Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
FI & FT Formulas
Hochgeladen von
Akshita Pillai0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
7 Ansichten1 SeiteCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
PDF, TXT oder online auf Scribd lesen
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
7 Ansichten1 SeiteFI & FT Formulas
Hochgeladen von
Akshita PillaiCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
Sie sind auf Seite 1von 1
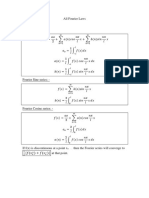
Fourier Integral Fourier Transform Inverse Fourier Transform
Complex form of Fourier Integral
∞
∞
1
𝑓(𝑥) = ∫ ∫ 𝑓(𝑡) ∙ 𝑒 𝑖𝑢(𝑡−𝑥) 𝑑𝑡 𝑑𝑢 ∞
2𝜋 −∞ ∞
𝟏
−∞
𝑭[𝒇(𝒖)] = ∫ 𝒇(𝒕). 𝒆𝒊𝒖𝒕 𝒅𝒕 𝒇(𝒙) = ∫ 𝑭[𝒇(𝒖)]𝒆−𝒊𝒖𝒙 𝒅𝒖
Fourier Integral −∞ 𝟐𝝅
∞ −∞
∞
𝟏
𝒇(𝒙) = ∫ ∫ 𝒇(𝒕) 𝐜𝐨𝐬 𝒖(𝒕 − 𝒙)𝒅𝒕 𝒅𝒖
𝝅 𝟎
−∞
Fourier Sine Integral ∞
∞
∞ ∞ 𝟐
𝟐 𝑭𝑺 [𝒇(𝒖)] = ∫ 𝒇(𝒕). 𝐬𝐢𝐧 𝒖𝒕 𝒅𝒕 𝒇(𝒙) = ∫ 𝑭𝒔 [𝒇(𝒖)] 𝐬𝐢𝐧 𝒖𝒙 𝒅𝒖
𝒇(𝒙) = ∫ 𝐬𝐢𝐧 𝒖𝒙 ∫ 𝒇(𝒕) 𝐬𝐢𝐧 𝒖𝒕 𝒅𝒕 𝒅𝒖 𝒕=𝟎 𝝅
𝝅 𝒖=𝟎
𝒖=𝟎 𝒕=𝟎
Fourier Cosine Integral ∞
∞
∞ ∞ 𝟐
𝟐 𝑭𝒄 [𝒇(𝒖)] = ∫ 𝒇(𝒕). 𝐜𝐨𝐬 𝒖𝒕 𝒅𝒕 𝒇(𝒙) = ∫ 𝑭𝒄 [𝒇(𝒖)] 𝐜𝐨𝐬 𝒖𝒙 𝒅𝒖
𝒇(𝒙) = ∫ 𝐜𝐨𝐬 𝒖𝒙 ∫ 𝒇(𝒕) 𝐜𝐨𝐬 𝒖𝒕 𝒅𝒕 𝒅𝒖 𝒕=𝟎 𝝅
𝝅 𝒖=𝟎
𝒖=𝟎 𝒕=𝟎
Note: There is no uniformity in the notations of Fourier integrals and Fourier transforms. Sometimes or are
used in place of u and s in place of t
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- La Integral de FourierDokument4 SeitenLa Integral de FourierTahic PNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sifat Fourier TransformDokument16 SeitenSifat Fourier TransformJessie Jessica ManurungNoch keine Bewertungen
- Clase 10 INTEGRALES IMPROPIASDokument6 SeitenClase 10 INTEGRALES IMPROPIASSolemns SotsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Inbound 1315471108848598509Dokument1 SeiteInbound 1315471108848598509Sidiabdalla MouemelNoch keine Bewertungen
- All Fourier LawsDokument4 SeitenAll Fourier Lawsahmed abdbastNoch keine Bewertungen
- FormelsammlungDokument3 SeitenFormelsammlungAnggie LopezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Realizar Las Siguientes IntegralesDokument1 SeiteRealizar Las Siguientes IntegralesEvelin JessicaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Taller Ejercicios Progreso 2 Davila - Ontaneda - AlulemaDokument4 SeitenTaller Ejercicios Progreso 2 Davila - Ontaneda - Alulemadiego alulemaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Transformadas de La PlaceDokument28 SeitenTransformadas de La PlacesergioNoch keine Bewertungen
- I1-TD5 Impropern Rieman & Parametric IntegralsDokument14 SeitenI1-TD5 Impropern Rieman & Parametric IntegralsHeng KimhengNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unidad 0 - Vectores Aleatorios - Sumayresta de V.A.Dokument1 SeiteUnidad 0 - Vectores Aleatorios - Sumayresta de V.A.luli2ferrarisNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fórmulas Unidad 3Dokument1 SeiteFórmulas Unidad 3Diana Fernanda Barbosa BecerraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Muest ReoDokument7 SeitenMuest ReoDaniel MedauraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Formulario Prueba 2 Modelos Discretos PDFDokument1 SeiteFormulario Prueba 2 Modelos Discretos PDFRodriguin ValenzuelaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Kajian PustakaDokument14 SeitenKajian PustakafitriyaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Limit 763Dokument2 SeitenLimit 763elisario JoseNoch keine Bewertungen
- P Unidad 3Dokument3 SeitenP Unidad 3Cristian Marcos DiazNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tugas Statmat Kelompok 7Dokument6 SeitenTugas Statmat Kelompok 7Femy KeransNoch keine Bewertungen
- FENODokument15 SeitenFENOELIZABETHNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tabla de IntegralesDokument1 SeiteTabla de IntegralesVirginiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Deber #17 Integrales Impropias Tipo 1 PDFDokument2 SeitenDeber #17 Integrales Impropias Tipo 1 PDFTeniente Dan TaylorNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 7 SolutionsDokument9 SeitenChapter 7 Solutionshappy062733Noch keine Bewertungen
- Formulario Prueba 2 Modelos Continuos PDFDokument1 SeiteFormulario Prueba 2 Modelos Continuos PDFRodriguin ValenzuelaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tabla de Transformada de LaplaceDokument2 SeitenTabla de Transformada de Laplacerogger cardenas tinocoNoch keine Bewertungen
- 4.3 Integrales ImpropiasDokument8 Seiten4.3 Integrales ImpropiasSeveroNoch keine Bewertungen
- Form Elsa MM Lung Hue FTDokument6 SeitenForm Elsa MM Lung Hue FTSabine BellmannNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tugas06Dokument3 SeitenTugas0640 Dani Firmansyah KurniawanNoch keine Bewertungen
- TP3 - STATMAT2 - Sitti Jusmiati - F1A219014Dokument6 SeitenTP3 - STATMAT2 - Sitti Jusmiati - F1A219014muhammad subarjan139Noch keine Bewertungen
- Limit FungsiDokument21 SeitenLimit Fungsilissadiyah190Noch keine Bewertungen
- Quiz-3 - ADokument2 SeitenQuiz-3 - AAbdulrahman SaadiNoch keine Bewertungen
- PROGRAMME DE 1ère ANNEE Finance Comptabilité Gestion Des EntreprisesDokument7 SeitenPROGRAMME DE 1ère ANNEE Finance Comptabilité Gestion Des EntreprisesrichmondnicaisekouassiNoch keine Bewertungen
- TrennstufenkonzeptDokument33 SeitenTrennstufenkonzeptAvicola El CarmenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Formelsammlung KDokument2 SeitenFormelsammlung KZakaria ImourigNoch keine Bewertungen
- Differential Equation - p10Dokument12 SeitenDifferential Equation - p10Rondio LopezNoch keine Bewertungen
- FormelsammlungDokument4 SeitenFormelsammlungThanh Tùng TrầnNoch keine Bewertungen
- FDokument1 SeiteFAndy LêNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dzexams Docs 3as 903902Dokument12 SeitenDzexams Docs 3as 903902rrca250Noch keine Bewertungen
- Taller #4, Polinomios OrtogonalesDokument14 SeitenTaller #4, Polinomios OrtogonalesAngelo CoyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Module 3.4 Improper IntegralsDokument1 SeiteModule 3.4 Improper IntegralsTonton SipaganNoch keine Bewertungen
- Formelsammlung Turbomaschinen PDFDokument35 SeitenFormelsammlung Turbomaschinen PDFmaildesantiagoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Formularioseriesytransf-1 230919 091437Dokument3 SeitenFormularioseriesytransf-1 230919 091437Juan SoteroNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mag - 2013 2 21Dokument30 SeitenMag - 2013 2 21Emma MillerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Grenzwertsätze ÜbersichtDokument1 SeiteGrenzwertsätze ÜbersichtJanNoch keine Bewertungen
- 101S127 CS27L01Dokument56 Seiten101S127 CS27L01e54114083Noch keine Bewertungen
- Statistika Matematika 1 - 5Dokument8 SeitenStatistika Matematika 1 - 5Ahmad NurhadiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Grupo 7 - GP. 11Dokument5 SeitenGrupo 7 - GP. 11JOSE ENRIQUE BENDEZU SANCHEZNoch keine Bewertungen
- Maphy4 KlausurDokument2 SeitenMaphy4 KlausurWNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tabla de CriteriosDokument1 SeiteTabla de CriteriosDaniela Rodríguez VilladaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Maphy4 Blatt2Dokument9 SeitenMaphy4 Blatt2WNoch keine Bewertungen
- Formulas 1 PDokument3 SeitenFormulas 1 PWilson Dario Sanchez MosqueraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Deret FourierDokument1 SeiteDeret FourierArsenna HasibuanNoch keine Bewertungen
- PT Formelsammlung 08 31Dokument2 SeitenPT Formelsammlung 08 31GeorgNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tabla de Transformada de FourierDokument3 SeitenTabla de Transformada de Fourierrogger cardenas tinocoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Función Delta Diracc y Fórmulas MatemáticasDokument2 SeitenFunción Delta Diracc y Fórmulas MatemáticasSebastian FloresNoch keine Bewertungen
- Integrales (Ejercicios Resueltos)Dokument8 SeitenIntegrales (Ejercicios Resueltos)Pedro Sturla PanequeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Aula de LimitesDokument4 SeitenAula de LimitescienciandomozNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tarea Criterio de La Integral. Calculo 111Dokument2 SeitenTarea Criterio de La Integral. Calculo 111Elizabeth SantosNoch keine Bewertungen