Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
The CNS Processes Sensory Input, Analyzing It To Determine If Any Adjustments Are Needed To Maintain Homeostasis
Hochgeladen von
jlcanja5Originaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
The CNS Processes Sensory Input, Analyzing It To Determine If Any Adjustments Are Needed To Maintain Homeostasis
Hochgeladen von
jlcanja5Copyright:
Verfügbare Formate
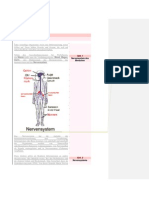
Nervous System Components
The central nervous system is made up of the brain and spinal cord.
The peripheral nervous system is made up of nerves that branch off from the spinal cord and
extend to all parts of the body.
Sensory input
describes the response our sensory organs (such as eyes, ears, mouth,
tongue, skin, etc.) have whenever it receives stimuli. That stimuli is what's
perceived by any of our 8 senses: smell, sight, touch, taste, hearing, and the
internal sensory systems (proprioceptive, vestibular, and interoceptive).
Integration and Processing
The CNS processes sensory input, analyzing it to determine if any adjustments are needed to
maintain homeostasis.
Coordination and Regulation
The CNS coordinates the body's response by sending signals through the PNS to effectors such
as muscles and glands.
Feedback Mechanisms:
Negative Feedback: Works to reverse deviations from the desired set point, helping to
maintain stability.
Positive Feedback: Amplifies deviations from the normal range, often in specific situations
such as childbirth.
Examples of Nervous System Regulation:
Temperature Regulation: Initiates responses such as sweating or shivering to maintain
optimal body temperature.
Blood Sugar Regulation: Helps regulate blood sugar levels through the release of hormones
like insulin and glucagon.
Importance of Homeostasis: Homeostasis is crucial for maintaining stable internal conditions
necessary for overall health and well-being.
This coordination and regulation by the nervous system ensure that the body's internal
environment remains within optimal ranges, allowing for proper cellular function and overall
health.
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Das Vagus Nerv Praxisbuch: Schritt für Schritt mit dem Selbstheilungsnerv Ihren Körper und Geist ins Gleichgewicht bringen und zufriedener leben - inkl. Vagusnerv - Übungen zum Bekämpfen von Stress, Depressionen, Migräne, innerer Unruhe und TinnitusVon EverandDas Vagus Nerv Praxisbuch: Schritt für Schritt mit dem Selbstheilungsnerv Ihren Körper und Geist ins Gleichgewicht bringen und zufriedener leben - inkl. Vagusnerv - Übungen zum Bekämpfen von Stress, Depressionen, Migräne, innerer Unruhe und TinnitusNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biopsychologie - Anatomie Des Nervensystems 20062015 - PraesentationDokument53 SeitenBiopsychologie - Anatomie Des Nervensystems 20062015 - PraesentationCésar Morales0% (1)
- Anti Stress StrategieDokument34 SeitenAnti Stress StrategiemysteinwayNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nervensystem BioDokument48 SeitenNervensystem Biotontonel31Noch keine Bewertungen
- Das NervensystemDokument30 SeitenDas NervensystemNirriti67% (3)
- Equinox-FFT - SoundDokument8 SeitenEquinox-FFT - SoundmarnesiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hormon-Food - das große E-Book: Nahrung ist auch MedizinVon EverandHormon-Food - das große E-Book: Nahrung ist auch MedizinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Methoden Der SelbstkontrolleDokument1 SeiteMethoden Der SelbstkontrolleschorleworleNoch keine Bewertungen
- Neurofundamentals leicht gemacht: Neurozentriertes Training verständlich erklärtVon EverandNeurofundamentals leicht gemacht: Neurozentriertes Training verständlich erklärtNoch keine Bewertungen
- Endokrines SystemDokument38 SeitenEndokrines SystemWilhelm Winsor100% (1)
- Ohrakupunktur und Psychosomatik: Einführung in die AurikulotherapieVon EverandOhrakupunktur und Psychosomatik: Einführung in die AurikulotherapieBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (1)
- Buhl - Vegetatives Nervensystem Und Energetische MedizinDokument33 SeitenBuhl - Vegetatives Nervensystem Und Energetische MedizinomadaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Access Keys Emotion Healing CodesDokument1 SeiteAccess Keys Emotion Healing CodesReikiportal100% (1)
- Nerven SystemDokument8 SeitenNerven SystemDavid RizkNoch keine Bewertungen
- FrequenzapothekeDokument54 SeitenFrequenzapothekemarnesia100% (1)
- Hormone sanft regulieren: Ausgewählte Schüßler-Salze für mehr Harmonie im DrüsensystemVon EverandHormone sanft regulieren: Ausgewählte Schüßler-Salze für mehr Harmonie im DrüsensystemBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (1)
- Eggetsberger ZellaktivierungDokument27 SeitenEggetsberger ZellaktivierungLuxNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ablauf ReflexzonentherapieDokument19 SeitenAblauf Reflexzonentherapiemariana vacusNoch keine Bewertungen
- ArbeitsanleitungDokument2 SeitenArbeitsanleitungBernd Berhard100% (1)
- Wie Funktionierten Diese PunkteDokument1 SeiteWie Funktionierten Diese PunkteReikiportalNoch keine Bewertungen
- (Ebook - German) - Vericon - Autogenes Training 01Dokument33 Seiten(Ebook - German) - Vericon - Autogenes Training 01MyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nervensystem, Muskulatur Und Koordination FinalDokument37 SeitenNervensystem, Muskulatur Und Koordination FinaljanekwujeschNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nebennierenschwäche ganzheitlich behandeln: Das Selbsthilfebuch für mehr Lebensqualität, Vitalität und Gesundheit - inkl. Lifestyle-Check, Stressmanagement und Ernährungsguide mit RezeptenVon EverandNebennierenschwäche ganzheitlich behandeln: Das Selbsthilfebuch für mehr Lebensqualität, Vitalität und Gesundheit - inkl. Lifestyle-Check, Stressmanagement und Ernährungsguide mit RezeptenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biologie Arbeit 1Dokument5 SeitenBiologie Arbeit 1ceydadenizkoyuncuNoch keine Bewertungen
- ZSM NervensystemeDokument9 SeitenZSM NervensystemesthebsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Flyer Für FussreflextherapieDokument3 SeitenFlyer Für Fussreflextherapiemariana vacusNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nervensystem Und EndikronologieDokument4 SeitenNervensystem Und EndikronologieYusuf ÖvüncNoch keine Bewertungen
- Burn-out: Quintessenz und Prävention: Über den Tellerrand hinausVon EverandBurn-out: Quintessenz und Prävention: Über den Tellerrand hinausNoch keine Bewertungen
- Neurozentriertes Training: So trainierst du Gleichgewicht und StabilitätVon EverandNeurozentriertes Training: So trainierst du Gleichgewicht und StabilitätNoch keine Bewertungen
- Stark, gelassen, stabil: Naturheilkunde für das ImmunsystemVon EverandStark, gelassen, stabil: Naturheilkunde für das ImmunsystemNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bewegungsapparat NotizenDokument1 SeiteBewegungsapparat Notizenfiona.c24dNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gesundheit ist kein Geheimnis: der kleine, große Wellness-RatgeberVon EverandGesundheit ist kein Geheimnis: der kleine, große Wellness-RatgeberNoch keine Bewertungen
- 10 Tipps Für Ein Gesundes LebenDokument26 Seiten10 Tipps Für Ein Gesundes LebenAtikah Nazlan100% (1)
- VEGETATIVES NERVENSYSTEM - ReferatDokument16 SeitenVEGETATIVES NERVENSYSTEM - ReferatpseudopinkoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Die unterschätzte Macht der Seele: Eine neue Sicht auf Seele und KörperVon EverandDie unterschätzte Macht der Seele: Eine neue Sicht auf Seele und KörperNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hormonen - ResumenDokument4 SeitenHormonen - ResumenPili cañasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Yurashi-Therapie: Homöostase der Muskulatur als Weg und ZielVon EverandYurashi-Therapie: Homöostase der Muskulatur als Weg und ZielNoch keine Bewertungen
- AnwendungserklärungDokument6 SeitenAnwendungserklärungJozsef Schiopu-VilciaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Regenerationsmaßnahmen für Sportler: Erfolgreiche Strategien im Fitness- und LeistungssportVon EverandRegenerationsmaßnahmen für Sportler: Erfolgreiche Strategien im Fitness- und LeistungssportNoch keine Bewertungen
- VAGUS NERV: Wie Sie Ihren Selbstheilungsnerv stimulieren und diverse Schmerzen, Stress, Depression, Hochsensibilität, Reizdarm uvm. nachhaltig loswerden - inkl. effektive Übungen für mehr GesundheitVon EverandVAGUS NERV: Wie Sie Ihren Selbstheilungsnerv stimulieren und diverse Schmerzen, Stress, Depression, Hochsensibilität, Reizdarm uvm. nachhaltig loswerden - inkl. effektive Übungen für mehr GesundheitNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2skript Sich Männlich Weiblich Divers FühlenDokument18 Seiten2skript Sich Männlich Weiblich Divers FühlentherainbowgrizzlyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Vagusnerv aktivieren für mehr inneren Ausgleich: Selbstheilungsnerv als Immun-Booster inkl. Vagus-Nerv ÜbungenVon EverandVagusnerv aktivieren für mehr inneren Ausgleich: Selbstheilungsnerv als Immun-Booster inkl. Vagus-Nerv ÜbungenBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (1)
- Mit Gelassenheit und Gorgonzola durch die WechseljahreVon EverandMit Gelassenheit und Gorgonzola durch die WechseljahreNoch keine Bewertungen
- Vagusnerv aktivieren für mehr inneren Ausgleich: Selbstheilungsnerv als Immun-Booster inkl. Vagus Nerv Übungen bei Angst, innerer Unruhe, Depressionen, Migräne, Stress, Tinnitus & VerdauungsstörungenVon EverandVagusnerv aktivieren für mehr inneren Ausgleich: Selbstheilungsnerv als Immun-Booster inkl. Vagus Nerv Übungen bei Angst, innerer Unruhe, Depressionen, Migräne, Stress, Tinnitus & VerdauungsstörungenBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (1)
- Raschke ArtenvArousalDokument8 SeitenRaschke ArtenvArousalminami.heartful.dayNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ratgeber besser aufstehen - Besser Schlafen und schöner aufwachen.: Nie mehr verschlafen - Tipps und Tricks einfacher aufstehen zu können.Von EverandRatgeber besser aufstehen - Besser Schlafen und schöner aufwachen.: Nie mehr verschlafen - Tipps und Tricks einfacher aufstehen zu können.Noch keine Bewertungen
- Vagusnerv - Dein Selbstheilungsnerv zur inneren Balance: Wie du ihn stimulierst und dein Wohlbefinden steigerstVon EverandVagusnerv - Dein Selbstheilungsnerv zur inneren Balance: Wie du ihn stimulierst und dein Wohlbefinden steigerstNoch keine Bewertungen
- Vagusnerv - Aktiviere den Selbstheilungsnerv: Mit Yoga, Meditation und praktischen Übungen zu mehr WohlbefindenVon EverandVagusnerv - Aktiviere den Selbstheilungsnerv: Mit Yoga, Meditation und praktischen Übungen zu mehr WohlbefindenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Schlaflosigkeit überwinden: Praktische Tipps und Strategien für einen erholsamen SchlafVon EverandSchlaflosigkeit überwinden: Praktische Tipps und Strategien für einen erholsamen SchlafNoch keine Bewertungen
- Thermoregulation KörpertemperaturDokument9 SeitenThermoregulation Körpertemperaturfiveten510Noch keine Bewertungen
- Vagusnerv - Dein Selbstheilungsnerv zur inneren Balance: Wie du ihn stimulierst & dein Wohlbefinden steigerstVon EverandVagusnerv - Dein Selbstheilungsnerv zur inneren Balance: Wie du ihn stimulierst & dein Wohlbefinden steigerstBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (1)
- Polyneuropathie | Epstein Barr Virus | Craniomandibuläre Dysfunktion | Rückenschmerzen: Das große 4 in 1 Buch! Wie Sie CMD, EBV, Nervenschmerzen oder Rückenprobleme ganz leicht selbst behandeln, lindern und heilenVon EverandPolyneuropathie | Epstein Barr Virus | Craniomandibuläre Dysfunktion | Rückenschmerzen: Das große 4 in 1 Buch! Wie Sie CMD, EBV, Nervenschmerzen oder Rückenprobleme ganz leicht selbst behandeln, lindern und heilenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Modul 1 Wissenschatl. Hintergr NdeDokument16 SeitenModul 1 Wissenschatl. Hintergr NdeluwonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Muskel: Der Muskel Als SinnesorganDokument11 SeitenMuskel: Der Muskel Als SinnesorgancharlotteelssNoch keine Bewertungen
- STPS17 0247a 04Dokument13 SeitenSTPS17 0247a 04Jeb RoshNoch keine Bewertungen
- Neurophysiology - Group ReportDokument21 SeitenNeurophysiology - Group ReportRonalyn SantiagoNoch keine Bewertungen