Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Erp Related Technologies
Hochgeladen von
Foru KharaOriginalbeschreibung:
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Erp Related Technologies
Hochgeladen von
Foru KharaCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
ERP & Related Technologies
Limitation of ERP
Managers cannot generate custom reports or queries without help from a programmer.
This restricts them from obtaining information quickly and act on it in this competitive market.
ERP system provide current status only such as open orders. The data in ERP is not integrated with other enterprise or division system and does not include external intelligence.
Overcoming the Limitations
There are many technologies that help to overcome these limitations. These technologies when used in conjunction with ERP system help for better decision making and also help in overcoming limitations of ERP. Organizations are constantly innovating methods to improve organizational efficiency, reduce cost, provide high quality, personalized customer service, customer satisfaction , increased profit margin.
Companies use these technologies to integrate it into core of their business planning and are ready to face the challenges of conducting business in this
Technologies
Some of these technologies when integrated with ERP system , enable companies to do business at internet speed. These technologies are :
Business Process Re-engineering (BPR).
Management Information System (MIS). Decision Support System (DSS).
Executive Information Systems (EIS). Data Warehousing. Data Mining. On-line Analytical Processing (OLAP).
Business Process Re-engineering (BPR).
Dr. Michael Hammer defines BPR as the fundamental rethinking and radical redesign of business processes to achieve dramatic improvements in critical, contemporary measures of performance such as cost, quality, services and speed. One of the main tools for making this change is the Information Technology(IT). Any BPR effort that fails to understand the importance of IT, and goes through the pre-BPR analysis and planning phases without considering the various IT options available, is bound to crash during take off.
Management Information System (MIS).
MIS is a computer based system that optimizes the collection, collation, transfer and presentation of information throughout an organization, through an integrated structure of databases and information flow. MIS supports data processing functions of transaction handling and record keeping. MIS uses an integrated database Integrates the information flow between functional areas. MIS provides operational, tactical and strategic
Decision Support System (DSS).
Managers spend a lot of time and effort in gathering and analyzing information before making decisions. Decision support systems are interactive information systems that rely on an integrated set of user-friendly software and hardware tools, to produce and present information targeted to support management in the decision making process. DSS allow manager to improve the quality of their decision.
DSS facilitates decision making process, choose between alternatives; automatically rank the alternatives.
DSS
designed to address semi-structured and unstructured problems. supports decision-making at the top management level. interactive, user-friendly.
Difference between MIS & DSS.
Executive Information System (EIS)
EIS is better and sophisticated DSS. EIS is a DSS especially made for senior level executives.
concerned with how decisions affect the entire organization.
An EIS takes the following into considerations:
vision and mission & the company goals. Strategic planning and objectives. Organizational structure. Crisis management/ contingency planning.
Data Warehousing
Operational data in the database increases as time passes Affects the performance of the ERP system. Better to archive data once its use is over. E.g. Once the financial year is over, the daily transaction data can be archive. As volume of data in the database increases , the performance of database and related application decreases. Solution :- separate operational data from non operational data (not archive data).
A data warehouse is designed to support decision making in organization. Data warehouse is a combination of different database across the organization. the data stored for the business analysis can be accessed most effectively by separating it from the data in operational systems. High performance and quick response time.
A data mart is a collection of database enabling managers for better decision making.
Usually smaller and focus on particular dept.
Data Mining
Data mining is the process of identifying valid, novel, potentially useful and ultimately comprehensible information from databases that is used to make crucial business decisions. Need for data mining :
enormous volume of existing and newly appearing data that require processing. The amount of data accumulated each day by various businesses, scientific and governmental organizations around the world is daunting. Research organizations, academic institutions and commercial organizations create and store huge amounts
Data mining is sorting through data to identify certain patterns and establish relationships among data. E.g . Data mining s/w can help retail companies to find customers with common interest. Data mining parameters include :
Association
Sequence Classification Clustering Forecasting (predictive analysis)
On-Line Analytical Processing (OLAP)
OLAP is a decision support s/w that allows users to quickly analyze information that has been summarized into multidimensional views.
OLAP is a s/w tool that provides analysis of data stored in the database.
Used to perform trend analysis on sales and financial information, marketing analysis, financial reporting and consolidation, budgeting and planning. Used in Data Mining. OLAP can be defined in five words Fast Analysis of Shared Multi-dimensional Information.
OLAP
FAST :
deliver most responses to users within about 5 seconds.
ANALYSIS :
system can cope with any business logic and statistical analysis relevant for the application and the user.
SHARED :
system implements all the security requirements for confidentiality. provide concurrent update locking at an appropriate level.
MULTI-DIMENSIONAL :-
OLAP is used in applications such as :
Product profitability
Pricing analysis
Activity based costing Manpower planning Quality analysis
Supply Chain Management (SCM)
A supply chain is a network of facilities and distribution options that performs the function of procurement of materials, transformation of these materials into intermediate and finished products and the distribution of these finished products to the customers. SCM plans all movement and storage of raw materials, work in progress, inventory and finished goods from point of origin to point of consumption. Need for SCM :
All the depts in organization along with supply chain operated independently.
CRM
GIS
Refer Alexis Leon PPTs
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Introduction To System Analysis and DesignDokument22 SeitenIntroduction To System Analysis and DesignHiranya100% (2)
- ERP and Related TechnologiesDokument6 SeitenERP and Related Technologiessadanand143Noch keine Bewertungen
- Fill in The BlanksDokument5 SeitenFill in The BlanksSaurabh GuptaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 4 - ERP A Manufacturing PerspectiveDokument18 SeitenChapter 4 - ERP A Manufacturing PerspectiveHarold Falip100% (1)
- WesternDokument3 SeitenWesternSakshi Khurana100% (2)
- Module 3 - Evaluation of Business PerformanceDokument17 SeitenModule 3 - Evaluation of Business PerformanceHoney Jane Tabugoc TajoraNoch keine Bewertungen
- ERP Unit 15 Future Directions in ERP PPT FinalDokument13 SeitenERP Unit 15 Future Directions in ERP PPT FinalAnonymous bTh744z7E6100% (1)
- IT - ERP NotesDokument103 SeitenIT - ERP Notesristadi_asoyNoch keine Bewertungen
- INVENTORY MANAGEMENT AbstractDokument2 SeitenINVENTORY MANAGEMENT AbstractKrishna Sudha67% (6)
- What Are The Benefits of A Financial Management Information SystemDokument5 SeitenWhat Are The Benefits of A Financial Management Information SystemSandra MagnoNoch keine Bewertungen
- ERP SyllabusDokument2 SeitenERP Syllabusmkjhaignou100% (3)
- BA7205 Information ManagementDokument20 SeitenBA7205 Information ManagementPalani Arunachalam0% (1)
- Case StudyDokument4 SeitenCase StudyBegemidircollegeof TeachersEducation0% (1)
- Chapter-I: Management System. We Understand That Payroll Management Systemin Not A Product To BeDokument22 SeitenChapter-I: Management System. We Understand That Payroll Management Systemin Not A Product To BeShankarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Maintain Business Records QuizDokument9 SeitenMaintain Business Records QuizSabah SiddiquiNoch keine Bewertungen
- CO 1. Nature and Scope of Operations ManagementDokument25 SeitenCO 1. Nature and Scope of Operations ManagementMahal SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- Management SystemDokument15 SeitenManagement SystemSatya Prakash MehraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Final Report On A Digital Library ProjectDokument14 SeitenFinal Report On A Digital Library ProjectAileen50% (2)
- Ch07 - Process Modeling, Process Improvement and ERP ImplementationDokument48 SeitenCh07 - Process Modeling, Process Improvement and ERP ImplementationMohammed FahadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Capacity Planning in BankingDokument3 SeitenCapacity Planning in BankingJithesh JanardhananNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assignment For Project Analysis and ManagementDokument3 SeitenAssignment For Project Analysis and Managementzemedu abebe100% (1)
- Management Information System: Unit - 1 Introduction (1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9)Dokument46 SeitenManagement Information System: Unit - 1 Introduction (1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9)gops234Noch keine Bewertungen
- MIS With Functional Areas of BusinessDokument29 SeitenMIS With Functional Areas of Businessariel0429100% (10)
- IkdDokument9 SeitenIkdickjdd50% (2)
- Objectives of A FirmDokument3 SeitenObjectives of A Firmyasheshgaglani100% (1)
- Advantages & Limitations of Operations ResearchDokument8 SeitenAdvantages & Limitations of Operations ResearchMayank Pandey100% (1)
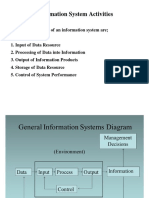
- Information System ActivitiesDokument6 SeitenInformation System ActivitiesDr. Shailendra Kumar Srivastava100% (2)
- Project TerminationDokument23 SeitenProject TerminationSanchit Batra100% (2)
- Project Title "Impact of Fii'S On Indian Stock Market"Dokument12 SeitenProject Title "Impact of Fii'S On Indian Stock Market"Ganaie AhmadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Enterprise Resource Planning - Lecture Notes, Study Material and Important Questions, AnswersDokument4 SeitenEnterprise Resource Planning - Lecture Notes, Study Material and Important Questions, AnswersM.V. TVNoch keine Bewertungen
- Financing DecisionsDokument14 SeitenFinancing DecisionsNandita ChouhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Difference Between A Functional Manager and A Project ManagerDokument7 SeitenDifference Between A Functional Manager and A Project ManageriftikharNoch keine Bewertungen
- Data Security Considerations - (Backups, Archival Storage and Disposal of Data)Dokument3 SeitenData Security Considerations - (Backups, Archival Storage and Disposal of Data)Dev SharmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mis SyllabusDokument1 SeiteMis SyllabusPrasanth KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Capstone Project 2016 FullDokument197 SeitenCapstone Project 2016 FullDu PhongNoch keine Bewertungen
- ERP - Unit 14 - ERP Vendors, Consultants, and Users - PPT - Final ReveiwDokument12 SeitenERP - Unit 14 - ERP Vendors, Consultants, and Users - PPT - Final ReveiwAnonymous bTh744z7E6Noch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 1Dokument76 SeitenChapter 1Jesty AlbagNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fact Finding TechniquesDokument11 SeitenFact Finding TechniquesValrie Coley-Brown100% (1)
- Business Finance: Review of Financial Statement Preparation, Analysis and InterpretationDokument33 SeitenBusiness Finance: Review of Financial Statement Preparation, Analysis and InterpretationMelissa BattadNoch keine Bewertungen
- EOC Questions: Dr. Faouzi MaddouriDokument6 SeitenEOC Questions: Dr. Faouzi MaddouriTara Mecca LunaNoch keine Bewertungen
- System Analysis and Design - BCADokument3 SeitenSystem Analysis and Design - BCARiyaz Sheikh50% (2)
- Social Issues in Tech. MGMTDokument2 SeitenSocial Issues in Tech. MGMTUtshav PoudelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Survey QuestionnaireDokument16 SeitenSurvey QuestionnaireNageshwar SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- CH 6Dokument2 SeitenCH 6Jao FloresNoch keine Bewertungen
- HRMS DocumentationDokument68 SeitenHRMS Documentationabuye king0% (1)
- Working Capital QuestionnaireDokument5 SeitenWorking Capital QuestionnairePriNcess Asma0% (1)
- Course Outline For Business Research MethodsDokument4 SeitenCourse Outline For Business Research MethodsaleneNoch keine Bewertungen
- Case1.1 Hershey's EnterpriseDokument2 SeitenCase1.1 Hershey's EnterpriseFatimah Altamimi100% (2)
- Systems Development Investigation and AnalysisDokument15 SeitenSystems Development Investigation and AnalysisAditya Singh100% (1)
- An Overview of Business ProcessDokument22 SeitenAn Overview of Business Processalemayehu100% (1)
- Executive Support SystemDokument9 SeitenExecutive Support SystemHemavathi Hema100% (1)
- Concept, Nature, Scope and Functions of ManagementDokument8 SeitenConcept, Nature, Scope and Functions of Managementrohan_jangid889% (18)
- Unit - 2 PDFDokument2 SeitenUnit - 2 PDFBandosNoch keine Bewertungen
- BBA MIS ch4Dokument62 SeitenBBA MIS ch4FrankNoch keine Bewertungen
- B. How Do Conventional Application Packages Differ From ERP Packages?Dokument5 SeitenB. How Do Conventional Application Packages Differ From ERP Packages?pad75Noch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 3Dokument13 SeitenChapter 3poojamudNoch keine Bewertungen
- Course Mba - 2 Semester Subject Management Information Systems Assignment MB0047 - Set 1Dokument25 SeitenCourse Mba - 2 Semester Subject Management Information Systems Assignment MB0047 - Set 1barthwalnishaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Name: Haseeb Mujeeb. Roll No: 033. Class: Bba. Samester: 5 (TH) - Subject: MIS. (CH.10) Submitted To: Sir - Aneeb LashariDokument7 SeitenName: Haseeb Mujeeb. Roll No: 033. Class: Bba. Samester: 5 (TH) - Subject: MIS. (CH.10) Submitted To: Sir - Aneeb LashariHaseeb MujeebNoch keine Bewertungen
- Enterprise Resource PlanningDokument106 SeitenEnterprise Resource Planningathulkannan100% (1)
- Management Information systems - MIS: Business strategy books, #4Von EverandManagement Information systems - MIS: Business strategy books, #4Noch keine Bewertungen
- Design of CouplingDokument75 SeitenDesign of CouplingVatsal BhalaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction To The Iceberg ModelDokument5 SeitenIntroduction To The Iceberg ModelAbhay Tiwari100% (1)
- AB-005-2020 Dated 10.09.2020 (SKF-Prestine)Dokument3 SeitenAB-005-2020 Dated 10.09.2020 (SKF-Prestine)AliasgarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Corometrics 170 Series BrochureDokument3 SeitenCorometrics 170 Series BrochureCesar MolanoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lifecycle of A Butterfly Unit Lesson PlanDokument11 SeitenLifecycle of A Butterfly Unit Lesson Planapi-645067057Noch keine Bewertungen
- Kazi Shafikull IslamDokument3 SeitenKazi Shafikull IslamKazi Shafikull IslamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Thesis StoryboardDokument5 SeitenThesis StoryboardJill Brown100% (2)
- Sample File: The Ultimate Adventurers Guide IDokument6 SeitenSample File: The Ultimate Adventurers Guide IDingusbubmisNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bug Life Cycle in Software TestingDokument2 SeitenBug Life Cycle in Software TestingDhirajNoch keine Bewertungen
- TOA Project Presentation (GROUP 5)Dokument22 SeitenTOA Project Presentation (GROUP 5)Khadija ShahidNoch keine Bewertungen
- Effect of IctDokument10 SeitenEffect of IctRVID PhNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assistant Bookkeeper Resume Sample - Best Format - Great Sample ResumeDokument4 SeitenAssistant Bookkeeper Resume Sample - Best Format - Great Sample ResumedrustagiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Video Tutorial: Machine Learning 17CS73Dokument27 SeitenVideo Tutorial: Machine Learning 17CS73Mohammed Danish100% (2)
- Dynamic Shear Modulus SoilDokument14 SeitenDynamic Shear Modulus SoilMohamed A. El-BadawiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Harmony Guide DatabaseDokument7 SeitenHarmony Guide DatabaseAya SakamotoNoch keine Bewertungen
- FoundationDokument98 SeitenFoundationManognya KotaNoch keine Bewertungen
- DYCONEX Materials en 2020 ScreenDokument2 SeitenDYCONEX Materials en 2020 ScreenhhaiddaoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lalkitab Varshphal Chart PDFDokument6 SeitenLalkitab Varshphal Chart PDFcalvinklein_22ukNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hayek - Planning, Science, and Freedom (1941)Dokument5 SeitenHayek - Planning, Science, and Freedom (1941)Robert Wenzel100% (1)
- R67068.0002 2 HB Profibus-Schnittstelle en KueblerDokument42 SeitenR67068.0002 2 HB Profibus-Schnittstelle en KueblerSabari StunnerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Static Power Conversion I: EEE-463 Lecture NotesDokument48 SeitenStatic Power Conversion I: EEE-463 Lecture NotesErgin ÖzdikicioğluNoch keine Bewertungen
- GoodElearning TOGAF Poster 46 - Adapting The ADMDokument1 SeiteGoodElearning TOGAF Poster 46 - Adapting The ADMFabian HidalgoNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2021 Bookmatter BasicSciencesOfNuclearMedicineDokument12 Seiten2021 Bookmatter BasicSciencesOfNuclearMedicineBeatriz MartinhoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Aerated Concrete Production Using Various Raw MaterialsDokument5 SeitenAerated Concrete Production Using Various Raw Materialskinley dorjee100% (1)
- Business Statistics: Fourth Canadian EditionDokument41 SeitenBusiness Statistics: Fourth Canadian EditionTaron AhsanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture 11 - Performance AppraisalsDokument23 SeitenLecture 11 - Performance AppraisalsCard CardNoch keine Bewertungen
- List of Important Books of PhysicsDokument6 SeitenList of Important Books of PhysicsAbubakar Mughal0% (1)
- Barack ObamaDokument3 SeitenBarack ObamaVijay KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- DICKSON KT800/802/803/804/856: Getting StartedDokument6 SeitenDICKSON KT800/802/803/804/856: Getting StartedkmpoulosNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dady - Piernas LargasDokument12 SeitenDady - Piernas LargasSarha NietoNoch keine Bewertungen