Exp To Conveyance Expenses Amount Particulars By Gross Profit b/d (Transferred from Trading A/c) By Rent from Tenants By Discount Received By Commission Received By interest on Investment By Dividend Received By Bad-Debts Recovered By profit on sale of assets By Net Loss (if any) (Transfd to Capital A/c)
Amity Business School
Amount
Amity Business School
Balance Sheet
The balance sheet (also called statement of financial position or statement of financial condition) is a snapshot of the financial status of an organization at a point in time.
Amity Business School
Need and Importance of Balance Sheet:
Ascertain the true financial position of a company Help in ascertaining the nature and cost of various assets of the business Help in determining the nature and amount of various liabilities of the business Gives information about amount of capital at year end and addition and deduction during the year Helps in finding whether the firm is solvent or insolvent Helps in preparing the opening entries at the beginning of the next year
Classification of Liabilities
Fixed or long-term liabilities Current or short-term liabilities Contingent Liabilities
Classification of Assets:
Fixed Assets Current Assets Liquid Assets Fictitious or Nominal Assets Wasting Assets Tangible and Intangible Assets
Liabilities Current Liabilities: Bank Overdraft Bills Payable Sundry Creditors Outstanding Expenses Unearned income Fixed Liabilities: Long Term loan Reserves Capital: Add : Net Profit Less : Drawings Less : Income Tax Less : Life insurance Premium
Form of Balance Sheet BALANCE SHEET (as on or as at..) Amount Assets
Amity Business School
Amount
Current Assets Cash in Hand Cash at Bank Bills Receivable Short term investment Sundry Debtors Closing Stock Prepaid Expenses Accrued Income Fixed Assets Furniture Loose Tools Motor Vehicle Long Term investments Plant and Machinery Land and Buildings Patents Goodwill
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Von EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Bewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (98)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeVon EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (5795)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeVon EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (537)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureVon EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (474)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceVon EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (588)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealVon EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (74)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryVon EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (231)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceVon EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (895)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItVon EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (838)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingVon EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (400)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersVon EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (345)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaVon EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (45)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnVon EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (234)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyVon EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (2259)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaVon EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (266)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerVon EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (271)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreVon EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Von EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Bewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesVon EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (821)
- Financial Reporting WDokument345 SeitenFinancial Reporting Wgordonomond2022Noch keine Bewertungen
- Inventory Cost Flow 1-4Dokument6 SeitenInventory Cost Flow 1-4Kailah CalinogNoch keine Bewertungen
- BBA203 Financial AccountingDokument3 SeitenBBA203 Financial AccountingRajdeep KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- ACC 124 - Week 1-3 QuizDokument14 SeitenACC 124 - Week 1-3 QuizJaneth BarreteNoch keine Bewertungen
- ACTREV 4 Business Combination 2019Dokument6 SeitenACTREV 4 Business Combination 2019Prom GloryNoch keine Bewertungen
- BFD NotesDokument84 SeitenBFD NotesFarukh NaveedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bharat Heavy Electricals Limited (BHEL) : June 2017Dokument38 SeitenBharat Heavy Electricals Limited (BHEL) : June 2017Sumit RoyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Annual Report of Rothschild Bank AG - 2008-2009Dokument64 SeitenAnnual Report of Rothschild Bank AG - 2008-2009Mossad NewsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Toyota & Honda Financial Ratios ComparisonDokument11 SeitenToyota & Honda Financial Ratios Comparisonuaintdown2100% (1)
- Araling Panlipunan: Quarter 3-Module 4 Ikalawang Yugto NG Kolonyalismo at ImperyalismoDokument18 SeitenAraling Panlipunan: Quarter 3-Module 4 Ikalawang Yugto NG Kolonyalismo at ImperyalismoKean Cleofas67% (3)
- Suzlon Energy Limited: Investor Presentation Q2, FY 2022-23Dokument25 SeitenSuzlon Energy Limited: Investor Presentation Q2, FY 2022-23Sathish JustinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Identify The IndustryDokument5 SeitenIdentify The IndustryLucas Dadone25% (4)
- DFNDFNDFNDFNDFDokument6 SeitenDFNDFNDFNDFNDFMohammad Ibnu LapaolaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Financial Statement Analysis For MBA StudentsDokument72 SeitenFinancial Statement Analysis For MBA StudentsMikaela Seminiano100% (1)
- This Study Resource WasDokument7 SeitenThis Study Resource Was수지Noch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 2 Financial Statement Analysis For StudentsDokument49 SeitenChapter 2 Financial Statement Analysis For StudentsRossetteDulinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ch10 - Soal Dan LatihanDokument29 SeitenCh10 - Soal Dan Latihanevelyn aleeza100% (3)
- Annual Report: Biafo Industries LimitedDokument61 SeitenAnnual Report: Biafo Industries LimitedjawadatatungNoch keine Bewertungen
- True" Car Rental LLCDokument35 SeitenTrue" Car Rental LLCHamza Malik100% (1)
- Nse Research Analysis 2020Dokument53 SeitenNse Research Analysis 2020Anuj ThapaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Exercises On Corporation FormationDokument6 SeitenExercises On Corporation FormationTommy AbrencilloNoch keine Bewertungen
- Financial Statement AnalysisDokument77 SeitenFinancial Statement AnalysisJebin Jacob100% (1)
- Erp Implementation of Ifrs For Smes: DissertationDokument68 SeitenErp Implementation of Ifrs For Smes: DissertationGaurav Kumar Kureel100% (1)
- PMBA PB6020 July2020 Cases Questions 23june2020Dokument24 SeitenPMBA PB6020 July2020 Cases Questions 23june2020Deepa GNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Cash Management in A Supper Market StoreDokument64 SeitenA Cash Management in A Supper Market Storechukwu solomon67% (3)
- FI-AA Post CapitalizationDokument5 SeitenFI-AA Post CapitalizationMinyongExpress VlogNoch keine Bewertungen
- HOBADokument20 SeitenHOBAJaira ClavoNoch keine Bewertungen
- 26 - LCCI L3 AC - Sep 2019 - ASE 20104 - MSDokument15 Seiten26 - LCCI L3 AC - Sep 2019 - ASE 20104 - MSKhin Zaw Htwe100% (6)
- Activity Review StatementDokument5 SeitenActivity Review Statementangel ciiiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Topic 6 - ACCA Cash Flow Q SDokument8 SeitenTopic 6 - ACCA Cash Flow Q SGeorge Wang100% (1)