Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Day 11 - Eukaryotic Cell Parts
Hochgeladen von
jy10107Originalbeschreibung:
Originaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Day 11 - Eukaryotic Cell Parts
Hochgeladen von
jy10107Copyright:
Verfügbare Formate
LECTURE PRESENTATIONS For CAMPBELL BIOLOGY, NINTH EDITION
Jane B. Reece, Lisa A. Urry, Michael L. Cain, Steven A. Wasserman, Peter V. Minorsky, Robert B. Jackson
Chapter 6
A Tour of the Cell
Click to edit Master subtitle style
Lectures by Erin Barley Kathleen Fitzpatrick
2011 Pearson Education, Inc.
The endomembrane system regulates protein traffic and performs metabolic functions in the cell
Components of the endomembrane system
Nuclear envelope Endoplasmic reticulum Golgi apparatus Lysosomes Vacuoles Plasma membrane
These components are either continuous or connected via transfer by vesicles
2011 Pearson Education, Inc.
Figure 6.11
Smooth ER Rough ER
Nucle ar envel ope
ER lumen Cistern ae
Ribosom es Transport vesicle Smooth ER
Transitional ER 200 nm
Rough ER
Figure 6.12
cis face (receiving side of Golgi apparatus)
0.1 m Cistern ae
trans face (shipping side of Golgi apparatus)
TEM of Golgi apparatus
Figure 6.15-3
Nucleus
Smooth ER cis Golgi
Rough ER
trans Golgi
Plasma membra ne
A pancreatic beta cell produces and secrete insulin (a protein hormone). Trace the pathway of production and export of this protein from the nucleus to the blood stream. Describe what happens at each stop along its way.
Brefeldin A is an antibiotic produced by fungal organisms. It interferes with transport from the ER to the Golgi apparatus (by blocking receiving end of the Golgi), leading to proteins accumulating inside the ER. What are the immediate and long-term consequences of this antibiotic on cell structure and function?
Concept 6.5: Mitochondria and chloroplasts change energy from one form to another
Mitochondria are the sites of cellular respiration
Chloroplasts are the sites of photosynthesis
2011 Pearson Education, Inc.
The Evolutionary Origins of Mitochondria and Chloroplasts
Mitochondria and chloroplasts have similarities with bacteria
Enveloped by a double membrane Contain free ribosomes and circular DNA molecules Grow and reproduce somewhat independently in cells
2011 Pearson Education, Inc.
Figure 6.17
Intermembrane space
Ou ter membran e
10 m Mitochond ria
Free ribosomes in the mitochond rial matrix (a) Diagram and TEM of mitochondrion
D N A Inn er membra ne Cristae Mat rix 0.1 m
Mitochondr ial DNA Nuclear DNA ( Network of mitochondria in a b protist ) cell (LM)
Figure 6.18
Ribosom es
Stro ma Inner and outer membra nes Gran um Chloropla sts (red)
50 m
DNA Intermembrane Thylak oid TEM of space (a) Diagram and chloroplast
1 m
(b) Chloroplasts in an algal cell
The Endosymbiont theory
An early ancestor of eukaryotic cells engulfed a nonphotosynthetic prokaryotic cell, which formed an endosymbiont relationship with its host The host cell and endosymbiont merged into a single organism, a eukaryotic cell with a mitochondrion At least one of these cells may have taken up a photosynthetic prokaryote, becoming the ancestor of cells that contain chloroplasts
2011 Pearson Education, Inc.
Figure 6.16
Engulfing of oxygenusing nonphotosynthetic prokaryote, which becomes a mitochondrion Mitochondri on
Endoplasm ic reticulum Nuclea r envelo pe
Nucleu s
Ancestor of eukaryotic cells (host cell) Engulfing of photosyntheti c prokaryote Chloropla st
Nonphotosynthet ic eukaryote
At least one cell
Mitochondri on Photosynthetic eukaryote
Figure 6.UN01a
Nucl eus
( E R )
Figure 6.UN01c
Functional group OH CH2 COOH NH2 SH PO4
Polar or Nonpolar?
Hydrophobic or Hydrophilic
Found in all proteins
Found in many proteins
Found in many lipids
carbohydrates Always contain P Generally contain no P* Always contain N Generally contain no N Frequently contain S
lipids
proteins
nucleic acids
Generally contain no S
Compare and contrast the two molecules below using the following criteria : A.the arrangement of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen atoms B.the types of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen atoms C.the number of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen atoms D. the number of covalent bonds E. Functional role in cell
The functional group of the amino acid threonine is -OH. The functional group of the amino acid valine is methyl. Where would you expect to find these amino acids in globular protein in aqueous solution? Draw a picture
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Von EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Bewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (121)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryVon EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (231)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceVon EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (588)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaVon EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (266)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItVon EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (838)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerVon EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingVon EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (400)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeVon EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (5794)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyVon EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (2259)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeVon EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (537)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreVon EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1090)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersVon EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (345)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnVon EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (234)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesVon EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (821)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceVon EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (895)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaVon EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (45)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureVon EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (474)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealVon EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (74)
- Contract Law: Offer & Acceptance CasesDokument8 SeitenContract Law: Offer & Acceptance CasesAudrey JongNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Von EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Bewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (98)
- BurnsDokument80 SeitenBurnsAlina IlovanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Zone Raiders (Sci Fi 28mm)Dokument49 SeitenZone Raiders (Sci Fi 28mm)Burrps Burrpington100% (3)
- Baccarat StrategyDokument7 SeitenBaccarat StrategyRenz Mervin Rivera100% (3)
- Tutorials in Complex Photonic Media SPIE Press Monograph Vol PM194 PDFDokument729 SeitenTutorials in Complex Photonic Media SPIE Press Monograph Vol PM194 PDFBadunoniNoch keine Bewertungen
- 10 Fonts For A Better WebsiteDokument3 Seiten10 Fonts For A Better WebsiteAlyzza Kara AcabalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sabena Belgian World Airlines vs. CADokument3 SeitenSabena Belgian World Airlines vs. CARhea CalabinesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Group Process in The Philippine SettingDokument3 SeitenGroup Process in The Philippine Settingthelark50% (2)
- Appendix H Sample of Coded Transcript PDFDokument21 SeitenAppendix H Sample of Coded Transcript PDFWahib LahnitiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 2Dokument16 SeitenChapter 2nannaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1654557191.969365 - Signed Contract Application 212143Dokument11 Seiten1654557191.969365 - Signed Contract Application 212143ella may sapilanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Outbreaks Epidemics and Pandemics ReadingDokument2 SeitenOutbreaks Epidemics and Pandemics Readingapi-290100812Noch keine Bewertungen
- The Impact of Video Gaming To The Academic Performance of The Psychology Students in San Beda UniversityDokument5 SeitenThe Impact of Video Gaming To The Academic Performance of The Psychology Students in San Beda UniversityMarky Laury GameplaysNoch keine Bewertungen
- Masterlist of Private Elem. Schools S.Y. 2016 2017 Cavite ProvinceDokument17 SeitenMasterlist of Private Elem. Schools S.Y. 2016 2017 Cavite ProvinceacinehhjNoch keine Bewertungen
- 01 History of Grammatical StudyDokument9 Seiten01 History of Grammatical StudyRomanNoch keine Bewertungen
- PctcostepoDokument4 SeitenPctcostepoRyan Frikkin MurgaNoch keine Bewertungen
- MNLG 4Dokument2 SeitenMNLG 4Kanchana Venkatesh39% (18)
- 105-0004 - Significant Characteristics For Compliance With Emission RegulationsDokument5 Seiten105-0004 - Significant Characteristics For Compliance With Emission RegulationsthisisjineshNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bahasa Inggris XIIDokument1 SeiteBahasa Inggris XIIclaudiaomega.pNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rainfall Runoff ModellingDokument23 SeitenRainfall Runoff ModellingmansikakaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- What Enables Close Relationships?Dokument14 SeitenWhat Enables Close Relationships?Clexandrea Dela Luz CorpuzNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 10: Third Party Non-Signatories in English Arbitration LawDokument13 SeitenChapter 10: Third Party Non-Signatories in English Arbitration LawBugMyNutsNoch keine Bewertungen
- 9 Prospect EvaluationDokument40 Seiten9 Prospect EvaluationgeorgiadisgNoch keine Bewertungen
- IPA Digital Media Owners Survey Autumn 2010Dokument33 SeitenIPA Digital Media Owners Survey Autumn 2010PaidContentUKNoch keine Bewertungen
- Definition Environmental Comfort in IdDokument43 SeitenDefinition Environmental Comfort in Idharis hambaliNoch keine Bewertungen
- 4.dynamic Analysis of Earth Quake Resistante Steel FrameDokument28 Seiten4.dynamic Analysis of Earth Quake Resistante Steel FrameRusdiwal JundullahNoch keine Bewertungen
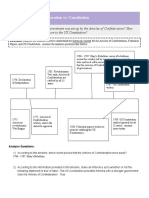
- ArticlesOfConfederation Constitution 3.0Dokument6 SeitenArticlesOfConfederation Constitution 3.0ChristinaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Disorders of NewbornDokument4 SeitenDisorders of NewbornBRUELIN MELSHIA MNoch keine Bewertungen
- Software Development Life CycleDokument70 SeitenSoftware Development Life CycleChaitanya MalikNoch keine Bewertungen