Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Saeure-Base Theorie-1
Hochgeladen von
ArtarmielCopyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Saeure-Base Theorie-1
Hochgeladen von
ArtarmielCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
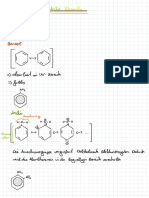
Lewis
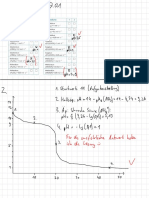
pH = -lg(cH3O+) Elektronepaarakzeptor Elektronenpaardonator pH = -lg(cOH-)
Stark Stark
Säure Säure-Base Theorie Base
Schwach
Schwach
pH = 1/2(pKs-lg(cHA) Protonenakzeptor
Protonendonator pH = 1/2(pKB-lg(cB)
Brönsted
Korrespondierende-Säure-Base-Paare Säure-Base
Redox
Varianten Fällungstitration
Puffer
Rücktitration
Protolyse
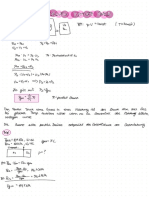
pH = pKs + log (A-/HA) enderson-Hasselbach-
H
Gleichung pKs
pKB Protolysegleichgewicht quantitative Bestimmung
Titration bis zur Neutralisation
Äquivalenzpunkt
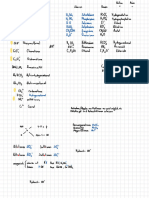
Lösungsmittel
Indikation
protische LM
aprotische LM polare LM
unpolare LM
Potentiometrie Farbindikatoren Konduktometrie
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Elektrotechnischer Handwerk BildzeichenDokument14 SeitenElektrotechnischer Handwerk BildzeichenejrgeioghioNoch keine Bewertungen
- Altklausur SS20Dokument8 SeitenAltklausur SS20Halal HaramNoch keine Bewertungen
- Formelsammlung Chemie AC1-AC54Dokument1 SeiteFormelsammlung Chemie AC1-AC54Andreas BohrerNoch keine Bewertungen
- SÃ Uren Und BasenDokument4 SeitenSÃ Uren Und BasenAmina KamolovaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ampnolyt: AbgebenDokument5 SeitenAmpnolyt: AbgebenMelanie GNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2.5 PH-Werte Starker Und Schwacher Säuren Und BasenDokument3 Seiten2.5 PH-Werte Starker Und Schwacher Säuren Und Basenkelang2677Noch keine Bewertungen
- Rhein-Weser - ExpressDokument7 SeitenRhein-Weser - ExpressLino ChanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Kap 4 - Protonen Und ElektronenübertragungsreaktionenDokument5 SeitenKap 4 - Protonen Und ElektronenübertragungsreaktionenNoorNoch keine Bewertungen
- Beiblatt14 Zustandsdiagramm WasserDokument3 SeitenBeiblatt14 Zustandsdiagramm Wassers.spam2Noch keine Bewertungen
- Säure-Base The Real OneDokument26 SeitenSäure-Base The Real OneduspakepseNoch keine Bewertungen
- A4vso LR2GN PDFDokument1 SeiteA4vso LR2GN PDFHaytham ElbazNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sap DictDokument512 SeitenSap DictDianamaxNoch keine Bewertungen
- LAC-CH01 Saeuren Und BasenDokument18 SeitenLAC-CH01 Saeuren Und BasenlieelisabelowerstNoch keine Bewertungen
- 22 Long Rifle GeDokument1 Seite22 Long Rifle GeJan LippertNoch keine Bewertungen
- DiagnosebytesDokument3 SeitenDiagnosebytesu4riktalentNoch keine Bewertungen
- Spickzettel Für Organische Chemie Für Midterm2015 Ucsc Chem110bDokument3 SeitenSpickzettel Für Organische Chemie Für Midterm2015 Ucsc Chem110bScribdTranslationsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Säuren & Basen Zusammenfassung 2Dokument4 SeitenSäuren & Basen Zusammenfassung 2tizian.alletNoch keine Bewertungen
- SchwermetallfällungDokument19 SeitenSchwermetallfällungBettina HinterbergerNoch keine Bewertungen
- T16 Sure Base 5Dokument23 SeitenT16 Sure Base 5Abdelkahar ErrafayNoch keine Bewertungen
- 16 DecDokument3 Seiten16 DecNigerian PhoneNoch keine Bewertungen
- AB11 TitrationDokument7 SeitenAB11 Titration9hcrhx9rfqNoch keine Bewertungen
- Vergleichbenzol - Tndori.Nitoonil-Nioi-Bennzooll - Li: AbnötigenDokument4 SeitenVergleichbenzol - Tndori.Nitoonil-Nioi-Bennzooll - Li: AbnötigenToni BorkumNoch keine Bewertungen
- 7,65 Browning CIPDokument1 Seite7,65 Browning CIPJan LippertNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mischungen Idealer GaseDokument2 SeitenMischungen Idealer GaseNejla MemićNoch keine Bewertungen
- Basilea Horario50Dokument8 SeitenBasilea Horario50JoseNoch keine Bewertungen
- Themen Der 2. Klausur SK 22-23Dokument1 SeiteThemen Der 2. Klausur SK 22-23joeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chemie ÜbungenDokument7 SeitenChemie Übungensofia.provotarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Katalog Radfahren Muensterland 2019Dokument72 SeitenKatalog Radfahren Muensterland 2019Münsterland e.V.Noch keine Bewertungen
- Chemie 17.01 PDFDokument1 SeiteChemie 17.01 PDFErwin SemicNoch keine Bewertungen
- Profitest Master ProntuarioDokument24 SeitenProfitest Master ProntuarioFrank GarziaNoch keine Bewertungen
- FESTPHASENEXTRAKTION (Roth - LABOR TEIL-Katalog) PDFDokument16 SeitenFESTPHASENEXTRAKTION (Roth - LABOR TEIL-Katalog) PDFDimitri KinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chemie HeftDokument3 SeitenChemie HeftDilara OkanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Beiblatt11 Thermische Zustandsflaeche ReinstoffeDokument3 SeitenBeiblatt11 Thermische Zustandsflaeche Reinstoffes.spam2Noch keine Bewertungen
- 8 X 57 Irs deDokument1 Seite8 X 57 Irs dehxntaiforredditNoch keine Bewertungen
- OrgchemDokument51 SeitenOrgchemVarda BalinoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ryan Jobe: RH... LH... RH..Dokument1 SeiteRyan Jobe: RH... LH... RH..ปฏิพัทธ์ ปรือปรังNoch keine Bewertungen
- 6 5 X 51 R Arisaka GeDokument1 Seite6 5 X 51 R Arisaka GehxntaiforredditNoch keine Bewertungen
- Skript pH-Wert Und NeutralisationDokument2 SeitenSkript pH-Wert Und Neutralisationyohido5904Noch keine Bewertungen
- 2-10-C-AB PufferDokument1 Seite2-10-C-AB Puffershushishu alsNoch keine Bewertungen
- BILIRUBIN TOTAL - BSOSR6x12 - ENDokument8 SeitenBILIRUBIN TOTAL - BSOSR6x12 - ENMustafaNoch keine Bewertungen
- IQB FormelsammlungDokument14 SeitenIQB Formelsammlungff55kykx8zNoch keine Bewertungen
- An Organ Is Che Chemie BasicsDokument22 SeitenAn Organ Is Che Chemie Basicssilvana9810Noch keine Bewertungen
- Brandschutz PraxihandbuchDokument60 SeitenBrandschutz Praxihandbuchnorma_fuentes_45Noch keine Bewertungen
- 6 Scweissverbindungen, Lotverindungen, KlebverbingungenDokument10 Seiten6 Scweissverbindungen, Lotverindungen, KlebverbingungenCătălina StoicanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Löten Von Kupfer Und KupferlegierungenDokument19 SeitenLöten Von Kupfer Und KupferlegierungenHagen_of_TronjeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Original Acryl NagelanleitungDokument9 SeitenOriginal Acryl NagelanleitungScribdTranslationsNoch keine Bewertungen