Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Znotes Org Caie Ig... 2
Hochgeladen von
Maheen EshalOriginaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Znotes Org Caie Ig... 2
Hochgeladen von
Maheen EshalCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Verbs
CHAPTERS
Verbs Conjuagation (present tense)
Verbs in German end with -en or -n.
Like: Haben, spazieren, aufstehen, essen, werden, beginnen, sein.
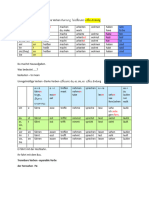
Personal Pronomen Verb (Wohnen)
Ich (I) Wohne(-e)
Du (you) Wohnst(-st)
Er/sie/es/man (he/she/it/one) Wohnt(-t)
Wir (we) Wohnen(-en)
Ihr (you pl.) Wohnt (-t)
sie/sie(you formal)/(they) Wohnen(-en)
Man means (one) and it always takes the same verb conjugation as (er and sie).
Irregular verbs
Verbs like essen, nehmen and sein, etc. have different conjugation patterns than
regular verbs.
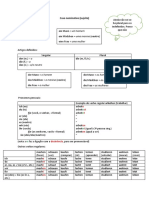
Eg. Sein (to be):
Ich bin
Du bist
Er/sie/es ist
wir sind
ihr seid
Sie/sie sind
Modal verben
Modal verbs come in the second position and cause the original verb to be at the
end of the sentence in its infinitive (not conjugated) form.
Modalverben are: Dürfen (allowed to/may), Können (can), Mögen (to like), Sollen
(ought to), Müssen (must), Wollen & Möchten(to want).
PersonalPronomen Dürfen Können Mögen
Ich Darf Kann Mag
Du Darfst Kannst Magst
Er/sie/es Darf Kann Mag
wir Dürfen Können Mögen
ihr Dürft Könnt Mögt
Sie/sie Dürfen Können Mögen
PersonalPronomen Wollen Sollen Müssen
Ich will soll muss
Du willst sollst musst
PersonalPronomen Wollen Sollen Müssen
Er/sie/es will soll muss
wir wollen sollen müssen
ihr wollt sollt müsst
Sie/sie wollen sollen müssen
*Möchten is conjugated like a regular verb.
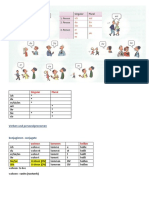
Seperable verbs
Ex: aufstehen, anrufen, einladen.
Prefix (auf, an, ein, usw…) is ’cut’ and sent to the end of the sentence.
Verb is conjugated like normal.
Ex: Ich wache jeden Tag um 6 Uhr auf*. (I wake up at 6 o’clock everyday.)*
P.S: Verbs are always in the second position in a normal sentence.
Impersonal verbs
Impersonal verbs are verbs that can only be used with ‘es’.
Ex: Es regnet, es schneit, es gefällt, es donnert, …..
Es schneit schon den ganzen Tag. (It snowed the entire day.)
Es donnert bereits. (There’s a thunderstorm already.)
Verbs (Continued)
Next chapter
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Italienisch lernen: unregelmäßige Verben (vollständig konjugiert in allen Zeiten)Von EverandItalienisch lernen: unregelmäßige Verben (vollständig konjugiert in allen Zeiten)Noch keine Bewertungen
- Caie Igcse German 0525 Grammar v2Dokument14 SeitenCaie Igcse German 0525 Grammar v2Kim DaizyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Grammatiktabellen Deutsch: Regelmäßige und unregelmäßige Verben, Substantive, Adjektive, Artikel und PronomenVon EverandGrammatiktabellen Deutsch: Regelmäßige und unregelmäßige Verben, Substantive, Adjektive, Artikel und PronomenBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (1)
- Schede Gramm Terza TEDDokument6 SeitenSchede Gramm Terza TEDastrid99Noch keine Bewertungen
- Kurzgrammatik der deutschen Sprache: Wörter und Sätze. Ein Überblick über die wichtigsten RegelnVon EverandKurzgrammatik der deutschen Sprache: Wörter und Sätze. Ein Überblick über die wichtigsten RegelnNoch keine Bewertungen
- Schede Gramm TEDDokument17 SeitenSchede Gramm TEDD Paolo ArenaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Schede Gramm Prima TEDDokument5 SeitenSchede Gramm Prima TEDoutmatrixNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gramatica Alemana - VerbosDokument19 SeitenGramatica Alemana - VerbosaprenderalemanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Awal ModalvDokument19 SeitenAwal Modalvawalrp0075176100% (1)
- Grammatik A2 1Dokument14 SeitenGrammatik A2 1ayoub charkaouiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gramatica AlemanaDokument22 SeitenGramatica AlemanaaprenderalemanNoch keine Bewertungen
- DEutsch Course A1-A2Dokument15 SeitenDEutsch Course A1-A2Aymane BekNoch keine Bewertungen
- German Grammar Reference Book V1 Nnjve0.pdf Extract 1Dokument6 SeitenGerman Grammar Reference Book V1 Nnjve0.pdf Extract 1sowanex219Noch keine Bewertungen
- Die KonjugationDokument3 SeitenDie KonjugationAnonymous KX7VeXNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rappels Grammaticaux 2Dokument7 SeitenRappels Grammaticaux 2anna.masse63Noch keine Bewertungen
- GrammatikDokument40 SeitenGrammatikAxel CuellarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Grammatik A1, A2, B1Dokument35 SeitenGrammatik A1, A2, B1Syah Aditya100% (1)
- German by LinaDokument36 SeitenGerman by LinaPatrícia Rrdr100% (1)
- German Grammar ChartsDokument3 SeitenGerman Grammar ChartsSalvadorManuelFernandezMirandaNoch keine Bewertungen
- VerbulDokument9 SeitenVerbulmihaifoxNoch keine Bewertungen
- Regeln Verben Mit Vokalwechsel e - I, A - ÄDokument6 SeitenRegeln Verben Mit Vokalwechsel e - I, A - ÄKateryna TscheredaNoch keine Bewertungen
- FiatDokument17 SeitenFiatJanejira SereeyotinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dokument 90Dokument4 SeitenDokument 90Nikola MoránNoch keine Bewertungen
- GrammatkDokument9 SeitenGrammatkМарія ЛисикNoch keine Bewertungen
- 56936bff-e5da-4e1e-ba41-6f97693a1723Dokument9 Seiten56936bff-e5da-4e1e-ba41-6f97693a1723월클히토미Noch keine Bewertungen
- Verb KonjugationenDokument2 SeitenVerb KonjugationenAmit JadhavNoch keine Bewertungen
- Die Konjugation Der Verben: 1-PräsensDokument5 SeitenDie Konjugation Der Verben: 1-PräsensFerdous BtrNoch keine Bewertungen
- Verb Und ZeitenDokument34 SeitenVerb Und ZeitenNicolò GrassoNoch keine Bewertungen
- ЗайменникDokument16 SeitenЗайменникАнна ОсипенкоNoch keine Bewertungen
- Prétérit CoursDokument1 SeitePrétérit CourswaliddaddimoussaNoch keine Bewertungen
- JermanDokument6 SeitenJermanNovrizalhadyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gramatyka Do Matury PDFDokument72 SeitenGramatyka Do Matury PDFDamianNoch keine Bewertungen
- ALEMÁNDokument3 SeitenALEMÁNAna María Marín AlcaideNoch keine Bewertungen
- Personalpronomen (All Cases)Dokument26 SeitenPersonalpronomen (All Cases)Govind MilaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introdução Ao Alemão - ApontamentosDokument3 SeitenIntrodução Ao Alemão - ApontamentosRicardo Filipe Afonso MangeronaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Personal Pro No MenDokument14 SeitenPersonal Pro No Mendr.fakebroNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tag 2 - Blatt 2 - Pronomen + VerbenDokument2 SeitenTag 2 - Blatt 2 - Pronomen + VerbenAlkaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Njemački GlagoliDokument21 SeitenNjemački Glagolidgng50% (2)
- Haben Und SeinDokument2 SeitenHaben Und SeinPamela Ramirez MoreraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Die Lernziele Und Der LernstoffDokument8 SeitenDie Lernziele Und Der LernstoffSteffanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Conjugaisons CompletDokument2 SeitenConjugaisons Completlilirosepasco41Noch keine Bewertungen
- AlemánDokument2 SeitenAlemánVanessa GutiérrezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Jerman 1Dokument9 SeitenJerman 1oktaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Futur Perfect PräteritumDokument12 SeitenFutur Perfect PräteritumSaid HmidouchNoch keine Bewertungen
- 04.verb Konjugation Regular and IrregularDokument2 Seiten04.verb Konjugation Regular and IrregularZeeshan AhmedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Student CopeDokument14 SeitenStudent CopeNarayan ThapaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Praesens UKRDokument3 SeitenPraesens UKROleh RadchenkoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Allemand Des VerbsDokument18 SeitenAllemand Des VerbsAnonymous rHUQNdrOT6Noch keine Bewertungen
- 2k - KonjunktivDokument14 Seiten2k - KonjunktivAlina RigerNoch keine Bewertungen
- A1 German GrammarDokument13 SeitenA1 German GrammarJakub WyrwińskiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Algunos Verbos Reg-IrregDokument3 SeitenAlgunos Verbos Reg-IrregCarlos A Ramírez RojasNoch keine Bewertungen
- present-irregular-verbs الافعال الشاذة الالمانيةDokument10 Seitenpresent-irregular-verbs الافعال الشاذة الالمانيةHussein RasheedNoch keine Bewertungen
- KonjugationDokument2 SeitenKonjugationvb6x5gffdsNoch keine Bewertungen
- ImperativDokument12 SeitenImperativKevinperry SohNoch keine Bewertungen
- German With Cow - ConjugationDokument16 SeitenGerman With Cow - ConjugationMohamed MohamedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Теперішній час вправиDokument24 SeitenТеперішній час вправиkstoliarchuk7Noch keine Bewertungen
- GramatikaDokument30 SeitenGramatikaArmis OkanovicNoch keine Bewertungen
- Zeitformen Im DeutschenDokument12 SeitenZeitformen Im DeutschenLiljana DimeskaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fremdsprachendidaktik: Eine EinführungVon EverandFremdsprachendidaktik: Eine EinführungBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (1)
- Read & Learn German - Deutsch lernen - Part 5: In der StadtVon EverandRead & Learn German - Deutsch lernen - Part 5: In der StadtBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (7)
- Deutsche Grammatik in Algorithmen: Grund- und Mittelstufe mit Aufgaben, Tests und LösungenVon EverandDeutsche Grammatik in Algorithmen: Grund- und Mittelstufe mit Aufgaben, Tests und LösungenBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (1)
- Wortbildung des modernen Deutschen: Ein Lehr- und ÜbungsbuchVon EverandWortbildung des modernen Deutschen: Ein Lehr- und ÜbungsbuchBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (1)
- Deutsche Grammatik: Die unverzichtbaren Grundlagen der SchriftspracheVon EverandDeutsche Grammatik: Die unverzichtbaren Grundlagen der SchriftspracheBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (10)
- Fragen Sie einfach!: Deutsche Grammatik in leichter SpracheVon EverandFragen Sie einfach!: Deutsche Grammatik in leichter SpracheBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (1)
- Arabisch Lernen - Paralleltext - Kurz Geschichten (Deutsch - Arabisch)Von EverandArabisch Lernen - Paralleltext - Kurz Geschichten (Deutsch - Arabisch)Bewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (2)
- Wörterbuch Deutsch - Polnisch - Englisch Niveau B1: Lernwortschatz B1 DEUTSCH zum erfolgreichen Selbstlernen für DeutschkursTeilnehmerInnen aus PolenVon EverandWörterbuch Deutsch - Polnisch - Englisch Niveau B1: Lernwortschatz B1 DEUTSCH zum erfolgreichen Selbstlernen für DeutschkursTeilnehmerInnen aus PolenBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (1)
- Spanisch Lernen - Paralleltext - Einfache Geschichten - Deutsch - Spanisch (Bilingual)Von EverandSpanisch Lernen - Paralleltext - Einfache Geschichten - Deutsch - Spanisch (Bilingual)Bewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (1)
- Read & Learn German - Deutsch lernen - Part 3: ArbeitenVon EverandRead & Learn German - Deutsch lernen - Part 3: ArbeitenBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (10)
- Easy Learning German Verbs: Trusted support for learningVon EverandEasy Learning German Verbs: Trusted support for learningNoch keine Bewertungen
- Read & Learn German - Deutsch lernen - Part 1: EinkaufenVon EverandRead & Learn German - Deutsch lernen - Part 1: EinkaufenBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (10)
- Sprachentwicklung und Sprachförderung: beobachten - verstehen - handelnVon EverandSprachentwicklung und Sprachförderung: beobachten - verstehen - handelnNoch keine Bewertungen
- Also Dann, Bitte Schön; Alemán para HispanohablantesVon EverandAlso Dann, Bitte Schön; Alemán para HispanohablantesBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (1)
- Sprachentwicklung und Sprachförderung in der Kita: beobachten - verstehen - handelnVon EverandSprachentwicklung und Sprachförderung in der Kita: beobachten - verstehen - handelnNoch keine Bewertungen
- Kinder lernen Sprache(n): Alltagsorientierte Sprachförderung in der KindertagesstätteVon EverandKinder lernen Sprache(n): Alltagsorientierte Sprachförderung in der KindertagesstätteNoch keine Bewertungen
- Deutsch Serbisch Lektion 1: Lernwortschatz Deutsch - Serbisch Kyrillisch + Latein A1 Lektion 1 Guten Tag + Kurs per InternetVon EverandDeutsch Serbisch Lektion 1: Lernwortschatz Deutsch - Serbisch Kyrillisch + Latein A1 Lektion 1 Guten Tag + Kurs per InternetBewertung: 3 von 5 Sternen3/5 (1)
- Bilinguales Buch - Das Leben der Kleopatra (Deutsch - Englisch)Von EverandBilinguales Buch - Das Leben der Kleopatra (Deutsch - Englisch)Bewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (1)