Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Physical Properties of Dental Materials
Hochgeladen von
manishpankaj123Originalbeschreibung:
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Physical Properties of Dental Materials
Hochgeladen von
manishpankaj123Copyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Physical Physical
Properties of Properties of
Dental Materials Dental Materials
These are properties which are not related to force These are properties which are not related to force
application application
1hese are: 1hese are:
11- - Mass Mass- -related properties: related properties:
Density Density
22- - Thermal properties: Thermal properties:
- - Thermal conductivity Thermal conductivity
- - Coefficient of thermal expansion and contraction Coefficient of thermal expansion and contraction
- - Heat of fusion & latent heat of fusion Heat of fusion & latent heat of fusion
- - Melting and freezing temperature Melting and freezing temperature
- - Specific heat Specific heat
33- - Less specific properties: Less specific properties:
- - Water sorption. Water sorption.
- - Fluidity, viscosity and plasticity. Fluidity, viscosity and plasticity.
44- - Optical properties Optical properties
Mass Mass- - Related Properties: Related Properties:
Density Density
It is the mass per unit volume of the material. It is the mass per unit volume of the material.
Units are gm/cm Units are gm/cm
33
or pound/in or pound/in
22
linical importance in Dentistry: linical importance in Dentistry:
11- - Retention of the upper denture. Retention of the upper denture.
22- - Weight of complete or partial denture. Weight of complete or partial denture.
33- - During casting. During casting.
Thermal Properties: Thermal Properties:
1 1- - Thermal Conductivity: Thermal Conductivity:
It is the amount of heat in calories or joules passing per It is the amount of heat in calories or joules passing per
second through a body second through a body 11cm thick, cm thick, 11cm cm
22
cross sectional cross sectional
area when the temperature difference is area when the temperature difference is 11C C
linical importance in Dentistry: linical importance in Dentistry:
11- - Metallic filling materials. Metallic filling materials.
Metallic denture base materials. Metallic denture base materials.
2 2- - Thermal Coefficient of expansion( Thermal Coefficient of expansion( o o) )
The change in length per unit length of the material The change in length per unit length of the material
for a for a 1 1C change in temperature is called the C change in temperature is called the
linear coefficient of thermal expansion( linear coefficient of thermal expansion(o o) )
L original L original - - L final L final o o
L original x ( L original x (C final C final- - C original) C original)
linical importance in Dentistry: linical importance in Dentistry:
of the coefficient of thermal of the coefficient of thermal 4se matching 4se matching
expansion ( expansion (o o) is important between: ) is important between:
11- -The The t44th t44th and the and the rest4rative materias rest4rative materias to prevent to prevent
.. margina eakage margina eakage
pening and closing of gap results in
breakage of marginal seal between
the filling and the cavity wall,
this breakage of seal
leads to: (marginal percolation)
i. Marginal leakage ii. Discoloration
iii. Recurrent caries iv. Hypersensitivity.
22- -!4rceain !4rceain and and meta meta in ceramometallic in ceramometallic
restorations (crowns and bridges) to provide restorations (crowns and bridges) to provide
bonding. bonding. metal ceramic metal ceramic
crazing crazing to avoid to avoid /enture base /enture base and and t44th t44th Artificia Artificia - - 3 3
33- - Heat of fusion Heat of fusion
Heat of fusion (L) is the amount of heat in calories or Heat of fusion (L) is the amount of heat in calories or
joules required to convert l gm of a material from the joules required to convert l gm of a material from the
solid to the liquid state at the melting temperature. solid to the liquid state at the melting temperature.
It is calculated as follows: It is calculated as follows:
is the heat of fusion. is the heat of fusion. L: L: Where Where Q Q
is the total heat absorbed. is the total heat absorbed. Q: Q: ---------------- ---------------- L L
mass of the substance melted mass of the substance melted m: m: m m
As long as the mass is molten, the heat of fusion is retained by the As long as the mass is molten, the heat of fusion is retained by the
, this heat is , this heat is When the liquid is frozen or solidified liquid. liquid.
liberated. It is called liberated. It is called "Latent heat of fusion". "Latent heat of fusion".
Latent heat of fusion Latent heat of fusion
It is the amount of heat in calories or joules It is the amount of heat in calories or joules
liberated when liberated when 1 1 gm of a material is converted gm of a material is converted
from liquid to solid state. from liquid to solid state.
Importance in dentistry: Importance in dentistry:
During casting, the metal must be heated During casting, the metal must be heated 100 100 C C
more than its melting temperature for proper more than its melting temperature for proper
melting melting
atent heat of fusion atent heat of fusion
Heat of fusion Heat of fusion
Dental significance Dental significance
During casting metal must be heated During casting metal must be heated J00 J00
above its melting temperature above its melting temperature
%2
%20
$
$
44- -Melting and freezing temperature Melting and freezing temperature
%2
%20
Dental Importance:
or the fabrication of indirect metallic restorations
(casting), the melting temperature of metals and alloys
is important in determining the melting machine used
for casting
- -Specific heat Specific heat
t is the quantity of heat needed to raise the temperature t is the quantity of heat needed to raise the temperature
of one gram of the substance of one gram of the substance JJ
1berefore 1berefore
Metals have low specific heat Metals have low specific heat, ,
while while non metals have high specific heat non metals have high specific heat
Importance in dentistry: Importance in dentistry:
Because of the low specific heat of dental gold alloys, prolonged heating is Because of the low specific heat of dental gold alloys, prolonged heating is
unnecessary, during casting unnecessary, during casting
Less specific properties Less specific properties
11- - Water Sorption: Water Sorption:
It represents the amount of water adsorbed on the It represents the amount of water adsorbed on the
surface and absorbed into the body of the surface and absorbed into the body of the
material. material.
Importance Importance: :
11- - Acrylic resin denture base materials have the Acrylic resin denture base materials have the
tendency for water sorption. tendency for water sorption.
22- - Hydrocolloid impression materials will imbibe Hydrocolloid impression materials will imbibe
water if immersed in it leading to dimensional water if immersed in it leading to dimensional
changes. changes.
22- -Fluidity, viscosity and Fluidity, viscosity and
plasticity: plasticity:
ui/ity ui/ity is the tendency of liquids to flow. is the tendency of liquids to flow.
Jisc4sity Jisc4sity is the resistance to flow. is the resistance to flow.
!asticity !asticity is a property related to solids or is a property related to solids or
semisolids and indicates that the material is semisolids and indicates that the material is
easily and permanently deformed under easily and permanently deformed under
force. force.
Optical Properties
The perception of the The perception of the Color Color of an object is of an object is
the result of a the result of a physiological response to a physiological response to a
physical stimulus (light). physical stimulus (light).
Light Light is an is an electromagnetic radiation electromagnetic radiation that can that can
be detected by the human eye. It can be seen be detected by the human eye. It can be seen
that the visible electromagnetic radiation is that the visible electromagnetic radiation is
in the range from in the range from 400 400- -700 700 nanometers. nanometers.
Properties of materials in relation to light
transmission and absorption
1ransparency
is a property of a material, that allows the passage of light in such a manner that little distortion takes is a property of a material, that allows the passage of light in such a manner that little distortion takes
place place so that objects can be so that objects can be clearly seen through them clearly seen through them
e.g. glass, pure acrylic resin. e.g. glass, pure acrylic resin.
1ransucency
is a property of the material, which allows the passage of some light and scatters or reflects is a property of the material, which allows the passage of some light and scatters or reflects
the rest . In such manner, the the rest . In such manner, the object cannot be clearly seen through them object cannot be clearly seen through them
Translucency decreases with increasing the scattering centers. Translucency decreases with increasing the scattering centers.
e.g. tooth enamel, porcelain, composite and pigmented acrylic resin. e.g. tooth enamel, porcelain, composite and pigmented acrylic resin.
pacity pacity is a property of the material that is a property of the material that
prevents the passage of light. Opaque prevents the passage of light. Opaque
material absorbs all of the light. Objects material absorbs all of the light. Objects
cannot be seen through them. cannot be seen through them.
- -Black Black color materials color materials absorb all light colors absorb all light colors..
- -White White color materials color materials reflect all light colors reflect all light colors..
- -Blue Blue color materials color materials absorb all light colors absorb all light colors
but reflect its color but reflect its color..
Interaction of light and matter Interaction of light and matter
When a beam of light encounters or falls on a When a beam of light encounters or falls on a
surface of a medium, the following may surface of a medium, the following may
occur : occur :
11- - Reflection: Reflection:
Reflections on a smooth surface give a Smooth surface: - A
Specular Reflection to the surface glossy appearance
angle of incidence = angle of reflection $2ootb .vrface:
%he restoration should have a highly smooth and polished
surface to simulate the tooth structure and match it.
B- Rough surface: Reflections of light on a rough surface are
diffused (i.e: in all directions). Diffuse Reflection
The surface appears to have little gloss (i.e dull)
22- - Refraction: Refraction:
It is the change of the direction of a beam of light on entering It is the change of the direction of a beam of light on entering
second medium. second medium.
#efracti4n #efracti4n results from the difference in refractive indices of the results from the difference in refractive indices of the
two media. two media.
4r perfect matching 4r perfect matching the refractive index of the restoration the refractive index of the restoration
should be should be `` ``equa equa to the refractive index of the tooth. to the refractive index of the tooth.
transparent solid transparent solid
while while `` `` arge /ifferences arge /ifferences result in result in opaque materials opaque materials..
Example: Example: Control of refractive index of the filler and Control of refractive index of the filler and
matrix phases in composite resins and porcelain. matrix phases in composite resins and porcelain.
Scattering: Scattering: - - 33
If light rays passing through a medium are obstructed by any different If light rays passing through a medium are obstructed by any different
inclusions it will be redirected in another direction and is attenuated. inclusions it will be redirected in another direction and is attenuated.
i.e i.e The original beam is weakened by scattering in a The original beam is weakened by scattering in a
direction away from the observer eye direction away from the observer eye
OPACITY OPACITY TRANSLUCENCY TRANSLUCENCY..
Importance in dentistry: Importance in dentistry:
1 1- - Opacifiers & pigments Opacifiers & pigments added to composite resins act as scattering centers that added to composite resins act as scattering centers that
give rise to opaque shades of the material. give rise to opaque shades of the material.
2 2- - Incorporated Incorporated air bubbles air bubbles
in a restoration act as in a restoration act as
scattering centers. scattering centers.
omplete %ransmission omplete %ransmission %ransparent %ransparent
ncomplete %ransmission ncomplete %ransmission %ranslucent %ranslucent
No %ransmission (absorption) No %ransmission (absorption) paque paque
. Transmission: . Transmission: 44
ight passing through an optical medium ight passing through an optical medium
without attenuation without attenuation
completely transmitted. completely transmitted.
%otal transmission occurs in perfectly %otal transmission occurs in perfectly transparent transparent materials. materials.
f part of the light is transmitted and part is reflected f part of the light is transmitted and part is reflected
( i.e. ( i.e. diffuse transmission diffuse transmission), the material appears ), the material appears translucent translucent. .
#
Color parameters: Color parameters:
A A- - Hue: Hue: It is the dominant wave length. It represents It is the dominant wave length. It represents
the the color color of the material, of the material,
i.e i.e yellow yellow, , green green, , red red and and blue blue..
BB- - Chroma: Chroma: It represents the It represents the strength of the color strength of the color or or
degree of saturation of the color (color intensity). degree of saturation of the color (color intensity).
A beaker of water containing one drop of colorant is lower in A beaker of water containing one drop of colorant is lower in
chroma than a beaker of water containing ten drops of the chroma than a beaker of water containing ten drops of the
same colorant. same colorant.
C C- - Value: Value:
It represents the It represents the lightness or darkness lightness or darkness of color of color
(the amount of grayness). (the amount of grayness).
A black standard is assigned a value of O, A black standard is assigned a value of O,
whereas a white standard is assigned whereas a white standard is assigned 10 10. .
A t44th 4f 4 vaue A t44th 4f 4 vaue appears appears
gray and non gray and non--vital vital DEAD DEAD, ,
therefore, it is therefore, it is the most important parameter the most important parameter. .
Because it is intimately related to the Because it is intimately related to the
aspect of aspect of vitality in human teeth vitality in human teeth..
Factors affecting coIor Factors affecting coIor
appearance and seIection appearance and seIection
$baae gviae $baae gviae is used for color matching. So, it is is used for color matching. So, it is
important to match colors under appropriate important to match colors under appropriate
conditions. conditions.
1 1- - Source: Source:
Different sources have different color Different sources have different color
content. i.e Incandesnt content. i.e Incandesnt light has a color light has a color
content different from that of content different from that of
fluorescent light. fluorescent light.
etamerism: etamerism: It is the change of color It is the change of color
matching of two objects under different matching of two objects under different
light sources light sources..
etameric pairs: etameric pairs: Two objects that are Two objects that are
matched in color under one light source matched in color under one light source
but are not matched under other light but are not matched under other light
sources form metameric pair. sources form metameric pair.
Is4meric pair: Is4meric pair: They are color They are color matched matched
under all light sources under all light sources..
1hus, if p4ssibe, c44r matching sh4u/ be /4ne 1hus, if p4ssibe, c44r matching sh4u/ be /4ne
un/er t4 4r m4re /ifferent ight s4urces un/er t4 4r m4re /ifferent ight s4urces..
22- - Surrounding: Surrounding:
Colors of wall, lips or clothes of the patient Colors of wall, lips or clothes of the patient
modify the type of light reaching the object. modify the type of light reaching the object.
33- - Object: Object:
A A- - Translucency: Translucency:
It controls lightness or darkness of color. It controls lightness or darkness of color.
High translucency gives a lighter color High translucency gives a lighter color
appearance (higher value) i.e more vital tooth appearance (higher value) i.e more vital tooth
appearance appearance
BB- - Surface texture (surface finish): Surface texture (surface finish):
This determines the relative amount of light This determines the relative amount of light
reflected from the surface, smooth surface reflected from the surface, smooth surface
appears brighter than rough surface. appears brighter than rough surface.
C C- - Presence of scattering centers as Presence of scattering centers as
inclusions or voids: inclusions or voids:
This increase opacity and lower the value This increase opacity and lower the value
(more dark) (more dark)
D D- - Fluorescene: Fluorescene:
It makes the teeth bright and vital, as it It makes the teeth bright and vital, as it
increases the brightness. increases the brightness.
EE- - Thickness: Thickness:
The thickness of a restoration can affect its The thickness of a restoration can affect its
appearance. appearance.
Increase in thickness, increase opacity, and Increase in thickness, increase opacity, and
lower the value. lower the value.
FF- - Metamerism Metamerism
44- - Observer: Observer:
A A- - Color response: Color response:
Eye responds differently among individuals. Eye responds differently among individuals.
BB- - Color Vision: Color Vision:
Some individuals may have color blindness Some individuals may have color blindness
and inability to distinguish certain colors. and inability to distinguish certain colors.
C C- - Color Fatigue: Color Fatigue:
Constant stimulus of one color decreases the Constant stimulus of one color decreases the
response to that color. response to that color.
aser aser
LLight ight A Amplification mplification by by S Stimulated timulated EEmission mission of of R Radiation adiation..
The principle of laser production is simply that an element The principle of laser production is simply that an element
or compound (medium) can be excited by high energy to or compound (medium) can be excited by high energy to
produce a special type of light called laser produce a special type of light called laser
baracteri.tic. of ta.er bea2: baracteri.tic. of ta.er bea2:
a a Monochromatic: Monochromatic:
all photons have the same wave length. all photons have the same wave length.
b b oherent oherent : :
all waves are bin phase (have the same speed ). all waves are bin phase (have the same speed ).
cc ollimated: ollimated:
all waves are parallel ( minimum divergence ) all waves are parallel ( minimum divergence )
Clinical applications of Clinical applications of
laser laser
aa- - Surgery for removal of soft Surgery for removal of soft
tissues. tissues.
b b- - Removal of initial carious Removal of initial carious
lesions. lesions.
cc- - Curing of composite resin Curing of composite resin
8 #
!rimary c44rs !rimary c44rs: :
Blue, green and red are primary colors. are primary colors.
Combining suitable proportions of wave lengths of the three Combining suitable proportions of wave lengths of the three
primary colors results in white. primary colors results in white.
$ec4n/ary c44rs $ec4n/ary c44rs: : Each secondary color Each secondary color
(cyan ,magenta & yellow) results from the combination of results from the combination of
two primary colors, e.g . green and red gives yellow, two primary colors, e.g . green and red gives yellow,
blue and red gives magenta, blue and green gives cyan. blue and red gives magenta, blue and green gives cyan.
4mpementary c44rs 4mpementary c44rs : : Two colors are complementary to Two colors are complementary to
each other when their combination results in white e.g . yellow is each other when their combination results in white e.g . yellow is
the complementary color of blue . the complementary color of blue .
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Gemstone and Crystal Reference Book EnglishDokument29 SeitenGemstone and Crystal Reference Book Englishsandu_livia100% (1)
- Sajjan M MBBS Learn ECG in A Day A Systemic ApproachDokument99 SeitenSajjan M MBBS Learn ECG in A Day A Systemic Approachv@r0_5100% (9)
- Major Connectors and Their Functions in Removable Partial DenturesDokument26 SeitenMajor Connectors and Their Functions in Removable Partial Denturesbkprostho100% (1)
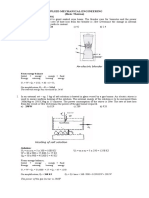
- APPLIED MECHANICAL ENGINEERING PROBLEM SOLVINGDokument4 SeitenAPPLIED MECHANICAL ENGINEERING PROBLEM SOLVINGKyle LoveNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biological Properties of Dental Materials 1-General Dentistry / Orthodontic Courses by Indian Dental AcademyDokument76 SeitenBiological Properties of Dental Materials 1-General Dentistry / Orthodontic Courses by Indian Dental Academyindian dental academyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Anchorage in OrthodonticsDokument64 SeitenAnchorage in Orthodonticsmanishpankaj1230% (1)
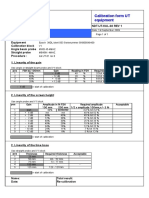
- Calibration Sheet Ultrasonic Test EquipmentDokument1 SeiteCalibration Sheet Ultrasonic Test EquipmentjohnNoch keine Bewertungen
- Occlusion IN Prosthodontics: Dr. Aeysha Siddika FCPS (Trainee) Department of Prosthodontics Faculty of Dentistry BsmmuDokument26 SeitenOcclusion IN Prosthodontics: Dr. Aeysha Siddika FCPS (Trainee) Department of Prosthodontics Faculty of Dentistry BsmmuArunNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dental CeramicsDokument434 SeitenDental Ceramicskirtiabhi100% (2)
- Role of Tongue N Floor of Mouth in CD TRTDokument18 SeitenRole of Tongue N Floor of Mouth in CD TRTashoorocksNoch keine Bewertungen
- Teeth Selection and ArrangementDokument118 SeitenTeeth Selection and Arrangementaakankshakanwar100% (2)
- The Design and Use of Special TraysDokument45 SeitenThe Design and Use of Special TrayskarthikNoch keine Bewertungen
- Final Biomechanics of Edentulous StateDokument114 SeitenFinal Biomechanics of Edentulous StateSnigdha SahaNoch keine Bewertungen
- CASTING (Lecture by DR - Muhammad Seddeek @AmCoFam)Dokument56 SeitenCASTING (Lecture by DR - Muhammad Seddeek @AmCoFam)AmericanCornerFamily100% (1)
- CGPISL Arrester Presentation HVPNDokument88 SeitenCGPISL Arrester Presentation HVPNAnonymous 42LkomNoch keine Bewertungen
- Occlusion in Complete DentureDokument20 SeitenOcclusion in Complete DentureBhushan ChavanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Determinants of Occlusion MorphologyDokument67 SeitenDeterminants of Occlusion Morphologydrsmriti100% (4)
- Basic Level of Dental Resins - Material Science & Technology: 4th Edition, 2nd VersionVon EverandBasic Level of Dental Resins - Material Science & Technology: 4th Edition, 2nd VersionNoch keine Bewertungen
- Direct RetainersDokument10 SeitenDirect RetainersSakinah SyahirahNoch keine Bewertungen
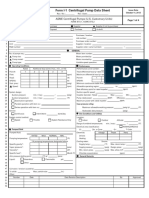
- Form I-1 Centrifugal Pump Data SheetDokument4 SeitenForm I-1 Centrifugal Pump Data SheetJohnNoch keine Bewertungen
- Impression techniques for RPDDokument29 SeitenImpression techniques for RPDمؤمل رياض سعد كاظمNoch keine Bewertungen
- LaMOT RD CatalogDokument20 SeitenLaMOT RD CatalogSasan Abbasi0% (1)
- Two-Visit CAD/CAM Milled Dentures in The Rehabilitation of Edentulous ArchesDokument27 SeitenTwo-Visit CAD/CAM Milled Dentures in The Rehabilitation of Edentulous ArchesVeena GoudNoch keine Bewertungen
- ZirconiaDokument12 SeitenZirconiaAna Massiel NarváezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Periodontal InstrumentsDokument10 SeitenPeriodontal Instrumentsmanishpankaj123100% (1)
- Relining and Rebasing of Complete Dentures: Bds MSC MRD Rcsed 4 Year/removable Prosthodontics 441-442Dokument33 SeitenRelining and Rebasing of Complete Dentures: Bds MSC MRD Rcsed 4 Year/removable Prosthodontics 441-442Aya ShahrouriNoch keine Bewertungen
- Posterior Palatal Seal ProsthoDokument64 SeitenPosterior Palatal Seal ProsthoAmit BhargavNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drugs During PregnancyDokument120 SeitenDrugs During Pregnancymanishpankaj123100% (1)
- Ruhrpumpen PDFDokument41 SeitenRuhrpumpen PDFMariano NogarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Stress Treatment Theorem For Implant Dentistry: Niranjana R I Year Postgraduate Department of ProsthodonticsDokument43 SeitenStress Treatment Theorem For Implant Dentistry: Niranjana R I Year Postgraduate Department of ProsthodonticsNiranjanaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Principles and Techniques of Oral BiopsyDokument45 SeitenPrinciples and Techniques of Oral BiopsyMahamoud IsmailNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physical Properties of Dental MaterialsDokument38 SeitenPhysical Properties of Dental MaterialsvelangniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Relining and Rebasing in Complete Dentures: Indian Dental AcademyDokument59 SeitenRelining and Rebasing in Complete Dentures: Indian Dental AcademyNajeeb UllahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Basic Principles in Impression Making M M DevanDokument6 SeitenBasic Principles in Impression Making M M Devanmfaheemuddin85100% (1)
- Lec 4 Prosthodontics PDFDokument7 SeitenLec 4 Prosthodontics PDFmustafa7calligrapherNoch keine Bewertungen
- Recent Advances in DentistryDokument2 SeitenRecent Advances in DentistrySudarsan SangeethaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Principles of Tooth PreparationDokument10 SeitenPrinciples of Tooth Preparationruchika100% (2)
- Finish LinesDokument17 SeitenFinish LinesWaseem AhmedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Occlusal Rims FabDokument8 SeitenOcclusal Rims FabSalon LamichhaneNoch keine Bewertungen
- Anterior Deprogramming Device Fabrication Using A Thermoplastic Material PDFDokument3 SeitenAnterior Deprogramming Device Fabrication Using A Thermoplastic Material PDFruli nurul amanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Relining and Rebasing of Complete DenturesDokument28 SeitenRelining and Rebasing of Complete DenturesPurnama SyahbaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Connector Design PrinciplesDokument24 SeitenConnector Design PrinciplesVikas Aggarwal100% (1)
- Anatomy and Physiology in Relation To Complete Denture ConstructionDokument4 SeitenAnatomy and Physiology in Relation To Complete Denture ConstructionCyril Almario CunananNoch keine Bewertungen
- Partial Retainer in FPD DR VikasDokument99 SeitenPartial Retainer in FPD DR VikasVikas AggarwalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Implant Systems: Dr. Unjum Bashir, Dr. Manas Gupta, Dr. Ravish AhujaDokument7 SeitenImplant Systems: Dr. Unjum Bashir, Dr. Manas Gupta, Dr. Ravish AhujaDr FarhatNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Review On Posterior Palatal SealDokument6 SeitenA Review On Posterior Palatal SealTanmay Srivastava100% (1)
- Major connectors support RPDsDokument15 SeitenMajor connectors support RPDsAmir KazimNoch keine Bewertungen
- Complete Denture Impression TechniquesDokument18 SeitenComplete Denture Impression TechniquesYashpreetsingh BhatiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Indian Dental Academy - Theories of Impression Making in Complete Denture Treatment PDFDokument15 SeitenIndian Dental Academy - Theories of Impression Making in Complete Denture Treatment PDFFaheemuddin MuhammadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Impression Techniques in RPDDokument82 SeitenImpression Techniques in RPDpramodaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Impression C DDokument48 SeitenImpression C DZaid KhameesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lingualized Occlusion ReviewDokument3 SeitenLingualized Occlusion ReviewJessy ChenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Retention Support Stability CDDokument53 SeitenRetention Support Stability CDAshraf GebreelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Try in FPDDokument40 SeitenTry in FPDharshini100% (1)
- A Hollow Bulb ObturatorDokument6 SeitenA Hollow Bulb ObturatorrekabiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nanotechnology in ProsthodonticsDokument7 SeitenNanotechnology in Prosthodonticsharshita parasharNoch keine Bewertungen
- Concept: Captek™ Are Crowns and Bridges That Mimic and Surpass Natural Teeth in Esthetic and FunctionDokument50 SeitenConcept: Captek™ Are Crowns and Bridges That Mimic and Surpass Natural Teeth in Esthetic and FunctionPolet Aline Sánchez SosaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Impression Registration Rpd-TechniqueDokument19 SeitenImpression Registration Rpd-TechniqueTaha AlaamryNoch keine Bewertungen
- Theories of Impression Making and Impression Procedure For Complete DentureDokument63 SeitenTheories of Impression Making and Impression Procedure For Complete DenturemanjulikaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Record Bases & Occlusion Rims GuideDokument34 SeitenRecord Bases & Occlusion Rims GuidemariahashrafNoch keine Bewertungen
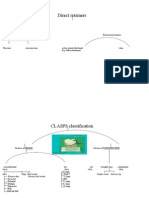
- RPD Clasp DesignDokument10 SeitenRPD Clasp DesignAmar BhochhibhoyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Aull. A Study of The Transverse Axis. (1963)Dokument11 SeitenAull. A Study of The Transverse Axis. (1963)Jose Enrique AvilaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Management of Alveolar Ridge ResorptionDokument29 SeitenManagement of Alveolar Ridge Resorptionفواز نميرNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pressure Indicating Media Loney KnechtelDokument5 SeitenPressure Indicating Media Loney KnechtelrochirrephttoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Prosthodontic Diagnostic Index (PDI) Classification SystemDokument1 SeiteProsthodontic Diagnostic Index (PDI) Classification SystemevvallartaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Impressions: Presented By: Dr. Mansi Sharma Department of Prosthodontics Crown and Bridge PG1 YearDokument61 SeitenImpressions: Presented By: Dr. Mansi Sharma Department of Prosthodontics Crown and Bridge PG1 YearshailjaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fixed Orthodontic Appliances: A Practical GuideVon EverandFixed Orthodontic Appliances: A Practical GuideBewertung: 1 von 5 Sternen1/5 (1)
- Physical Properties of Dental MaterialsDokument37 SeitenPhysical Properties of Dental MaterialsAly SayedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physical Properties of Dental MaterialsDokument37 SeitenPhysical Properties of Dental MaterialsAly SayedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physical PropertiesDokument22 SeitenPhysical Propertiesshereensalah1357Noch keine Bewertungen
- Physical Properties of Dental MaterialsDokument55 SeitenPhysical Properties of Dental MaterialsSaiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physical Properties 2Dokument20 SeitenPhysical Properties 2bavly waidyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physical and Chemical Properties of MaterialsDokument3 SeitenPhysical and Chemical Properties of MaterialsRoland EmersonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Operative Dept Clincial Instruction Guide 11-12Dokument62 SeitenOperative Dept Clincial Instruction Guide 11-12manishpankaj123Noch keine Bewertungen
- Orthodontics Treatment GuideDokument23 SeitenOrthodontics Treatment Guidemanishpankaj123Noch keine Bewertungen
- Dental CariesDokument26 SeitenDental Cariesmanishpankaj123Noch keine Bewertungen
- Orthodontics Treatment GuideDokument23 SeitenOrthodontics Treatment Guidemanishpankaj123Noch keine Bewertungen
- Anatomy Guide for Complete and Partial DenturesDokument31 SeitenAnatomy Guide for Complete and Partial Denturesaziz2007Noch keine Bewertungen
- ANKYLOSIS of TMJ Oral SurgeryDokument52 SeitenANKYLOSIS of TMJ Oral SurgeryAbhishek ChauhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Permanent Mandibular First MolarDokument65 SeitenPermanent Mandibular First Molarmanishpankaj123Noch keine Bewertungen
- Retention and Stability of Complete DentureDokument7 SeitenRetention and Stability of Complete Denturemanishpankaj123Noch keine Bewertungen
- Surgical InstrumentationDokument42 SeitenSurgical Instrumentationmanishpankaj123Noch keine Bewertungen
- Serial ExtractionDokument38 SeitenSerial Extractionmanishpankaj123Noch keine Bewertungen
- Marsupial IzationDokument23 SeitenMarsupial Izationmanishpankaj123Noch keine Bewertungen
- Red and White Lesions of Oral MucosaDokument16 SeitenRed and White Lesions of Oral Mucosamanishpankaj123Noch keine Bewertungen
- Difference between Mandibular First and Second MolarsDokument51 SeitenDifference between Mandibular First and Second Molarsmanishpankaj123100% (3)
- Oral Thrush Net DoctorDokument2 SeitenOral Thrush Net Doctormanishpankaj123Noch keine Bewertungen
- R A D I o G R A P H I CDokument4 SeitenR A D I o G R A P H I Cmanishpankaj123Noch keine Bewertungen
- HematologyDokument40 SeitenHematologymanishpankaj123Noch keine Bewertungen
- Spectrophotometric Determination of The Equilibrium Constant of A Reaction DraftDokument3 SeitenSpectrophotometric Determination of The Equilibrium Constant of A Reaction DraftFem T. BartolomeNoch keine Bewertungen
- 5-1-14 Recueil Methodes Vol 1 en 2012Dokument488 Seiten5-1-14 Recueil Methodes Vol 1 en 2012James Quynh NguyenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Optical Properties of Semiconductor NanocrystalsDokument259 SeitenOptical Properties of Semiconductor Nanocrystalsanhthigl25Noch keine Bewertungen
- Article1379594984 - Sivakumar and GomathiDokument7 SeitenArticle1379594984 - Sivakumar and GomathiEdda GeregetanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Uncertainty IR PDFDokument8 SeitenUncertainty IR PDFluisNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 6 Final A5 EditDokument16 SeitenChapter 6 Final A5 EditkINGNoch keine Bewertungen
- Analysis and Testing of Asymmetric GearsDokument10 SeitenAnalysis and Testing of Asymmetric GearsgramuiitmNoch keine Bewertungen
- BOSCH Bio DecontaminationH2O2Dokument25 SeitenBOSCH Bio DecontaminationH2O2Davide GrioniNoch keine Bewertungen
- TPO Product CatalogDokument210 SeitenTPO Product CatalogMiguel BrionesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Airfoil Lift Procedures PDFDokument12 SeitenAirfoil Lift Procedures PDFmatthias.s.sommer3656Noch keine Bewertungen
- OIL-Xplus Filtros Aire ComprimidoDokument8 SeitenOIL-Xplus Filtros Aire ComprimidoMario Vazquez BNoch keine Bewertungen
- Operating Instructions for Clinical AutoclavesDokument11 SeitenOperating Instructions for Clinical AutoclavesEduardo0% (1)
- BMW Fault Codes OBDDokument15 SeitenBMW Fault Codes OBDtitibacsiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Carga de Bolas - Molino KopperDokument4 SeitenCarga de Bolas - Molino KopperIngridkferNoch keine Bewertungen
- B.SC 2nd and 3rd Year Syllabus SVUDokument16 SeitenB.SC 2nd and 3rd Year Syllabus SVUSrinivasulu Pudu100% (1)
- SITI SOLEHAH BINTI OMAR (2015834112) /EH224 7A1 Heuristics of ReactorDokument2 SeitenSITI SOLEHAH BINTI OMAR (2015834112) /EH224 7A1 Heuristics of ReactorSolehah OmarNoch keine Bewertungen
- MZ2000W PDS EnglishDokument3 SeitenMZ2000W PDS EnglishLeandroNoch keine Bewertungen
- Benzene Structure and Delocalised Model ExplainedDokument8 SeitenBenzene Structure and Delocalised Model ExplainedHisham Jafar AliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Flowserve Lined Flush BottomDokument32 SeitenFlowserve Lined Flush BottomDevdatt WaghuleNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chemigrams and CyanotypesDokument4 SeitenChemigrams and Cyanotypesapi-481057728Noch keine Bewertungen
- Flash Point and Fire Point - FinalDokument33 SeitenFlash Point and Fire Point - FinalAnonymous QM0NLqZONoch keine Bewertungen