Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Hefteintrage 1
Hochgeladen von
deliyahOriginaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Hefteintrage 1
Hochgeladen von
deliyahCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
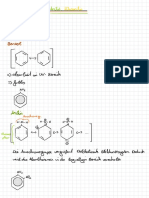
Reaktionsmechanismus zur Bromierung von Heptan
Der Reaktionsmechanismus ist Charakter isch für eine radikalische Substitution , wobei ein Wasserstoffatom
durch ein Radikal ersetzt wird .
Start reaktion :
Das Brom molekül wird durch Licht
gleichmäßig . Brom Radikal
Licht
homolytisch gespalten .
4. Br
.
→
Es entstehen 2 Brom Radikale -
mit einem freien Elektron .
Br
2.
Br Kettenreaktion :
no no no
②
Das Brom Radikal -
greift das Wasserstoffatom am
O A on on
Hexan an & bildet ein Bromwasserstoff Molekül -
"
no no no Das Hexan Radikal
-
bleibt übrig .
Dieses bindet schließlich
¥
on on on ein Brom Radikal
-
zum Produkt Bromhexan
no no no
Hexan Radikal -
O A on on
Abbruch reaktion /nicht dargestellt ) :
Bromhexan
no no no
Zwei Radikale gehen eine
Bindung zu einem Molekül ein
0 " on on
zum Beispiel :
Br -
+ Br . → Br Br
Startreaktion
homolytische des chlor moleküls
Spaltung
Cl Cl > 21cL .
ZU zwei Chlor -
Radikalen
Kettenreaktion
H
H
I
H C + Cl +
H Cl Bildung von Chlorwasserstoff & Methyl Radikal
q
H •
H - . - -
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Chemie ArbeitsblätterDokument1 SeiteChemie Arbeitsblätterour90452nezid.comNoch keine Bewertungen
- ZusammenfassungDokument12 SeitenZusammenfassungasdfqNoch keine Bewertungen
- Die Macht Des Silbers Karolingische SchaDokument192 SeitenDie Macht Des Silbers Karolingische Schafelix ruschNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chemie Lernzettel Q1Dokument17 SeitenChemie Lernzettel Q1lisabeth.geskeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Atombau 21.3.22Dokument13 SeitenAtombau 21.3.22jazmineNoch keine Bewertungen
- AP Verkauf 2019 12Dokument1 SeiteAP Verkauf 2019 12Maris ZieglerNoch keine Bewertungen
- U Bahn Plan - KomplettDokument1 SeiteU Bahn Plan - KomplettiyibilginalpNoch keine Bewertungen
- Vergleichbenzol - Tndori.Nitoonil-Nioi-Bennzooll - Li: AbnötigenDokument4 SeitenVergleichbenzol - Tndori.Nitoonil-Nioi-Bennzooll - Li: AbnötigenToni BorkumNoch keine Bewertungen
- Campusplan (2017)Dokument1 SeiteCampusplan (2017)muggNoch keine Bewertungen
- HefteintrageDokument1 SeiteHefteintragedeliyahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hefteintrage 4Dokument2 SeitenHefteintrage 4deliyahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hefteintrage 3Dokument2 SeitenHefteintrage 3deliyahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hefteintrage 2Dokument1 SeiteHefteintrage 2deliyahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hefteintrage 5Dokument2 SeitenHefteintrage 5deliyahNoch keine Bewertungen