Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Economics For Managers - Session 13
Hochgeladen von
Abimanyu NNCopyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Economics For Managers - Session 13
Hochgeladen von
Abimanyu NNCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
ECONOMICS FOR MANAGERS
PSG INSTITUTE OF MANAGEMENT MBA 2011-13 BATCH I Trimester
Session XIII- For Batch C and D Markets and Competition- Monopolistic Competition
1 EFM faculty P.Uday Shankar 26/09/11
What is Monopolistic Competition ?
Pure monopoly and perfect competition are two extreme cases of market structure. In reality, there are markets having large number of producers competing with each other in order to sell their product in the market. Thus, there is monopoly on one hand and perfect competition on other hand. Such a mixture of monopoly and perfect competition is called as monopolistic competition. It is a case of imperfect competition. The credit of introducing Monopolistic Competition goes to American Economist Prof. Edward Chamberlin, who had described it in his book 'Theory of Monopolistic Competition' published in 1933.
2 EFM faculty P.Uday Shankar 26/09/11
What is Monopolistic Competition?
As the name monopolistic competition suggests, the industry shares characteristics of both a perfectly competitive industry and a monopoly. Like perfect competition, a monopolistic competitive industry has many firms, or if there are not many firms, there are at least many competing products that are almost identical in nature. Consider the Laptop industry. There are several major producers of Laptops (e.g. Toshiba, HP, DELL, ACER, HCL) and each produces a laptop and many other variations that can fit the consumers desire. In addition, there are a good number of smaller specialty brands that produce laptops such as Apple. EFM faculty P.Uday Shankar 26/09/11
Monopolistic Competition- Characteristics
No.of sellers: There are large number of sellers producing differentiated products. So, competition among them is very keen. Since number of sellers is large, each seller produces a very small part of market supply. So no seller is in a position to control price of product. Every firm is limited in its size. 2. No.of buyers: They are also large in number and have a the choice of a variety of substitutes of a product. 3. Product Differentiation: It is one of the most important features of monopolistic competition. In perfect competition, products are homogeneous in nature. On the contrary, here, every producer tries to keep his product dissimilar than his rival's product in order to maintain his separate identity. This boosts up the competition in market. So, every firm acquires some monopoly power. EFM faculty P.Uday Shankar 26/09/11
1.
Monopolistic Competition- Characteristics
4. Freedom of Entry and Exit: There are minimal barriers
to entry of sellers. The goods and services produced are easy to replicate by other firms that represent potential competition. If economic profits are present, new firms will enter into the industry. Entry of new firms happens mostly in the long run. 5. Selling Cost: It is a unique feature of monopolistic competition. In such type of market, due to product differentiation, every firm has to incur some additional expenditure in the form of selling cost. This cost includes sales promotion expenses, advertisement expenses, salaries of marketing staff, etc. But on account of homogeneous product in perfect competition and zero competition in monopoly, selling cost does not exist there. 6. Interdependence among sellers: Large numbers of firms
5
are different in their size. Each firm has its own production and marketing policy. So no firm is influenced by other firm. EFM faculty P.Uday Shankar 26/09/11 All are independent.
Monopolistic Competition- Characteristics
7. Demand Curve: In monopolistic competition, a firm is facing downward sloping demand curve i.e. elastic demand curve. It means one can sell more at lower price and vice versa. 8. Behaviour in a Short Run: Firms in monopolistic competition can behave like monopolies in the short run by having considerable market power to generate profit. 9. Behaviour in the Long Run: In the long run new firms enter the market and the benefits of differentiation (which existed during the short run) decrease with the competition. The market then behaves more like in the perfect competition where firms cannot gain economic profit. 10. Behaviour of the Consumer: If consumers lack rationality and innovativeness in choosing the products and if heuristics is required to determine consumer choice the market will fall under natural monopoly (in the absence of government regulation/control).
6 EFM faculty P.Uday Shankar 26/09/11
Monopolistic Competition- Characteristics
11. Competition: There exists a two dimensional
competition. Price competition i.e. firms compete with each other on the basis of price. Non price competition i.e. firms compete on the basis of brand, product quality advertisement.
EFM faculty P.Uday Shankar
26/09/11
Monopolistic Competition- Short Run Profits
EFM faculty P.Uday Shankar
26/09/11
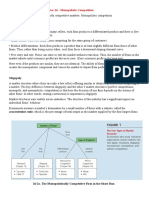
Monopolistic Competition- Short Run Profits
The above figure shows the short run behavior of the monopolistically competitive firm. As in the case of a perfectly competitive firm or a monopoly, the monopolistically competitive firm produces at a profit maximizing level of output where marginal cost equals marginal revenue (Point A). The firm finds the price it will charge customers at the profit maximizing level of output (Q*) from the demand curve at Point B, and sets price to P*. As we can see from the shaded region, the firm is earning economic profits since price exceeds average total cost at the profit maximizing level of output.
9 EFM faculty P.Uday Shankar 26/09/11
Monopolistic Competition- Short Run Profit and Loss
10
EFM faculty P.Uday Shankar
26/09/11
Monopolistic Competition- Long Run
11
EFM faculty P.Uday Shankar
26/09/11
Monopolistic Competition- Long Run
12
Unlike a monopoly industry, new firms can enter the monopolistically competitive industry. And like a perfectly competitive industry, economic profits attract new firms seeking a share of those profits into the industry. The long run outcome for the monopolistically competitive firm is zero economic profits. This is shown in the figure above. Demand shrinks from D0 to D1 eventually settling at a point where the demand curve is tangent to the average total cost curve, resulting in zero economic profits (Point B). Note that the marginal revenue and marginal cost curves are excluded from the figure to EFM faculty P.Uday presentation clearer. make the Shankar 26/09/11
Monopolistic Competition- Long Run
13
As we can see from the figure above, unlike a perfectly competitive firm that produces at the minimum point of its average total cost curve and where price equals marginal cost, the monopolistically competitive firm does not produce at an economically efficient point in the long run. This does not mean to say that monopolistic competition is undesirable in comparison to perfect competition. Consumers value choice, and monopolistic competition offers variety in good or service. In contrast, perfectly competitive firms produce a generic, homogenous product offers consumers no EFM faculty differences. 26/09/11 productP.Uday Shankar
Monopolistic Competition- Long Run
Monopolistic competition also encourages continuous product innovation. Innovative firms that introduce new or better products gain an edge, increase market share and can realize extra profits while their competitors attempt to catch up. A key to success for many firms in monopolistically competitive industries, especially in the information technology area, is constant innovation to maintain and expand market share.
14
EFM faculty P.Uday Shankar
26/09/11
Thanks
http://spot.colorado.edu Thanks for the graphs and material.
15
EFM faculty P.Uday Shankar
26/09/11
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Porter's Five Forces: Understand competitive forces and stay ahead of the competitionVon EverandPorter's Five Forces: Understand competitive forces and stay ahead of the competitionBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (10)
- Monopolistic CompetitionDokument17 SeitenMonopolistic CompetitionAlok ShuklaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Monopolistic Competition: A Microeconomic AnalysisDokument20 SeitenMonopolistic Competition: A Microeconomic AnalysisTarif HaqueNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Market Makers (Review and Analysis of Spluber's Book)Von EverandThe Market Makers (Review and Analysis of Spluber's Book)Noch keine Bewertungen
- Resume of Principles of Economics Chapter on Firms in Competitive MarketsDokument4 SeitenResume of Principles of Economics Chapter on Firms in Competitive MarketsWanda AuliaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 8 - Managing in Competitive, Monopolistic, and Monopolistically Competitive MarketsDokument6 Seiten8 - Managing in Competitive, Monopolistic, and Monopolistically Competitive MarketsMikkoNoch keine Bewertungen
- What Is Monopolistic CompetitionDokument9 SeitenWhat Is Monopolistic CompetitionParag BorleNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture Chapter6Dokument7 SeitenLecture Chapter6Angelica Joy ManaoisNoch keine Bewertungen
- Eco Assignment 2Dokument7 SeitenEco Assignment 2prabhat kumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Monopolistic CompetitionDokument3 SeitenMonopolistic Competitionjoshcastv27Noch keine Bewertungen
- Economics For Managers - Session 12Dokument27 SeitenEconomics For Managers - Session 12Abimanyu NNNoch keine Bewertungen
- Monopolistic Competition and Product DifferentiationDokument18 SeitenMonopolistic Competition and Product DifferentiationSurya PanwarNoch keine Bewertungen
- What Is Economics?Dokument10 SeitenWhat Is Economics?Abdulrahman AlyousifNoch keine Bewertungen
- COMPETITION AND DIFFERENTIATED PRODUCTSDokument19 SeitenCOMPETITION AND DIFFERENTIATED PRODUCTSPowli HarshavardhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- 7 Most Important Features of Monopolistic CompetitionDokument11 Seiten7 Most Important Features of Monopolistic CompetitionLopez guerreroNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 9Dokument16 SeitenChapter 9BenjaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assignment - Market StructureDokument5 SeitenAssignment - Market Structurerhizelle19Noch keine Bewertungen
- Chap011 RevDokument12 SeitenChap011 RevBlackbubbleNoch keine Bewertungen
- Monopolistic Competition:: Large Number of Small FirmsDokument7 SeitenMonopolistic Competition:: Large Number of Small FirmsSohaib SangiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Essentials of Economics 3rd Edition Brue Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFDokument32 SeitenEssentials of Economics 3rd Edition Brue Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFgwennhungnzvmo100% (14)
- AAU Micro II ModuleDokument245 SeitenAAU Micro II Moduleyiho83% (6)
- Subject-Business Economics Project Report On Different MarketsDokument5 SeitenSubject-Business Economics Project Report On Different MarketsMegha PatelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit III Monopolistic CompitionDokument6 SeitenUnit III Monopolistic CompitionPrashant ShahaneNoch keine Bewertungen
- Monopolistic Competition and OligopolyDokument94 SeitenMonopolistic Competition and OligopolyVardaanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Monopolistic CompetitionDokument12 SeitenMonopolistic CompetitionMishika AdwaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- EconomicsDokument2 SeitenEconomicsIrish Mae T. EspallardoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Economics AssignmentDokument4 SeitenEconomics AssignmentFarman RazaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1.5.monopolistic CompetitionDokument13 Seiten1.5.monopolistic CompetitionManhin Bryan KoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Solution Manualch13Dokument33 SeitenSolution Manualch13StoneCold Alex Mochan80% (5)
- ME. MonopolisticDokument141 SeitenME. MonopolisticAndrewson BautistaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Micro 7 and 8Dokument36 SeitenMicro 7 and 8amanuelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Microeconomics-II - Ch-2-Monopolistic Competition-1Dokument23 SeitenMicroeconomics-II - Ch-2-Monopolistic Competition-1Mustefa UsmaelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Monopolistic CompetitionDokument5 SeitenMonopolistic CompetitionSyed BabrakNoch keine Bewertungen
- Astu Micro II ModuleDokument247 SeitenAstu Micro II Modulezemede zelekeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 16 - MicroeconomicsDokument9 SeitenChapter 16 - MicroeconomicsFidan MehdizadəNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 4 CC 4 PDFDokument49 SeitenUnit 4 CC 4 PDFKamlesh AgrawalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Study Questions (Final Exam)Dokument7 SeitenStudy Questions (Final Exam)Ashley Ann StocktonNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Market Structure Characterized by A Large Number of Small FirmsDokument9 SeitenA Market Structure Characterized by A Large Number of Small FirmsSurya PanwarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pure CompetitionDokument7 SeitenPure CompetitionEricka TorresNoch keine Bewertungen
- Monopolistic Competition: Registration For Wikiconference India 2011, Mumbai Is Now OpenDokument6 SeitenMonopolistic Competition: Registration For Wikiconference India 2011, Mumbai Is Now Openakhilthambi123Noch keine Bewertungen
- Chap 8 - Managing in Competitive, Monopolistic, and Monopolistically Competitive MarketsDokument48 SeitenChap 8 - Managing in Competitive, Monopolistic, and Monopolistically Competitive MarketsjeankerlensNoch keine Bewertungen
- Oligopoly Market StructureDokument3 SeitenOligopoly Market StructureJulie ann YbanezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 7 Market Structures Teacher NotesDokument10 SeitenChapter 7 Market Structures Teacher Notesresendizalexander05Noch keine Bewertungen
- Summary Chapter 8,9 Keat N YoungDokument7 SeitenSummary Chapter 8,9 Keat N YoungIqbal Faisal AkhmadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chap 8-Monopolistic CompetitionDokument2 SeitenChap 8-Monopolistic CompetitionrnjugunaNoch keine Bewertungen
- (A) Oligopoly What Is Oligopoly?: University of London International ProgrammesDokument10 Seiten(A) Oligopoly What Is Oligopoly?: University of London International ProgrammesVivian LeeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Monopolistically CompetitiveDokument26 SeitenMonopolistically Competitivebeth el100% (1)
- Chap10 Monopolistic Competition 11.05.2021Dokument17 SeitenChap10 Monopolistic Competition 11.05.2021CIELICA BURCANoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter Two: Monopolistic Competition MarketDokument36 SeitenChapter Two: Monopolistic Competition MarketSitra AbduNoch keine Bewertungen
- Monopolistic CompetitionDokument25 SeitenMonopolistic Competitionmurthy2009Noch keine Bewertungen
- Define Monopoly and Its Characteristics With Examples Final PawanDokument5 SeitenDefine Monopoly and Its Characteristics With Examples Final PawanPawan KhatriNoch keine Bewertungen
- E. Break-Even PointDokument2 SeitenE. Break-Even PointMarfe BlancoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Market Pricing StrategiesDokument23 SeitenMarket Pricing StrategiesPikki LovarajuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture 12 - Chapter 16 - Monopolistic CompetitionDokument21 SeitenLecture 12 - Chapter 16 - Monopolistic Competitionvuquangtruong13122002Noch keine Bewertungen
- Micro Ch179PresentationDokument25 SeitenMicro Ch179Presentationfoz100% (1)
- Monopolistic Competition Is A Form ofDokument8 SeitenMonopolistic Competition Is A Form ofjcipriano_1Noch keine Bewertungen
- Economics For Managers - Session 14Dokument26 SeitenEconomics For Managers - Session 14Abimanyu NNNoch keine Bewertungen
- Market Structures by Dedicatoria, Intino, VillaramaDokument14 SeitenMarket Structures by Dedicatoria, Intino, VillaramaAlpha CapacitorNoch keine Bewertungen
- Micro Ch17 PresentationDokument24 SeitenMicro Ch17 PresentationErsin TukenmezNoch keine Bewertungen
- SI Mills AssociationDokument1 SeiteSI Mills AssociationAbimanyu NNNoch keine Bewertungen
- Stationaries in South AfricaDokument15 SeitenStationaries in South AfricaAbimanyu NNNoch keine Bewertungen
- Scanned Mark Sheets PDFDokument21 SeitenScanned Mark Sheets PDFAbimanyu NNNoch keine Bewertungen
- News ClippingsDokument1 SeiteNews ClippingsAbimanyu NNNoch keine Bewertungen
- MC - ReportDokument13 SeitenMC - ReportAbimanyu NNNoch keine Bewertungen
- Heart of ChangeDokument63 SeitenHeart of ChangeAbimanyu NN100% (4)
- ComplianceDokument2 SeitenComplianceAbimanyu NNNoch keine Bewertungen
- Employees Provident Fund OrganizationDokument2 SeitenEmployees Provident Fund OrganizationAbimanyu NNNoch keine Bewertungen
- Southern Indian Mills AssociationDokument5 SeitenSouthern Indian Mills AssociationAbimanyu NNNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hurconomic SDokument16 SeitenHurconomic SAbimanyu NNNoch keine Bewertungen
- Asia and The Pacific On The Move: Workers and Refugees, A Challenge To Nation StatesDokument16 SeitenAsia and The Pacific On The Move: Workers and Refugees, A Challenge To Nation StatesAbimanyu NNNoch keine Bewertungen
- Persuasive Communication - Ineffective AdvertisementDokument7 SeitenPersuasive Communication - Ineffective AdvertisementAbimanyu NNNoch keine Bewertungen
- Psgim CV - AbimanyuDokument3 SeitenPsgim CV - AbimanyuAbimanyu NNNoch keine Bewertungen
- National Culture in Organization DevelopmentDokument26 SeitenNational Culture in Organization DevelopmentAbimanyu NNNoch keine Bewertungen
- USA - An AnalysisDokument84 SeitenUSA - An AnalysisAbimanyu NNNoch keine Bewertungen
- Presentation On Nokia Transportation Feasibility StudyDokument53 SeitenPresentation On Nokia Transportation Feasibility StudyAbimanyu NNNoch keine Bewertungen
- Arun Case StudyDokument20 SeitenArun Case StudyAnmol VermaNoch keine Bewertungen
- TISCODokument15 SeitenTISCOAbimanyu NNNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bible and HRMDokument17 SeitenBible and HRMAbimanyu NN100% (10)
- Economics For Managers - Session 18Dokument14 SeitenEconomics For Managers - Session 18Abimanyu NNNoch keine Bewertungen
- Performance Review & CounselingDokument17 SeitenPerformance Review & CounselingAbimanyu NNNoch keine Bewertungen
- HRM Project - HR InterviewDokument42 SeitenHRM Project - HR InterviewAbimanyu NNNoch keine Bewertungen
- Economics For Managers - Session 07Dokument10 SeitenEconomics For Managers - Session 07Abimanyu NNNoch keine Bewertungen
- 11AC01 - Video Presentation - Organ DonationDokument12 Seiten11AC01 - Video Presentation - Organ DonationAbimanyu NN0% (1)
- Economics of Petroleum As A Natural ResourceDokument14 SeitenEconomics of Petroleum As A Natural ResourceAbimanyu NNNoch keine Bewertungen
- Economics For Managers - Session 17Dokument13 SeitenEconomics For Managers - Session 17Abimanyu NNNoch keine Bewertungen
- Economics For Managers - Session 16Dokument8 SeitenEconomics For Managers - Session 16Abimanyu NNNoch keine Bewertungen
- Economics For Managers - Session 14Dokument26 SeitenEconomics For Managers - Session 14Abimanyu NNNoch keine Bewertungen
- Economics For Managers - Session 15Dokument20 SeitenEconomics For Managers - Session 15Abimanyu NNNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1 Minute Witness PDFDokument8 Seiten1 Minute Witness PDFMark Aldwin LopezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Easy Gluten Free RecipesDokument90 SeitenEasy Gluten Free RecipesBrandon Schmid100% (1)
- Das Aufkommen Eines Neuen Pseudoephedrinprodukts Zur Bekämpfung Des MethamphetaminmissbrauchsDokument17 SeitenDas Aufkommen Eines Neuen Pseudoephedrinprodukts Zur Bekämpfung Des Methamphetaminmissbrauchszossel ringoNoch keine Bewertungen
- DC Rebirth Reading Order 20180704Dokument43 SeitenDC Rebirth Reading Order 20180704Michael MillerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pharmacology of GingerDokument24 SeitenPharmacology of GingerArkene LevyNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1995 - Legacy SystemsDokument5 Seiten1995 - Legacy SystemsJosé MªNoch keine Bewertungen
- 52 Codes For Conscious Self EvolutionDokument35 Seiten52 Codes For Conscious Self EvolutionSorina LutasNoch keine Bewertungen
- GEA 1000 Tutorial 1 SolutionDokument12 SeitenGEA 1000 Tutorial 1 SolutionAudryn LeeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Financial Accounting & ReportingDokument4 SeitenFinancial Accounting & Reportingkulpreet_20080% (1)
- Bach Invention No9 in F Minor - pdf845725625Dokument2 SeitenBach Invention No9 in F Minor - pdf845725625ArocatrumpetNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mechanics of Solids Unit - I: Chadalawada Ramanamma Engineering CollegeDokument1 SeiteMechanics of Solids Unit - I: Chadalawada Ramanamma Engineering CollegeMITTA NARESH BABUNoch keine Bewertungen
- Extra Grammar Exercises (Unit 6, Page 64) : Top Notch 3, Third EditionDokument4 SeitenExtra Grammar Exercises (Unit 6, Page 64) : Top Notch 3, Third EditionA2020Noch keine Bewertungen
- Work, Energy and Power: Checkpoint 1 (p.194)Dokument12 SeitenWork, Energy and Power: Checkpoint 1 (p.194)U KILLED MY DOGNoch keine Bewertungen
- How Should Management Be Structured British English StudentDokument7 SeitenHow Should Management Be Structured British English Studentr i s uNoch keine Bewertungen
- The 4Ps of Labor: Passenger, Passageway, Powers, and PlacentaDokument4 SeitenThe 4Ps of Labor: Passenger, Passageway, Powers, and PlacentaMENDIETA, JACQUELINE V.Noch keine Bewertungen
- Fundamentals of Analytics in Practice /TITLEDokument43 SeitenFundamentals of Analytics in Practice /TITLEAcad ProgrammerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Krittika Takiar PDFDokument2 SeitenKrittika Takiar PDFSudhakar TomarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Synthesis of The ArtDokument2 SeitenSynthesis of The ArtPiolo Vincent Fernandez100% (1)
- Configure Initial ISAM Network SettingsDokument4 SeitenConfigure Initial ISAM Network SettingsnelusabieNoch keine Bewertungen
- Destination Management OverviewDokument5 SeitenDestination Management OverviewMd. Mamun Hasan BiddutNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rebekah Hoeger ResumeDokument1 SeiteRebekah Hoeger ResumerebekahhoegerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Foundations of Public Policy AnalysisDokument20 SeitenFoundations of Public Policy AnalysisSimran100% (1)
- CH 2 Short Questions IXDokument2 SeitenCH 2 Short Questions IXLEGEND REHMAN OPNoch keine Bewertungen
- Eng9 - Q3 - M4 - W4 - Interpret The Message Conveyed in A Poster - V5Dokument19 SeitenEng9 - Q3 - M4 - W4 - Interpret The Message Conveyed in A Poster - V5FITZ100% (1)
- A Random-Walk-Down-Wall-Street-Malkiel-En-2834 PDFDokument5 SeitenA Random-Walk-Down-Wall-Street-Malkiel-En-2834 PDFTim100% (1)
- VT JCXDokument35 SeitenVT JCXAkshay WingriderNoch keine Bewertungen
- Causes of WWI: Alliances, Militarism & AssassinationDokument4 SeitenCauses of WWI: Alliances, Militarism & AssassinationJoshua De Leon TuasonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Accounting Notes - 1Dokument55 SeitenAccounting Notes - 1Rahim MashaalNoch keine Bewertungen
- 6 Lesson Writing Unit: Personal Recount For Grade 3 SEI, WIDA Level 2 Writing Kelsie Drown Boston CollegeDokument17 Seiten6 Lesson Writing Unit: Personal Recount For Grade 3 SEI, WIDA Level 2 Writing Kelsie Drown Boston Collegeapi-498419042Noch keine Bewertungen
- Mixed-Use Proposal Dormitory and Hotel High-RiseDokument14 SeitenMixed-Use Proposal Dormitory and Hotel High-RiseShanaia BualNoch keine Bewertungen