Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Amity School of Business: BBA IV Semester Marketing Management II
Hochgeladen von
Anchit GautamOriginalbeschreibung:
Originaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Amity School of Business: BBA IV Semester Marketing Management II
Hochgeladen von
Anchit GautamCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Amity School of Business
Amity School of Business
BBA IV Semester Marketing Management II
Amity School of Business
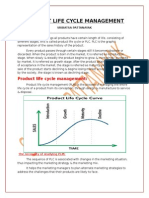
PRODUCT LIFE CYCLE
STAGES & STRATEGIES
Amity School of Business
Popularized by Theodore Levitt, 1965 PLC can be applied to: Product category (Watch) Product style (Digital) A product item/brand (Timex)
Amity School of Business
To say that a product has a life cycle is to assert four things: Product has a limited life Product sales pass through distinct stages, each posing different challenges, Opportunities, and problems to the seller Profits rise and fall at different stages of the product life cycle Products require different marketing, financial, manufacturing, purchasing and HR strategies in each stage
Amity School of Business
Sales and Profits (Rs) Sales
Profits Time Product Development Losses/ Investments (Rs) Introduction Growth Maturity Decline
Amity School of Business
INTRODUCTION STAGE Its a period of slow growth rate Profit is low or negative Promotional expenditure are high Prices tends to be high because costs are high
Amity School of Business
Strategies that can be pursued: Rapid skimming Slow skimming Rapid promotion Slow penetration Pioneer advantage
Amity School of Business
GROWTH STAGE
The salient features of the growth stage are: 1. Rapid climb in sales. 2. New competitors enter the market and introduce new produc thereby expanding distribution. 3. Prices almost remain the same. 4. Promotional expenditures remain the same. 5. Decline in Promotion-sales ratio. 6. Profits increase because of promotion. 7. Unit-manufacturing cost falls.
Strategies used at this stage
:
Amity School of Business
Sustain rapid market growth through 1. Improves product quality. 2. Add new features. 3. Enter new segments. 4. Increase distribution coverage. 5. Lower price to attract buyers.
Amity School of Business
MATURITY STAGE
The salient features are: 1. Sales growth will slow down. 2. This stage lasts longer. 3. Challenges to marketing management. 4. Overcapacity because of sales slow down. 5. Intense competition because of point 4 6. Increase advertising and R&D budgets. 7. Weaker competitors withdraw from the market. 8. Basic market drive is to increase market share. 9. Abandon weaker products and concentrate on profitable products.
Amity School of Business
MATURITY STAGE
Strategies A) Market modification B) Product modification and C) Marketing mix modification
Amity School of Business
A) Market modification: Now in order to expand the market volume the company follows the strategy formulated as Volume = number of brand users x usage rate per user
Expand the number of brand users by Trying to convert nonusers. Enter new market segments. Win competitors customers.
Amity School of Business
Expand Volume by Get the new customers to increase the usage. Interest users to use more of the product on each occasion. Try to discover new product uses and then convince people to use them.
Amity School of Business
B) Product modification: This can be done through 1.Improving quality This basically aims at increasing the products functional performance through durability, reliability, speed and taste.
2.Feature improvement Amity School of Business This aims at adding new features like size, weight, additives, accessories etc., this expands products versatility, safety and convenience. Advantages of the strategy: a) Builds companys image. b) Win loyalty of market segments. Disadvantage: a) Feature improvements are easily imitated. b) Needs first mover advantage. 3.Style improvement. This aims at increasing the products aesthetic appeal.
Amity School of Business
) Marketing mix modification This is done through asking question on certain marketing mi a) Prices: Would a cut attract new customers? Is it better to raise price to signal quality? b) Distribution: Can more outlets be penetrated? Can the company obtain more market support? c) Advertising: Should the expenditures be increased? Should the media mix be changed?
C
Amity School of Business
d) Sales promotion: Should we set up sales promotion? e) Personal selling: Should the number or quality of sales people be increased? Can we improve sales planning? f) Services: Can the company speed up the sales delivery. Can we extend more credit?
Amity School of Business
Characteristics Sales Costs Profits Customers Competitors Marketing Objectives Introduction Low Sales High -ve Innovators Few Create Product Awareness and trial Growth Rising sales Average Rising Early Adopters growing Maximize market share Maturity Peak sales Low High Middle Majority Stable Maximize market share while defending profit Decline Declining sales Low Declining Laggards Declining Reduce expenditure and milk brand.
Strategies Product
Offer a basic product
Offer product extensions, Diversify brands and service, warranty items.
Phase out weak models
Price
Charge cost-plus
Price to penetrate market Price to match or best competitors Build intensive distribution Build more intensive distribution system
Cut price
Distribution
Build selective distribution
Go selective: phase out unprofitable outlets
Advertising
Build product awareness among early adopters and dealers Use heavy sales promotion
Build awareness and interest in the mass market.
Stress brand differences and benefits
Reduce to level needed to retain hard core loyal
Sales promotion
Reduce to take advantage Increase to encourage of heave consumer brand switching demand
Reduce to minimal levels.
Amity School of Business
DECLINE STAGE
Profits erode (destroyed) Intense price cutting and many more products are withdrawn from the market Profits can be improved by reducing marketing spend and cost cutting
Amity School of Business
LIMITATIONS
PLC critiques: 1. The life cycle patterns are too variable in their shape and duration. 2. PLC lacks what living organisms have- namely, a fixed sequence of stages and a fixed length of each stage. 3. A product may appear mature when it has only reached a plateau before up-surge.
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Product Life Cycle & Marketing StrategiesDokument17 SeitenProduct Life Cycle & Marketing Strategiesakansha02Noch keine Bewertungen
- Product Life Cycle Stages & StrategiesDokument18 SeitenProduct Life Cycle Stages & StrategiesDolly ParhawkNoch keine Bewertungen
- Product Life Cycle Marketing StrategiesDokument15 SeitenProduct Life Cycle Marketing StrategiesDheeraj TiwariNoch keine Bewertungen
- Product Life Cycle & Marketing StrategiesDokument17 SeitenProduct Life Cycle & Marketing StrategiesAkshi BhagiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 11 Life Cycle StrategiesDokument7 Seiten11 Life Cycle StrategiesSarthak GuptaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Marketing StrategiesDokument41 SeitenMarketing StrategiesSairaj MohantyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Product Life Cycle - Vivek Singh - 169Dokument15 SeitenProduct Life Cycle - Vivek Singh - 1692007vivekNoch keine Bewertungen
- Product Life Cycle PPT PilotDokument13 SeitenProduct Life Cycle PPT Pilotadiba10mktNoch keine Bewertungen
- Product Life Cycle & Marketing StrategiesDokument16 SeitenProduct Life Cycle & Marketing StrategiessanjaysundayNoch keine Bewertungen
- To Say That A Product Has A Life Cycle Asserts Four ThingsDokument2 SeitenTo Say That A Product Has A Life Cycle Asserts Four ThingsamorviernesNoch keine Bewertungen
- PLC BasicDokument28 SeitenPLC BasicTwinkal chakradhariNoch keine Bewertungen
- MM Product Life-CycleDokument19 SeitenMM Product Life-Cycleabhishek00lohiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Product, Services, and Branding StrategiesDokument29 SeitenProduct, Services, and Branding StrategiesMd Alamgir HossainNoch keine Bewertungen
- Summary Sheet: Decline StageDokument4 SeitenSummary Sheet: Decline Stagekhurram_shehzad303Noch keine Bewertungen
- Strategy Product-PLCDokument19 SeitenStrategy Product-PLCKikiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Marketing Strategy and The Product LifeDokument23 SeitenMarketing Strategy and The Product LifeIsmatullah ZazaiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Model Answers On PBMDokument6 SeitenModel Answers On PBMJnanaranjan NayakNoch keine Bewertungen
- Describe The Stages of The Product Life Cycle and How Marketing Strategies Change During The Product Life Cycle?Dokument6 SeitenDescribe The Stages of The Product Life Cycle and How Marketing Strategies Change During The Product Life Cycle?Fassy ur RehmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Presented To: Ms. Rupali MadanDokument19 SeitenPresented To: Ms. Rupali MadanNeha BhograNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Product Life Cycle and New ProductsDokument86 SeitenThe Product Life Cycle and New Productssimran bhatiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Product Life Cycle StagesDokument21 SeitenProduct Life Cycle StagesTaukir KhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- You Should Answer Question 2 From The Below Text. You Must Give Example From Your Own. There Are Several Topics Sepereted by Lines.Dokument8 SeitenYou Should Answer Question 2 From The Below Text. You Must Give Example From Your Own. There Are Several Topics Sepereted by Lines.Mohammad Golam MostafaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Product Life CycleDokument14 SeitenProduct Life Cyclenikhil58555Noch keine Bewertungen
- Product Life Cycle: BY Arun Tripathi Abhishek Ojha Amrinder Singh BakshiDokument36 SeitenProduct Life Cycle: BY Arun Tripathi Abhishek Ojha Amrinder Singh Bakshiabhi9998Noch keine Bewertungen
- Adbms New ProductDokument23 SeitenAdbms New ProductPinkNoch keine Bewertungen
- Kotler On Marketing: Watch The Product Life CycleDokument18 SeitenKotler On Marketing: Watch The Product Life Cycleashwin saiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Session 12 and 13Dokument21 SeitenSession 12 and 13Kuldip BaravaliyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Product Life CycleDokument11 SeitenThe Product Life CycleamritabhosleNoch keine Bewertungen
- +3 Comm. MM - Unit - 3Dokument7 Seiten+3 Comm. MM - Unit - 3Rashmi Ranjan PanigrahiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Product Portfolio ManagementDokument22 SeitenProduct Portfolio ManagementAbhay Bajwa100% (1)
- Ch-12 Addressing Competition and Driving Growth: Product Life CycleDokument20 SeitenCh-12 Addressing Competition and Driving Growth: Product Life CycleAditya KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ch-12 Addressing Competition and Driving Growth: Product Life CycleDokument20 SeitenCh-12 Addressing Competition and Driving Growth: Product Life CycleAditya KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ch-12 Addressing Competition and Driving Growth: Product Life CycleDokument20 SeitenCh-12 Addressing Competition and Driving Growth: Product Life CycleAditya KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Presentation On Product Life Cycle (PLC) & Marketing Strategies by Dr.J.R.Das Associate Professor SOA UniversityDokument19 SeitenA Presentation On Product Life Cycle (PLC) & Marketing Strategies by Dr.J.R.Das Associate Professor SOA UniversitySantosh kumar sahooNoch keine Bewertungen
- New Product Development and Product Life-Cycle Strategies: Prof. Ahimpreet Jurrymarketing Managementpgp/Ss/2010-12//Sem1Dokument20 SeitenNew Product Development and Product Life-Cycle Strategies: Prof. Ahimpreet Jurrymarketing Managementpgp/Ss/2010-12//Sem1vishakha_rm2000Noch keine Bewertungen
- Product Lifecycle: 1. Introduction StageDokument3 SeitenProduct Lifecycle: 1. Introduction StageLinensia KanyembaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Competitive Dynamics: D4 Manajemen Pemasaran Fakultas Ekonomi Universitas Negeri YogyakartaDokument16 SeitenCompetitive Dynamics: D4 Manajemen Pemasaran Fakultas Ekonomi Universitas Negeri Yogyakarta08. fidyana rizkyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Product Life Cycle AnswerDokument5 SeitenProduct Life Cycle AnswerRituNoch keine Bewertungen
- PDT Life CycleDokument15 SeitenPDT Life CycleBhumika SharmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Product Life Cycle ManagementDokument11 SeitenProduct Life Cycle ManagementmsmgectNoch keine Bewertungen
- Marketing Management IDokument10 SeitenMarketing Management IDamodar SharmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- New-Product Development and Product Life-Cycle StrategiesDokument37 SeitenNew-Product Development and Product Life-Cycle StrategiesHusnain Usman KhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- CH.9. New Product Development and PLCDokument21 SeitenCH.9. New Product Development and PLCDina Abdelaziz EltaweelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Amity Business SchoolDokument26 SeitenAmity Business SchoolAnonymous GVWIlk3ZNoch keine Bewertungen
- Session 5 - PLCDokument11 SeitenSession 5 - PLCShameel JavedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 6 MKTGDokument35 SeitenChapter 6 MKTGpviñezaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assignment On Marketing ManagementDokument29 SeitenAssignment On Marketing Managementdiplococcous90% (10)
- The Product Life CycleDokument3 SeitenThe Product Life Cyclechowa fellonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Product Life CycleDokument13 SeitenProduct Life Cycleadiba10mktNoch keine Bewertungen
- Product Life Cycle FinalDokument27 SeitenProduct Life Cycle FinalPrathamesh Gawade100% (1)
- Product Life Cycle and Marketing StrategiesDokument4 SeitenProduct Life Cycle and Marketing StrategiesManju KeerthiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Market Share, Intensive & Integrative StrategiesDokument10 SeitenMarket Share, Intensive & Integrative StrategiesAyush VarshneyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Kotler On Marketing: Watch The Product Life Cycle But More Important, Watch The Market Life CycleDokument16 SeitenKotler On Marketing: Watch The Product Life Cycle But More Important, Watch The Market Life CycleDinesh RaghavendraNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Product Life CycleDokument10 SeitenThe Product Life CycleZer GuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Product Life Cycle Topic Summary and The Brita Product Company Case Analysis - Group 9Dokument4 SeitenProduct Life Cycle Topic Summary and The Brita Product Company Case Analysis - Group 9Himanshu AgrawalNoch keine Bewertungen
- NPD N PLCDokument40 SeitenNPD N PLCShivam TrivediNoch keine Bewertungen
- New-Product Development and Product Life-Cycle StrategiesDokument24 SeitenNew-Product Development and Product Life-Cycle StrategiesKamran AzizNoch keine Bewertungen
- Big Picture Strategy: The Six Choices That Will Transform Your BusinessVon EverandBig Picture Strategy: The Six Choices That Will Transform Your BusinessNoch keine Bewertungen
- Overcoming Sales Growth Obstructions : Avoid Common Mistakes and Increase Your SalesVon EverandOvercoming Sales Growth Obstructions : Avoid Common Mistakes and Increase Your SalesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sales Promotion: All the tactics you need to turn an outbound prospect into a customerVon EverandSales Promotion: All the tactics you need to turn an outbound prospect into a customerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Understanding Marketing Management Within Global ContextDokument10 SeitenUnderstanding Marketing Management Within Global ContextShiela Mae ArcuenoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Marketing Management: Culinarian Cookware AssignmentDokument5 SeitenMarketing Management: Culinarian Cookware AssignmentrizqighaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fundamentals of Marketing Sylabus 2022 - 2 Oct.10th 2022Dokument6 SeitenFundamentals of Marketing Sylabus 2022 - 2 Oct.10th 2022sofiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Marketing Management Course OutlineDokument3 SeitenMarketing Management Course Outlineabraha gebruNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lunar International CollegeDokument9 SeitenLunar International Collegesimeneh getinetNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Impact of Marketing Strategy On Profitability in Medical Jordanian CorporationsDokument8 SeitenThe Impact of Marketing Strategy On Profitability in Medical Jordanian CorporationsMbeeNoch keine Bewertungen
- MKTG Session 1 PDFDokument42 SeitenMKTG Session 1 PDFSiddhartha AgarwalNoch keine Bewertungen
- L2-Bus 204 PDFDokument13 SeitenL2-Bus 204 PDFBeka GideonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Difference Between Marketing and Sales ManagementDokument6 SeitenDifference Between Marketing and Sales ManagementAdi PatelNoch keine Bewertungen
- NMIMS Masters 1Dokument30 SeitenNMIMS Masters 1Sameer BeheraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Marketing ManagementDokument390 SeitenMarketing ManagementFotini Diafa100% (3)
- Kotler Pom15 Im 03Dokument26 SeitenKotler Pom15 Im 03Muhammad Umair100% (2)
- S&D Group 1 Assignment CDokument9 SeitenS&D Group 1 Assignment Cm omprakashNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 2 - Practice: Quiz 0Dokument3 SeitenUnit 2 - Practice: Quiz 0Senthil Kumar GanesanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mba6101: Business Economics Mba6101: Business Economics Mba6101: Business Economics Mba6101: Business EconomicsDokument4 SeitenMba6101: Business Economics Mba6101: Business Economics Mba6101: Business Economics Mba6101: Business EconomicsDeepak ToniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pankajakasthuri Herbals PVT LTDDokument87 SeitenPankajakasthuri Herbals PVT LTDArun Padmakumar100% (6)
- Scheme of Work Mkt646Dokument5 SeitenScheme of Work Mkt646Micheal PruittNoch keine Bewertungen
- Full Download Preface To Marketing Management 15th Edition Peter Test BankDokument35 SeitenFull Download Preface To Marketing Management 15th Edition Peter Test Banksillskarylus100% (40)
- Himanshu's ResumeDokument4 SeitenHimanshu's ResumeK L AutomobilesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Kotler MM 14e 01 IpptDokument35 SeitenKotler MM 14e 01 IpptAbdul Subhan AbbasiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Spring 2023 - MGT501 - 1Dokument3 SeitenSpring 2023 - MGT501 - 1Usman AliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Syllabus Grad SchoolDokument3 SeitenSyllabus Grad SchoolAnonymous Uya1CUAqjNoch keine Bewertungen
- Customer Relationship Management (CRM) Is A ManagementDokument59 SeitenCustomer Relationship Management (CRM) Is A Managementhi2sam007Noch keine Bewertungen
- Mangold & Faulds 2009 - Social MediaDokument9 SeitenMangold & Faulds 2009 - Social MediaMadalina Elena100% (1)
- MARketing PlanDokument13 SeitenMARketing PlanIshmit Oberoi22% (9)
- Principles of Marketing Kotler 15th Edition Solutions ManualDokument32 SeitenPrinciples of Marketing Kotler 15th Edition Solutions ManualShannon Young100% (33)
- Marketing ManagementDokument23 SeitenMarketing ManagementandhakannanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Malabar Fruit Products Company: A Project Report On Organizational Study atDokument43 SeitenMalabar Fruit Products Company: A Project Report On Organizational Study atAnees SalihNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chhattisgarh Swami Vivekanand Technical Syllabus of Mba 3 SemDokument61 SeitenChhattisgarh Swami Vivekanand Technical Syllabus of Mba 3 SemSurbhi ChauhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Welingkar's Prospectus - PGDM Proof-CompressedDokument12 SeitenWelingkar's Prospectus - PGDM Proof-CompressedPriteshNoch keine Bewertungen