Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Chapter 011
Hochgeladen von
api-36973260 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
79 Ansichten25 SeitenHealth history: chronic illness, medications, how keep it healthy, sun exposure, changes in skin (look / feel / sensation) past medical / family history: past problems, family member with problem; skin cancer / autoimmune disorder? Examination Techniques: Skin General survey (color, pigmentation, vascularity, lesions, discolorations, odors)
Originalbeschreibung:
Copyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Verfügbare Formate
PPT, PDF, TXT oder online auf Scribd lesen
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenHealth history: chronic illness, medications, how keep it healthy, sun exposure, changes in skin (look / feel / sensation) past medical / family history: past problems, family member with problem; skin cancer / autoimmune disorder? Examination Techniques: Skin General survey (color, pigmentation, vascularity, lesions, discolorations, odors)
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Verfügbare Formate
Als PPT, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
79 Ansichten25 SeitenChapter 011
Hochgeladen von
api-3697326Health history: chronic illness, medications, how keep it healthy, sun exposure, changes in skin (look / feel / sensation) past medical / family history: past problems, family member with problem; skin cancer / autoimmune disorder? Examination Techniques: Skin General survey (color, pigmentation, vascularity, lesions, discolorations, odors)
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Verfügbare Formate
Als PPT, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
Sie sind auf Seite 1von 25
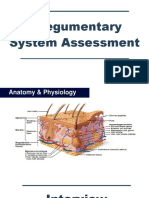
Skin, Hair, and Nails
Chapter 11
Copyright © 2005, Mosby, Inc. All rights reserved.
Health History:
General History
• Present health status: chronic illness,
medications, how keep it healthy, sun
exposure, changes in skin (look/feel/
sensation)
• Past medical/family history: past
problems, family member with problem;
skin cancer/autoimmune disorder?
Copyright © 2005, Mosby, Inc. All rights reserved.
Problem-Based History: Skin
• Pruritus—when started (suddenly/over time), where,
what makes worse/better, treatment, circumstances
when first noticed, dry/sensitive skin?
• Rash—when, where, initial appearance, itch/burn,
how long, what makes better/worse, treatment, other
symptoms, allergies, medications, irritants, exposure,
other family members have?
• Pain/discomfort—describe: started, location,
extend/spread, surface/deep, describe type, intensity,
constant/intermittent, what
Copyright © 2005, Mosby, Inc. All rights reserved.
Problem-Based History
• Lesions/changes in moles: describe,
location, first noticed, other symptoms,
appearance changed (describe)?
• Changes in skin color: generalized/
localized changes?
• Skin texture: how changed, excessively
dry/oily, when occurs, treatment?
• Wounds: location, how long, treatment,
wound healing problems?
Copyright © 2005, Mosby, Inc. All rights reserved.
Problem-Based History
• Hair: change experiencing, when, rate of
change, contributing factors, hair products,
diet change, distribution change?
• Nails: problems, when, chemical exposure,
brittle, pitting, chew, infection, keeping
clean, appear dirty?
Copyright © 2005, Mosby, Inc. All rights reserved.
Examination Techniques: Skin
• General survey (color, pigmentation, vascularity,
bruising, lesions, discolorations, odors)
– Systematic examination
• Head to toe exam: do with systematic examination
– Adequate lighting; may miss subtle changes
• Inspect for color: uniformity (consistent over
body surface) except vascular areas
– Whitish pink to olive tones to deep brown
– Sun exposed is darker
Copyright © 2005, Mosby, Inc. All rights reserved.
Examination Techniques: Skin
• Abnormal findings: evidence of
local/systemic disease
– Cyanosis
– Pallor
– Jaundice
Copyright © 2005, Mosby, Inc. All rights reserved.
Examination Techniques: Skin
• Inspect for localized color variation
– Intentional: tattoos, coining patterns
– Normal localized variations
• Moles, freckles, patches, striae
Copyright © 2005, Mosby, Inc. All rights reserved.
Examination Techniques: Skin
• Palpate for:
– Texture: smooth, soft, intact, even surface
(calluses)
– Temperature and moisture: warm/dry
– Mobility and turgor: move easily when lifted,
immediate return after released
– Thickness: varies with age/area (palms/soles
–thickest, eyelids thinnest)
• Callus: thick from friction/pressure
Copyright © 2005, Mosby, Inc. All rights reserved.
Examination Techniques: Skin
• Inspect/palpate for skin lesions: observable
change in structure
– Characteristics
• Light: color, elevation, borders
• Ruler: size (cm)
– Documentation: location, distribution, color,
pattern, edges, flat/raised, size
• )
Copyright © 2005, Mosby, Inc. All rights reserved.
Examination Procedures: Hair
• Inspect and palpate
– Scalp: surface characteristic; smooth without
flaking, scaling, redness, lesions;
• Hair: shiny, soft
– Quantity/distribution: balding patterns/hair loss
(male patterned)
– Texture: fine/coarse
– Color
• Inspect facial/body hair
– Distribution/quantity/texture: gender
differences
Copyright © 2005, Mosby, Inc. All rights reserved.
Examination Procedures: Nails
• Inspect:
– Shape: smooth/rounded; nail base angle =
160°
– Contour: flat/slightly rounded
– Consistency
– Color: pink, blanch (dark skinned,
yellow/brown with vertical lines)
– Thickness: smooth, uniform
– Cleanliness
• Palpate: nail base; firm/adheres to bed
Copyright © 2005, Mosby, Inc. All rights reserved.
Examination: Nails
• Abnormal nail findings
– Clubbing
– Thinning/brittleness
– Inflammation
Copyright © 2005, Mosby, Inc. All rights reserved.
Age-Related Variations:
Older Adults
• Anatomy and physiology: drier, decreased
perspiration decreased sebaceous/sweat
gland activity)
• Appearance (thin, parchment) decreased
dermal vascularity
– Folding/wrinkled appearance: loss of dermal
elasticity, collagen, mass
– Sharp/angular appearance over joints/bones,
deepening of hollows: decreased cutaneous
tissue
Copyright © 2005, Mosby, Inc. All rights reserved.
Age-Related Variations:
Older Adults
• Hair affected by hormonal changes
– Decreased melanin causes graying
– Thinning of scalp, axillary, pubic hair
– Follicles change size; terminal hair to vellus hair
(age-associated baldness)
– Transition of vellus to terminal hair in nares, on
tragus (men)
– Females develop facial hair (increased androgen,
increased estrogen)
– Loss of hair from trunk, extremities, axillary, pubic
area
Copyright © 2005, Mosby, Inc. All rights reserved.
Age-Related Changes:
Older Adults
• Hormonal changes (cont.)
– Decreased peripheral circulation: nail growth
slowed
– Nails get thicker, brittle, hard, yellow; ridges,
splitting
• Health history: same as for adults
Copyright © 2005, Mosby, Inc. All rights reserved.
Age-Related Changes:
Older Adults
• Examination: extra care; correlate history with
lesions (normal aging vs. cancer)
• Normal/abnormal findings
– ↑ pigmentation (sun exposure), hypopigmentation
– ↑ sun exposure causes ruddy, thickened skin
– Solar lentigo (liver spots): pigmented macules from
sun
– Seborrheic keratoses: warty lesions on face/ trunk,
(differentiate from actinic keratoses; premalignant)
Copyright © 2005, Mosby, Inc. All rights reserved.
Age-Related Variations:
Older Adults
• Normal/abnormal findings (cont.)
– Acrochordons (skin tags): tags of skin on
neck/chest
– Sebaceous hyperplasia: yellowish flat papules
with central depression
• Thin parchment skin over bony
prominences, dorsal surface: hands, feet,
forearms, lower leg
• Loose hanging skin on frame: loss of
adipose tissue/elasticity (tenting)
Copyright © 2005, Mosby, Inc. All rights reserved.
Age-Related Variations:
Older Adults
• Hair: gray, thin, coarse
– Symmetric balding in males
– Decreased amount of body hair (pubic,
axillary)
– Men: increase in amount/coarseness
nasal/eyebrow hair; women: increase in
coarse facial hair
Copyright © 2005, Mosby, Inc. All rights reserved.
Clients with Situational Variations
• Limited mobility: at risk for skin breakdown
– Secondary to pressure, body fluid pooling,
decreased ability to feel/change position
– Assess bony prominences
– Hands: calluses from operating wheelchair
Copyright © 2005, Mosby, Inc. All rights reserved.
Clients with Situational Variations
• Normal/abnormal findings
– Skin pressure points: initial pallor with pressure;
rapid return of color when removed
– If no blanching: stage I pressure ulcer
• Stages
– I: increased redness, unbroken skin
– II: partial-thickness skin loss (abrasion, blister)
– III: full-thickness skin loss; damage to
subcutaneous tissue
– IV: full thickness; invasion into deeper tissue/
bone
Copyright © 2005, Mosby, Inc. All rights reserved.
Health Promotion: Skin Cancer
• Most common of cancers (50% of all)
– Open sore more than 3 weeks, not healing,
bleeds, oozes, crusts
• Reddish patch may/not itch or hurt
Copyright © 2005, Mosby, Inc. All rights reserved.
Common Problems and
Conditions: Skin
• Hyperkeratosis (corn)
• Lesions (viral): warts, herpes simplex, H.
varicella, H. zoster, rubeola
• Lesions (fungal): tinea, candidiasis
• Lesions (bacterial): cellulitis, impetigo,
folliculitis, furuncle
Copyright © 2005, Mosby, Inc. All rights reserved.
Common Problems and
Conditions: Skin
• Lesions (arthropods): scabies, Lyme
disease, spider bites
• Lesions (abuse): bruise, bites, burns
Copyright © 2005, Mosby, Inc. All rights reserved.
Common Problems and Conditions
• Hair
– Pediculosis, alopecia areata, hirsuitism
• Nails
– , ingrown toenail
Copyright © 2005, Mosby, Inc. All rights reserved.
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Florida 16-Hour Hair Braider Course: Hair for YouVon EverandFlorida 16-Hour Hair Braider Course: Hair for YouNoch keine Bewertungen
- Skin Sense!: A Dermatologist's Guide to Skin and Facial Care; Third EditionVon EverandSkin Sense!: A Dermatologist's Guide to Skin and Facial Care; Third EditionBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (12)
- Health Assessment of Integument SystemDokument57 SeitenHealth Assessment of Integument SystemkuhakuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Integumentary SystemDokument35 SeitenIntegumentary SystemnaltrisilvianNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 015Dokument21 SeitenChapter 015api-3697326Noch keine Bewertungen
- Assessing The Integumentary SystemDokument199 SeitenAssessing The Integumentary SystemHyacinth Jane Dela PeñaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Integ Skeletal MmsDokument88 SeitenInteg Skeletal MmsTobit Andre CaballoNoch keine Bewertungen
- 05 Skin AssessmentDokument31 Seiten05 Skin AssessmentHerlinaNababanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 024Dokument23 SeitenChapter 024api-3697326Noch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 027Dokument66 SeitenChapter 027api-3697326Noch keine Bewertungen
- Skin, Hair, and Nails AssessmentDokument44 SeitenSkin, Hair, and Nails Assessmentعمر حليم omar haleem100% (1)
- Skin AssessmentDokument45 SeitenSkin AssessmentAbdurehman AyeleNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 013Dokument12 SeitenChapter 013api-3697326Noch keine Bewertungen
- Changes After Death: Dr. Raid JastaniaDokument37 SeitenChanges After Death: Dr. Raid JastaniaRoman MamunNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 025Dokument34 SeitenChapter 025api-3697326Noch keine Bewertungen
- Integumentary System: Rights ReservedDokument15 SeitenIntegumentary System: Rights ReservedMichael RamirezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Integumentary: Mark Ebony C. SumalinogDokument89 SeitenIntegumentary: Mark Ebony C. SumalinogAngel FiloteoNoch keine Bewertungen
- NRSG 102 06tissue Integrity-2Dokument14 SeitenNRSG 102 06tissue Integrity-2Sam Mule SchultzNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCM101 Lesson Guide 7Dokument28 SeitenNCM101 Lesson Guide 7Yahra DatangNoch keine Bewertungen
- UNIT - IV Assesment of Skin Head and NeckDokument48 SeitenUNIT - IV Assesment of Skin Head and Neckraima ayazNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assessment of The Skin: Pat Jackson AllenDokument104 SeitenAssessment of The Skin: Pat Jackson Allenbuzz Q100% (4)
- Facial DiagnosisDokument28 SeitenFacial DiagnosisMonaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Skin Disorders and Diseases: Copied, or Duplicated, or Posted To A Publicly Accessible Website, in Whole or in PartDokument37 SeitenSkin Disorders and Diseases: Copied, or Duplicated, or Posted To A Publicly Accessible Website, in Whole or in PartsofiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction To Dermatology Assessment of A Dermatologic PatientDokument86 SeitenIntroduction To Dermatology Assessment of A Dermatologic PatientAtifNoch keine Bewertungen
- History and Physical Assessment of Integumentary System: By: Mr. M - Shiva Nanda ReddyDokument84 SeitenHistory and Physical Assessment of Integumentary System: By: Mr. M - Shiva Nanda ReddyNilakshi Barik MandalNoch keine Bewertungen
- PLSP Cnahs Assessment of Hair and NailsDokument66 SeitenPLSP Cnahs Assessment of Hair and NailsHarold BarrentoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Skin - Integumentary System (PDFDrive)Dokument97 SeitenSkin - Integumentary System (PDFDrive)Andrew MeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 023Dokument12 SeitenChapter 023api-3697326Noch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction To DermatologyDokument40 SeitenIntroduction To DermatologyGudeta shegerNoch keine Bewertungen
- SKIN, HAIR, NAILS NewDokument35 SeitenSKIN, HAIR, NAILS NewHind Sabahaldin100% (1)
- L1,2,3 - Intro, Anatomy, Language of Dermatologydr. Almontaser BellahDokument102 SeitenL1,2,3 - Intro, Anatomy, Language of Dermatologydr. Almontaser BellahTOMMYNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 024Dokument35 SeitenChapter 024api-3697326Noch keine Bewertungen
- History and Physical Assessment of Integumentary System: Mrs - Nilakshi Barik LecturerDokument84 SeitenHistory and Physical Assessment of Integumentary System: Mrs - Nilakshi Barik LecturerNilakshi Barik MandalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hygiene PresDokument31 SeitenHygiene Presgalaxy113Noch keine Bewertungen
- Examination of Swelling: DR Santosh Mishra Assistant Professor Department of Orthopaedics Gandhi Medical College, BhopalDokument34 SeitenExamination of Swelling: DR Santosh Mishra Assistant Professor Department of Orthopaedics Gandhi Medical College, BhopalSantosh KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 016Dokument23 SeitenChapter 016api-3697326Noch keine Bewertungen
- Skinhairnails330 Gsu F 09 090902153538 Phpapp02Dokument42 SeitenSkinhairnails330 Gsu F 09 090902153538 Phpapp02Trisha Mae BalladNoch keine Bewertungen
- Terminology in DermatologyDokument8 SeitenTerminology in DermatologyHesbon MomanyiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physical Assessment of The Skin, Head, and NeckDokument81 SeitenPhysical Assessment of The Skin, Head, and NeckPark chin-haeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Identification of The Living and The DeadDokument38 SeitenIdentification of The Living and The DeadSoleh RamlyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Skin AssessmentDokument50 SeitenSkin AssessmentNayel ZeeshanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Internal DiseasesDokument409 SeitenInternal DiseasesPatrick Igbinoba - MFNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 003Dokument15 SeitenChapter 003api-3697326Noch keine Bewertungen
- Skin Hair NailsDokument27 SeitenSkin Hair NailsKristine Joy Librando EscalanteNoch keine Bewertungen
- INDIVIDUAL HYGIENE REQUIREMENTS - KopyaDokument160 SeitenINDIVIDUAL HYGIENE REQUIREMENTS - KopyaIlker AlpçetinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 021Dokument6 SeitenChapter 021api-3697326Noch keine Bewertungen
- Skin - Hair.Nails Head & Neck Eyes. Ears. Nose. Sinuses Mouth. PharynxDokument92 SeitenSkin - Hair.Nails Head & Neck Eyes. Ears. Nose. Sinuses Mouth. PharynxAT4-11 HUMSS 2 CEDRICK ILAO100% (1)
- Human AnaPhy C3 - The Integumentary SystemDokument55 SeitenHuman AnaPhy C3 - The Integumentary SystemSandy CaliguiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Skins - : Starting OffDokument25 SeitenSkins - : Starting OffSilviuNoch keine Bewertungen
- External Examination: Dr. Ibnu Gilang SyawaliDokument24 SeitenExternal Examination: Dr. Ibnu Gilang SyawaliIbnu Gilang SyawaliNoch keine Bewertungen
- LM4 - (I) Identification & DNA FingerprintingDokument119 SeitenLM4 - (I) Identification & DNA FingerprintingBa ShangNoch keine Bewertungen
- Elderly Skin CareDokument46 SeitenElderly Skin CareRobbyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Integumentary System PDFDokument29 SeitenIntegumentary System PDFGayathri SNoch keine Bewertungen
- Med1 NotesDokument3 SeitenMed1 NotesEly Lyoid SingzonNoch keine Bewertungen
- ws08 Elderly Skin CareDokument46 Seitenws08 Elderly Skin CareRobbyNoch keine Bewertungen
- 3 Physical Assessment of The IntegumentDokument64 Seiten3 Physical Assessment of The IntegumentRex CaasiNoch keine Bewertungen
- L2 Integumentary Assessment PDFDokument46 SeitenL2 Integumentary Assessment PDFElizabeth AbellaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Wound and Skin CareDokument146 SeitenWound and Skin CareMichael Villavert100% (1)
- Physical Nursing Care of Older AdultsDokument20 SeitenPhysical Nursing Care of Older AdultsKaren Joyce Costales MagtanongNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dr. R. Sekhon - Dermatology Telehealth Jan 27 MRDokument45 SeitenDr. R. Sekhon - Dermatology Telehealth Jan 27 MRAnissa ADNoch keine Bewertungen
- Review For CBF Exam ONEDokument2 SeitenReview For CBF Exam ONEapi-3697326Noch keine Bewertungen
- Instructors's DP Spring 07Dokument1 SeiteInstructors's DP Spring 07api-3697326Noch keine Bewertungen
- 9cc97fec Bbed 44bf b69c 5e52a52a9faeDokument49 Seiten9cc97fec Bbed 44bf b69c 5e52a52a9faeapi-3697326Noch keine Bewertungen
- Cha 0011Dokument7 SeitenCha 0011api-3697326Noch keine Bewertungen
- Cha 0012Dokument6 SeitenCha 0012api-3697326100% (1)
- Daily PlanDokument2 SeitenDaily Planapi-3697326100% (1)
- Mental Health and Mental IllnessDokument13 SeitenMental Health and Mental Illnessapi-36973260% (1)
- Peripheral Arterial Disease of The Lower ExtremitiesDokument25 SeitenPeripheral Arterial Disease of The Lower Extremitiesapi-3697326100% (1)
- Cha 0014Dokument9 SeitenCha 0014api-3697326Noch keine Bewertungen
- RNSG 1331 Exam 2 Blueprint v2Dokument2 SeitenRNSG 1331 Exam 2 Blueprint v2api-3697326Noch keine Bewertungen
- Respiratory 3Dokument36 SeitenRespiratory 3api-3697326Noch keine Bewertungen
- CH 09Dokument20 SeitenCH 09api-3697326100% (1)
- Cha 0009Dokument8 SeitenCha 0009api-3697326Noch keine Bewertungen
- Cha 0001Dokument7 SeitenCha 0001api-3697326Noch keine Bewertungen
- Fe 4Dokument36 SeitenFe 4api-3697326Noch keine Bewertungen
- P A I N 1my Power PointDokument38 SeitenP A I N 1my Power Pointapi-3697326100% (1)
- Learning Guide: Central Texas College Department of NursingDokument26 SeitenLearning Guide: Central Texas College Department of Nursingapi-3697326Noch keine Bewertungen
- Respiratory 4 Spring 07Dokument26 SeitenRespiratory 4 Spring 07api-3697326Noch keine Bewertungen
- Fe 2Dokument26 SeitenFe 2api-3697326Noch keine Bewertungen
- Respirations 1Dokument42 SeitenRespirations 1api-3697326Noch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 027Dokument66 SeitenChapter 027api-3697326Noch keine Bewertungen
- Fe 1Dokument36 SeitenFe 1api-3697326Noch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 021Dokument6 SeitenChapter 021api-3697326Noch keine Bewertungen
- FE2 OutlineDokument9 SeitenFE2 Outlineapi-3697326Noch keine Bewertungen
- FE3 ABbalanceoutlineDokument9 SeitenFE3 ABbalanceoutlineapi-3697326Noch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 023Dokument12 SeitenChapter 023api-3697326Noch keine Bewertungen
- Fe 3Dokument43 SeitenFe 3api-3697326Noch keine Bewertungen
- Class Schedule TableDokument1 SeiteClass Schedule Tableapi-3697326Noch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 024Dokument23 SeitenChapter 024api-3697326Noch keine Bewertungen
- Alopecia: By. Mr. P. Dhilip KumarDokument9 SeitenAlopecia: By. Mr. P. Dhilip Kumarpreet kaur100% (1)
- Pingen, Kathleen Joy R. BSN 3A Management of CancerDokument2 SeitenPingen, Kathleen Joy R. BSN 3A Management of CancerKathleen Joy PingenNoch keine Bewertungen
- AlopeciaDokument1 SeiteAlopeciachoobiNoch keine Bewertungen
- AumosaloDokument142 SeitenAumosaloPatita García100% (1)
- RL AlopeciaDokument2 SeitenRL AlopeciabelgianwafflingNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hairdressing LASDokument82 SeitenHairdressing LASGracelyn Gador100% (3)
- Describing Famous PeopleDokument3 SeitenDescribing Famous PeopleSandra AmeixinhaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biotin Benefits PDFDokument8 SeitenBiotin Benefits PDFRocco LamponeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Katherine Jackson V AEG Live Transcripts of Debbie Rowe (MJ's Ex Wife-Dr Klein's Ex Assistant August 15th 2013Dokument69 SeitenKatherine Jackson V AEG Live Transcripts of Debbie Rowe (MJ's Ex Wife-Dr Klein's Ex Assistant August 15th 2013TeamMichael80% (5)
- Materi - AlopeciaDokument27 SeitenMateri - Alopecia6130015013 MOCHAMMAD SULUNG NOVIYANTO SKMNoch keine Bewertungen
- Kesh Dant NakhDokument6 SeitenKesh Dant Nakhdouble slit photon50% (2)
- UC Davis Koret Shelter Medicine Program - Flea Treatment in Animal Shelters - 2013-10-09Dokument2 SeitenUC Davis Koret Shelter Medicine Program - Flea Treatment in Animal Shelters - 2013-10-09Kitt KaosNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dry Dandruff With Meaning and PictureDokument3 SeitenDry Dandruff With Meaning and PictureMargie Ballesteros ManzanoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Merchant Marine Academy 2nd Semester - P. Papaleonidas - 2011-89-99Dokument11 SeitenMerchant Marine Academy 2nd Semester - P. Papaleonidas - 2011-89-99Наталья ЛандикNoch keine Bewertungen
- PRP in DermatologyDokument36 SeitenPRP in DermatologySuryakant HayatnagarkarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Microsoft PowerPoint - Hair N Nail - PPT (Compatibility Mode)Dokument4 SeitenMicrosoft PowerPoint - Hair N Nail - PPT (Compatibility Mode)kamalab04Noch keine Bewertungen
- Addictions - Homeopathic Treatment of AddictionsDokument183 SeitenAddictions - Homeopathic Treatment of Addictionsbuscador0077100% (3)
- Planetary Secrets of BaldnessDokument9 SeitenPlanetary Secrets of BaldnessJayasree Saranathan50% (2)
- Vitamin D & Alopecia AreataDokument2 SeitenVitamin D & Alopecia AreataMohitNoch keine Bewertungen
- QLM Insurance BenefitsDokument13 SeitenQLM Insurance BenefitsJasmin RacaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Beauty WP March 2023Dokument43 SeitenBeauty WP March 2023OrochiNoch keine Bewertungen
- 206897hair Transplant in Turkey ClinicDokument3 Seiten206897hair Transplant in Turkey ClinichairtransplantmailtronlineabcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxNoch keine Bewertungen
- Trichology PDFDokument10 SeitenTrichology PDFDr-Arun Chugh33% (3)
- The Truth About Hair LossDokument14 SeitenThe Truth About Hair LossxdgddgsdgddNoch keine Bewertungen
- Health AssessmentDokument165 SeitenHealth AssessmentJen Gatchalian100% (1)
- 10 Tips For Natural Hair Regrowth 2Dokument2 Seiten10 Tips For Natural Hair Regrowth 2Tom TambeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Annotated BibliographyDokument2 SeitenAnnotated Bibliographyapi-288338012Noch keine Bewertungen
- ThesisDokument20 SeitenThesisKaiye Rasonable100% (1)
- News Broadcast LessonDokument4 SeitenNews Broadcast LessonConnie Diaz CarmonaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tricho ScanDokument10 SeitenTricho ScanFenni OktoberryNoch keine Bewertungen