Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Praes ED Kap 1
Hochgeladen von
fasanwas0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
10 Ansichten2 SeitenCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
PDF, TXT oder online auf Scribd lesen
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
10 Ansichten2 SeitenPraes ED Kap 1
Hochgeladen von
fasanwasCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
Sie sind auf Seite 1von 2
1
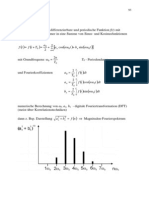
1.Physikalische Grundgren und Maxwellsche Gleichungen
a) Physikalische Grundgren
Raumladungsdichte elektrische Ladung elektrische Spannung elektrische Feldstrke (elektrisches Feld) elektrische Flussdichte (dielektrische Verschiebung) Permittivitt des Vakuums relative Dielektrizittskonstante elektrischer Strom Stromdichte Leitfhigkeit magnetische Feldstrke (magnetisches Feld) magnetische Flussdichte (magnetische Induktion) Permeabilitt des Vakuums relative Permeabilittskonstante Q dV
V
[] = As/m3 [Q] = As = C [U] = V [E] = N/As = V/m [D] = As/m2
U E D r 0 E 0 = 8.854 10-12 As/Vm r dQ I dt j mit I j da a mit j E H B 0 r H 0 = 4 107 Vs/Am r
[I] = A [j] = A/m2 [] = A/Vm [H] = A/m [B] = Vs/m2
b) Maxwellsche Gleichungen
1. Gaussches Gesetz Integrale Form D ds Qumschlossen
s
(Gausscher Integralsatz)
Differentielle Form div D
2. Nichtexistenz magnetischer Monopole (magnetischer Ladungen) B ds 0
s
(Gausscher Integralsatz)
div B 0
3. Verallgemeinertes Ampresches Gesetz (Durchflutungsgesetz)
(Stokescher Integralsatz)
d H d l I D da dt A c
D rot H j t
4. Induktionsgesetz
(Stokescher Integralsatz)
d E d l B da dt A c
B rot E t
Materialgleichungen: j E D r 0 E 1 H B 0 r
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Kapillarrohr AuslegungDokument4 SeitenKapillarrohr AuslegungfasanwasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Übung Chemie1Dokument1 SeiteÜbung Chemie1fasanwasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mathe 6Dokument1 SeiteMathe 6fasanwasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Uebungsklausur 21 01 08Dokument2 SeitenUebungsklausur 21 01 08fasanwasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Exphysikaufgaben 14 11 2007Dokument1 SeiteExphysikaufgaben 14 11 2007fasanwasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Exphysikaufgaben 28 11 2007Dokument1 SeiteExphysikaufgaben 28 11 2007fasanwasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chemie 12Dokument1 SeiteChemie 12fasanwasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chemie 8Dokument1 SeiteChemie 8fasanwasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Praes ED Kap 4 4Dokument7 SeitenPraes ED Kap 4 4fasanwasNoch keine Bewertungen
- 16 04 2008Dokument1 Seite16 04 2008fasanwasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Praes ED Kap 5 4 2 DFTDokument1 SeitePraes ED Kap 5 4 2 DFTfasanwasNoch keine Bewertungen
- V5Dokument6 SeitenV5fasanwasNoch keine Bewertungen
- V3 Volumina-KorrDokument8 SeitenV3 Volumina-KorrfasanwasNoch keine Bewertungen
- V3 Siedediagramme KorrDokument14 SeitenV3 Siedediagramme KorrfasanwasNoch keine Bewertungen