Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Lecture 4
Hochgeladen von
gsathyascewCopyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Lecture 4
Hochgeladen von
gsathyascewCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
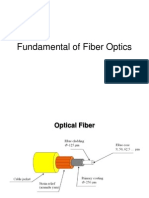
EE 230: Optical Fiber Communication Lecture 4
From the movie
Warriors of the Net
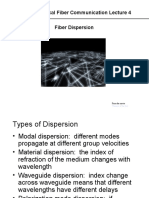
Fiber Dispersion
Types of Dispersion
Modal dispersion: different modes
propagate at different group velocities
Material dispersion: the index of
refraction of the medium changes with
wavelength
Waveguide dispersion: index change
across waveguide means that different
wavelengths have different delays
Polarization mode dispersion: if
waveguide is birefringent
Definitions
Group velocity
Group delay
Dispersion
1
|
.
|
\
|
c
c
=
e
|
g
v
k c c
c
=
c
c
=
|
e
|
t
1
t
c
c
= D
Wave Packet Construction
Group and Phase Velocity
Transform Limited Frequency Spread
Optics-Hecht & Zajac
Rectangular Pulse
Pulse modulated Sine wave
Gaussian modulated Sine wave
Spectral properties of digitally modulated signals1
No spectral component at the clock frequency
For Non-Return to Zero Encoded Data
Pulse Propagation through Fibers
Fundamentals of Photonics - Saleh and Teich
Response of a multi-mode fiber to a single
short pulse
Broadening of a short pulse after transmission
through different types of fibers
Material Dispersion
Refractive Index of Pure Silica and its derivatives
Fiber Optic Communications-Palais
Material Dispersion Parameter for pure silica
and germanium doped silica
Optical Fiber Communications-Keiser
Zero Dispersion Slope
Fiber Optics Communication Technology-Mynbaev & Scheiner
Fiber Dispersion
Pulse Degradation from Dispersion
Ray optics View of the origin of waveguide dispersion
Typical fiber Dispersion Curve
Dispersion:The change in speed of propagation with wavelength
Polarization Mode Dispersion
Polarization Maintaining Fiber
Non-Polarization Maintaining Fiber
Random power transfer occurs between different polarization modes
as the pulse propagates, if the two modes have different propagation velocities
then the pulse will broaden
Representative Fiber Characteristics
Dispersion for various Fiber Types
Dispersion Shifted and Dispersion
Flattened Fibers
Fundamentals of Photonics - Saleh and Teich
Waveguide Dispersion mechanism
As l, Mode field diameter l
More of the mode travels in the cladding.
Cladding index is lower so pulse velocity l
resulting in dispersion
Chromatic Dispersion Parameters of
a singlemode fiber
Comparison of Dispersion Characteristics
Propagation of Gaussian Pulses
Input Pulse Output Pulse
chirped and broadened
Input Pulse
Already Positively
Chirped
After some distance
the chirp is removed
and the pulse assumes its
minimum possible width
Upon further propagation
the pulse will continue to broaden
and acquire chirp.
|
2
<0 for standard single mode silica fiber
and Ld ~ 1800 km at 2.5 Gb/s and ~115 km at 10 Gb/s
Optical Networks a Practical Perspective-Ramaswami and Sivarajan
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- EE 230: Optical Fiber Communication Lecture 4 Fiber DispersionDokument17 SeitenEE 230: Optical Fiber Communication Lecture 4 Fiber DispersionmofiwNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit-1 and 2 OpticalDokument278 SeitenUnit-1 and 2 OpticalGuru VelmathiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Optical Fiber-Dispersion SP 2014Dokument19 SeitenOptical Fiber-Dispersion SP 2014Ajay DillikarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dispersion FODokument18 SeitenDispersion FODorinel IonascuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dispersion in Optical FiberDokument36 SeitenDispersion in Optical FiberSonakshi GuptaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture5 DispersionDokument20 SeitenLecture5 DispersionVandana NathNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fiber Optics: Understanding the BasicsDokument6 SeitenFiber Optics: Understanding the BasicsAsaduzzaman KhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pertemuan 5 - 6 - DISPERSIONDokument8 SeitenPertemuan 5 - 6 - DISPERSIONGita Sukma DevyanaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dispersion Management Techniques and Their Limitations in Optical Communication SystemsDokument84 SeitenDispersion Management Techniques and Their Limitations in Optical Communication SystemsAbhinav ChoukseyNoch keine Bewertungen
- EE 5551 10gDokument12 SeitenEE 5551 10gPMVamsiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ofc Assign02Dokument4 SeitenOfc Assign02Asad MalikNoch keine Bewertungen
- Optical fiber waveguides modes and typesDokument73 SeitenOptical fiber waveguides modes and typesgeorge samyNoch keine Bewertungen
- UNIT - 2 DispersionDokument20 SeitenUNIT - 2 DispersionNGSNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dispersion in Fiber Systems: EE 548 Spring 2005Dokument24 SeitenDispersion in Fiber Systems: EE 548 Spring 2005Bui TheQuanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dispersion 1 PP TDokument21 SeitenDispersion 1 PP TShivani Ekant YadavNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fiber Optics: Fiber Basics: The Fiber As A Dielectric Wave-Guide: Fiber ModesDokument6 SeitenFiber Optics: Fiber Basics: The Fiber As A Dielectric Wave-Guide: Fiber ModesDhani KatariaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lect 4Dokument28 SeitenLect 4george samyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Power Point Presentation On Analysis and Reduction of Polarization Mode DispersionDokument12 SeitenPower Point Presentation On Analysis and Reduction of Polarization Mode Dispersiongvr11100% (1)
- Signal Degradation in Optical FibersDokument5 SeitenSignal Degradation in Optical FibersijeteeditorNoch keine Bewertungen
- Study Dispersion Optical Fiber CommunicationDokument9 SeitenStudy Dispersion Optical Fiber CommunicationFaez FawwazNoch keine Bewertungen
- 02 B AnuragY Dispersion SlidesDokument11 Seiten02 B AnuragY Dispersion SlidesDeepansh AgrawalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Optical Communication 2mark PDFDokument20 SeitenOptical Communication 2mark PDFAnant ShankarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Optical Fiber Communication Lecture 1Dokument57 SeitenOptical Fiber Communication Lecture 1Achala DeshmukhNoch keine Bewertungen
- Wave Guide DispersionDokument3 SeitenWave Guide DispersionSriraj ChinnaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Optics Fundamentals and Applications of Optical FibersDokument12 SeitenOptics Fundamentals and Applications of Optical FibersFadil N.Muhammad58% (12)
- Ofcli 5Dokument9 SeitenOfcli 5ALINoch keine Bewertungen
- Fiber Optics Part IDokument46 SeitenFiber Optics Part ImariahvahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fiber Optic Communication FundamentalsDokument201 SeitenFiber Optic Communication FundamentalsMax DurendNoch keine Bewertungen
- Optical Communication Question BankDokument24 SeitenOptical Communication Question BankdhivyakrishnaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Optical Fibers: High-Speed, Long-Distance Data TransmissionDokument9 SeitenOptical Fibers: High-Speed, Long-Distance Data Transmissionmuhammad atiqNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fibre Optic Communication PDFDokument199 SeitenFibre Optic Communication PDFBiswarup MukherjeeNoch keine Bewertungen
- OPTICAL ASSIGNMENTDokument28 SeitenOPTICAL ASSIGNMENTKayonde VanessaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lec13 ES475 2023 UploadDokument38 SeitenLec13 ES475 2023 UploadUmar AhmadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lec12 ES475 2023 UploadDokument21 SeitenLec12 ES475 2023 UploadUmar AhmadNoch keine Bewertungen
- What Is Chromatic DispersionDokument8 SeitenWhat Is Chromatic DispersionNishad PatilNoch keine Bewertungen
- OFC TechnologyDokument52 SeitenOFC TechnologyBattinapati ShivaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Optical Fiber Measurements, Advanced Multiplexing StrategiesDokument14 SeitenOptical Fiber Measurements, Advanced Multiplexing StrategiesNAGASWATHI NIDAMANURINoch keine Bewertungen
- Optical Fiber Dispersion: Understanding Pulse Broadening in FibersDokument6 SeitenOptical Fiber Dispersion: Understanding Pulse Broadening in FibersAgnivesh SharmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture: Signal Distortion On Optical Fibers - DispersionDokument12 SeitenLecture: Signal Distortion On Optical Fibers - DispersionMuhammad OwaisNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lec.4 - COMM 554 Optical Communication SystemsDokument23 SeitenLec.4 - COMM 554 Optical Communication SystemsMahmoud SayedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fiber Optics Module 1Dokument63 SeitenFiber Optics Module 1Ravi Teja AJNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dielectric Waveguides and Optical Fibers: Slab Waveguide, Modes, V-Number Modal, Material, and Waveguide DispersionsDokument34 SeitenDielectric Waveguides and Optical Fibers: Slab Waveguide, Modes, V-Number Modal, Material, and Waveguide Dispersionszoex924Noch keine Bewertungen
- Sec5 Optical FiberDokument22 SeitenSec5 Optical Fiberaelsheikh834Noch keine Bewertungen
- Optical Fiber Signal Attenuation Causes and Dispersion EffectsDokument44 SeitenOptical Fiber Signal Attenuation Causes and Dispersion Effectskumarnath jNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture4 150124043507 Conversion Gate02 PDFDokument17 SeitenLecture4 150124043507 Conversion Gate02 PDFVijay JanyaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Oc Module 1-6 PDFDokument162 SeitenOc Module 1-6 PDFTintu TrmNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lec14 ES475 2023 Upload PDFDokument32 SeitenLec14 ES475 2023 Upload PDFEmad RazaNoch keine Bewertungen
- OFC EquipmentDokument135 SeitenOFC Equipmentlvsaru0% (2)
- Ofc TheoryDokument69 SeitenOfc TheorynainaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 4: Optical Fibers and Their ParametersDokument19 SeitenChapter 4: Optical Fibers and Their ParameterszqandahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dispersion: in This ChapterDokument6 SeitenDispersion: in This ChapterlvsaruNoch keine Bewertungen
- Optic FiberDokument31 SeitenOptic Fiberkeregi100% (1)
- OC - Lect - 05 Aziz AlhaidariDokument34 SeitenOC - Lect - 05 Aziz Alhaidariabdulaziz saif ali mansoorNoch keine Bewertungen
- Optical Fiber SensorsDokument39 SeitenOptical Fiber SensorsShahrukh KhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- OC-Module 2aDokument24 SeitenOC-Module 2aRaju PaladuguNoch keine Bewertungen
- SolitonDokument19 SeitenSolitonMustafa_elecNoch keine Bewertungen
- OpticalDokument90 SeitenOpticalsachin50% (4)
- EE3110 Oscillator FundamentalsDokument26 SeitenEE3110 Oscillator Fundamentalsaaljuhani123Noch keine Bewertungen
- Phase Shift OscillatorsDokument51 SeitenPhase Shift OscillatorsJainuddin ShNoch keine Bewertungen
- Grammar RulesDokument9 SeitenGrammar RulesgsathyascewNoch keine Bewertungen
- CAIIB Financial Management Module ADokument100 SeitenCAIIB Financial Management Module Amukesh271248Noch keine Bewertungen
- Capture by A Phase-Locked Loop: By: Walter Banzhaf, P.EDokument3 SeitenCapture by A Phase-Locked Loop: By: Walter Banzhaf, P.EgsathyascewNoch keine Bewertungen
- Digital CommunicationDokument45 SeitenDigital CommunicationgsathyascewNoch keine Bewertungen
- Computers For Bank Exams - Guide4BankExamsDokument82 SeitenComputers For Bank Exams - Guide4BankExamsShiv Ram Krishna100% (4)
- EE3110 Oscillator FundamentalsDokument26 SeitenEE3110 Oscillator Fundamentalsaaljuhani123Noch keine Bewertungen
- MicroDokument127 SeitenMicronarayanan07Noch keine Bewertungen
- Digital CommunicationDokument9 SeitenDigital CommunicationgsathyascewNoch keine Bewertungen
- E D F A: Seminar By: Geno G James EE-566 Optical CommunicationDokument17 SeitenE D F A: Seminar By: Geno G James EE-566 Optical CommunicationgsathyascewNoch keine Bewertungen
- Adc Notes 1Dokument20 SeitenAdc Notes 1gsathyascewNoch keine Bewertungen
- Digital Comommunication For VtuDokument59 SeitenDigital Comommunication For Vtu9964484036Noch keine Bewertungen
- Wireless CommunicationsDokument68 SeitenWireless CommunicationsSriramNoch keine Bewertungen
- Viettel PresentationDokument25 SeitenViettel PresentationDuy NguyenNoch keine Bewertungen
- JVC KD r540 Manual de InstruccionesDokument16 SeitenJVC KD r540 Manual de InstruccionesJesus FloresNoch keine Bewertungen
- Solucionario Libro Infotech 4th EditionDokument32 SeitenSolucionario Libro Infotech 4th EditionGisella Espinoza BarberenaNoch keine Bewertungen
- PT2313L PDFDokument3 SeitenPT2313L PDFMaugrys Castillo100% (1)
- Schlumberger Basic MWDDokument20 SeitenSchlumberger Basic MWDMo'men AlyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Infineon IRFZ44N DataSheet v01 - 01 ENDokument9 SeitenInfineon IRFZ44N DataSheet v01 - 01 ENIkram RidhoNoch keine Bewertungen
- 74HC4060Dokument12 Seiten74HC4060jnax101Noch keine Bewertungen
- Milesight AI Outdoor Parking Management Camera Datasheet enDokument5 SeitenMilesight AI Outdoor Parking Management Camera Datasheet enAntonia ZhangNoch keine Bewertungen
- MSP 430 G 2452Dokument63 SeitenMSP 430 G 2452Đặng Quốc HuyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Basic Principles of Fiber Optic CommunicationDokument3 SeitenBasic Principles of Fiber Optic CommunicationHumayra Anjumee100% (2)
- 01-Basics of AntennasDokument39 Seiten01-Basics of AntennasHenrique NetoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Eflash: Contractual Information For Partners: Phase-OutDokument2 SeitenEflash: Contractual Information For Partners: Phase-OutMoises ReznikNoch keine Bewertungen
- Suntrio Plus 12-20K-Datasheet 201907Dokument1 SeiteSuntrio Plus 12-20K-Datasheet 201907ali ahmadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Iot Based Toll Booth Management System: Aadish Joshi, Gaurav Bhide, Shreyas Patil, R. D. KomatiDokument5 SeitenIot Based Toll Booth Management System: Aadish Joshi, Gaurav Bhide, Shreyas Patil, R. D. Komatiakash mishraNoch keine Bewertungen
- UC2505Dokument5 SeitenUC2505Angelo ZuñigaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Xdca4252 SB51Dokument1 SeiteXdca4252 SB51Eong Huat Corporation Sdn BhdNoch keine Bewertungen
- Adva FSP 3000Dokument16 SeitenAdva FSP 3000giorgio802000Noch keine Bewertungen
- Hardware Design of a Data Controller for NAND Flash MemoryDokument33 SeitenHardware Design of a Data Controller for NAND Flash MemoryDevasish BhagawatiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Is Now Part ofDokument18 SeitenIs Now Part ofSOLUCIÓN ELECTRÓNICANoch keine Bewertungen
- Mobile PhoneDokument22 SeitenMobile PhoneelisiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 300tpx 400tpx EngDokument1 Seite300tpx 400tpx EngNiraj YadavNoch keine Bewertungen
- Radio WavesDokument14 SeitenRadio WavesSian Dasstin TanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Acm Mixer Study GuideDokument3 SeitenAcm Mixer Study Guidegistoledo1911Noch keine Bewertungen
- Onkyo HTR 580 Service ManualDokument94 SeitenOnkyo HTR 580 Service ManualCarlosRobertoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Man Handwheel UfoDokument2 SeitenMan Handwheel UfoAloisio GonzagaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cipt1 Vol 1&2 PDFDokument864 SeitenCipt1 Vol 1&2 PDFSid Ali Oulad SmaneNoch keine Bewertungen
- Stepper Motor Controller Guide Using L298 and L297 DriversDokument6 SeitenStepper Motor Controller Guide Using L298 and L297 DriversmoannaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Canon A1 SPT Guide PDFDokument10 SeitenCanon A1 SPT Guide PDFWeijia MaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Research Bookbind Upd 6Dokument41 SeitenResearch Bookbind Upd 6MattJimuelQuililanNoch keine Bewertungen