Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Project Sample
Hochgeladen von
api-37986400 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
168 Ansichten11 SeitenProject management in today's environment rapid change BPR The project plan management and communications Organizational, people, political issues Stakeholders Tools and methodologies (c) 2004 Superfactory(tm). All Rights Reserved. Customers= Needs / requirements Establish mission what products / services we provide Identify customers functional (direct) political (indirect) survey customers what expectations / perceptions exist? criteria for measuring them? triggers?
Originalbeschreibung:
Copyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Verfügbare Formate
PPT, PDF, TXT oder online auf Scribd lesen
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenProject management in today's environment rapid change BPR The project plan management and communications Organizational, people, political issues Stakeholders Tools and methodologies (c) 2004 Superfactory(tm). All Rights Reserved. Customers= Needs / requirements Establish mission what products / services we provide Identify customers functional (direct) political (indirect) survey customers what expectations / perceptions exist? criteria for measuring them? triggers?
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Verfügbare Formate
Als PPT, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
168 Ansichten11 SeitenProject Sample
Hochgeladen von
api-3798640Project management in today's environment rapid change BPR The project plan management and communications Organizational, people, political issues Stakeholders Tools and methodologies (c) 2004 Superfactory(tm). All Rights Reserved. Customers= Needs / requirements Establish mission what products / services we provide Identify customers functional (direct) political (indirect) survey customers what expectations / perceptions exist? criteria for measuring them? triggers?
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Verfügbare Formate
Als PPT, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
Sie sind auf Seite 1von 11
Project Management
Superfactory Excellence Program™
www.superfactory.com
© 2004 Superfactory™. All Rights Reserved. 1
Outline
PM in today’s environment
rapid change
BPR
The project plan
Management & communications
Organizational, people, political issues
Stakeholders
Tools & methodologies
© 2004 Superfactory™. All Rights Reserved. 2
Three Disciplines
© 2004 Superfactory™. All Rights Reserved. 3
Why Projects Succeed
User involvement
Exec management support
unequivocal sponsorship
Clear understanding & statement
of requirements
Effective planning
Realistic expectations
Standish Group survey of IT execs
© 2004 Superfactory™. All Rights Reserved. 4
Customers= Needs/Requirements
Needs analyst traits:
strong ability to deal with customers
political skills
technically competent
open-minded & imaginative
high tolerance for ambiguity
articulate
Technicians tend to produce Mercedes not the Hyundai that=s
wanted
© 2004 Superfactory™. All Rights Reserved. 5
Attaining Political Credibility
Establish mission
what products/services we provide
Identify customers
functional (direct)
political (indirect)
Survey customers
what expectations/perceptions exist?
criteria for measuring them?
triggers for them?
© 2004 Superfactory™. All Rights Reserved. 6
Sources of Project Risk
General sources
environmental (largely uncontrollable)
external, e.g. government regulations
internal, e.g. new division VP
technical
market
financial
people
© 2004 Superfactory™. All Rights Reserved. 7
Realistic Estimating
Lots of reasons for poor estimates
inexperience, technical problems, changes optimists, low-
balling, politics
Bottom-up cost estimating
rollup the WBS packages
Top-down or Parametric estimating
from experience to complex models
© 2004 Superfactory™. All Rights Reserved. 8
Configuration Management (CM)
Resist change via bureaucracy
Change control via CM
Rigorously screen changes
formal process for assessing merit
major or minor impact?
if major goes to Change Control Board (CCB)
document changes
update baseline
© 2004 Superfactory™. All Rights Reserved. 9
Earned Value Approach
Developed in 1960s for large defense projects; now used in smaller
projects
50-50 rule assumes task 50% complete when started, 100% when
completed
Compare earned value to planned costs
Collecting data
large projects employ cost account managers
for smaller projects, use 50-50 rule, take advantage of
milestones, or can guess using experience
Limitations of earned value
availability of accurate, timely data
educational; need organizational understanding
© 2004 Superfactory™. All Rights Reserved. 10
Post-Implementation Audit
Evaluate project’s achievements against plan
budget, deadlines, specifications, quality of deliverables,
client satisfaction
Six questions:
1. Project goal achieved?
2. On time, within budget & per specs?
3. Client (stakeholder) satisfied?
4. Business value realized?
5. PM lessons learned?
6. What worked, what didn’t?
© 2004 Superfactory™. All Rights Reserved. 11
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Von EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Bewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (98)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeVon EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (5795)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeVon EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (537)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureVon EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (474)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceVon EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (588)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealVon EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (74)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryVon EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (231)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceVon EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (895)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItVon EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (838)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingVon EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (400)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersVon EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (345)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaVon EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (45)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnVon EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (234)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyVon EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (2259)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaVon EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (266)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerVon EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (271)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreVon EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Von EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Bewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesVon EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (821)
- 1968CCG TeleComms Report ART SinglesDokument20 Seiten1968CCG TeleComms Report ART SinglesTarek HassanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Eaton V LDR711A Week 7 Reflective Leadership PlanDokument7 SeitenEaton V LDR711A Week 7 Reflective Leadership PlanvjeatonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Leadership Theories - 8 Major Leadership Theories: Kendra CherryDokument8 SeitenLeadership Theories - 8 Major Leadership Theories: Kendra CherryPoornima Ramar100% (1)
- Leadership Chapter 9 NotesDokument14 SeitenLeadership Chapter 9 NotesPřàñíťh KümâřNoch keine Bewertungen
- Contoh MGT162Dokument16 SeitenContoh MGT162miss jia50% (2)
- ISO 9001-2015 Client-Transition-Checklist - Add Your Co NameDokument11 SeitenISO 9001-2015 Client-Transition-Checklist - Add Your Co NameTomBerendsenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Managing Organizational CommunicationDokument9 SeitenManaging Organizational CommunicationBeatriz VidalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Portrait of An ESTJDokument7 SeitenPortrait of An ESTJNurulFazleenNoch keine Bewertungen
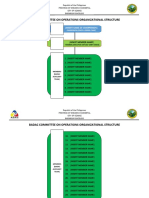
- Badac Organizational StructureDokument5 SeitenBadac Organizational StructureBarangay BacolodNoch keine Bewertungen
- MCQ in Bba Core - 1 Historical Perspective of ManagementDokument9 SeitenMCQ in Bba Core - 1 Historical Perspective of ManagementAamir Khan0% (1)
- Social Systems & Organizational CultureDokument61 SeitenSocial Systems & Organizational CultureClaribelle Haber100% (1)
- Internal CRMDokument10 SeitenInternal CRMRahulRahejaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 3 PowerPointDokument37 SeitenChapter 3 PowerPointDana FolignoNoch keine Bewertungen
- 5 The Central Role of Comparative Politics in Political Analysis PDFDokument10 Seiten5 The Central Role of Comparative Politics in Political Analysis PDFirenecalabriascribdNoch keine Bewertungen
- BSBLDR502 Sahil AssignmentDokument22 SeitenBSBLDR502 Sahil AssignmentShamili SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- Strategic Management Ch12 Strategic Leadership - LachowiczDokument35 SeitenStrategic Management Ch12 Strategic Leadership - LachowiczRushabh VoraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Book Summary - The 17 Indisputable Laws of TeamworkDokument3 SeitenBook Summary - The 17 Indisputable Laws of Teamworkragul lugarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Module # 1: The Perspective of 21st Century Instructional Leader DAY 3, Session No. 5Dokument60 SeitenModule # 1: The Perspective of 21st Century Instructional Leader DAY 3, Session No. 5Ireen Mercene MagtibayNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1-Nature and ScopeDokument13 Seiten1-Nature and ScopeLopa Manish ShahiNoch keine Bewertungen
- 7 JitDokument36 Seiten7 JitFatima AsadNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Leader Who Had No Title AmDokument42 SeitenThe Leader Who Had No Title Ammahesh415100% (1)
- Work Style Assessment Report SampleDokument25 SeitenWork Style Assessment Report SamplePersephona13Noch keine Bewertungen
- Session26 PPT SHRMDokument41 SeitenSession26 PPT SHRMakansha bhatia100% (1)
- Lead Program Coordinator PD FINALDokument4 SeitenLead Program Coordinator PD FINALroberto_333100% (1)
- The Impact of Organizational Behaviour On Employees Behaviour in Pharmaceutical Companies in Selected Locations of MaharashtravizDokument56 SeitenThe Impact of Organizational Behaviour On Employees Behaviour in Pharmaceutical Companies in Selected Locations of Maharashtravizmayur bhirudNoch keine Bewertungen
- Global Leadership Program 2017Dokument14 SeitenGlobal Leadership Program 2017joannamanngoNoch keine Bewertungen
- CU MBA SEM I Leadership & Organizational Behavior Second DraftDokument271 SeitenCU MBA SEM I Leadership & Organizational Behavior Second Draftshuchim guptaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Industrial PsychologyDokument178 SeitenIndustrial PsychologySonal AgarwalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Solution Manual - Chapter 1Dokument5 SeitenSolution Manual - Chapter 1psrikanthmbaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Winter, 1997Dokument7 SeitenWinter, 1997Mariana LyraNoch keine Bewertungen