Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Indirekte Rede
Hochgeladen von
Alexandria Theresa F.B.Originaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Indirekte Rede
Hochgeladen von
Alexandria Theresa F.B.Copyright:
Verfügbare Formate
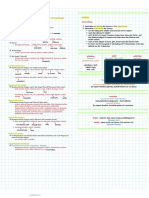
INDIREKTE REDE
Saturday, May 7, 2022 11:03 PM
INDIRECT SPEECH/ Indirekte Rede INDIRECT QUESTION/Indirekte Frage
The German indirect speech allows to report what someone has said FORMING AN INDIRECT QUESTION
without repeating their exact words. Indirect questions = main clause and a subordinate clause
FORMATION: WORD ORDER = (Question word + subject + object + finite verb)
1. First, the change of verb form: (mostly in the subjunctive) Z.B: (Introduction words)
1. Er fragt sich,
“Er hat Fussball gespielt.” – “Er sagte, er habe Fussball gespielt” 2. Sie möchte wissen,
3. Ihr sagt ihm
2. Second, the change of pronouns: 4. Kannst du mir erklären,
5. Wir wissen nicht,
“Er sagte: Ich habe Oliver Kahn gesehen!”
6. Sie verstehen nicht,
“Er sagte, er habe Oliver Kahn gesehen.”
7. Ich bin nicht sicher,
8. Kannst du mir sagen,
3. Third, if neccessary, the change of details about place and time: 9. Er hat mich gefragt,
10. Ich habe gefragt,
“Er sagte, Philip war gestern hier.”
“Er sagte, Philip sei am Tag zuvor da gewesen.”
OB = Ja/Nein Frage (closed questions)
With ‘ob’ we transform yes / no questions in a indirect question.
GRAMMATICAL STRUCTURES:
FORMAT: Introduction words, + ob + subject + object + finite verb
DECLARATIVE SENTENCES
Can be without conjunction/Adding "dass" to the introductory clause
INDIRECT QUESTIONS WITH THE W = open questions
FORMAT: Introduction words , + wann/wo/wie/wer/was/warum… + subject
“Ich habe Philip gesehen.”
+ object + finite verb
“Er sagt, dass er Philip gesehen habe.”
QUESTIONS SENTENCES
can simply introduce it by using the question word PUNCTUATION
IF HAUPTSATZ = DECLARATIVE CLAUSE + (.)
“Er fragte: Wo is Philip?”
“Er fragte, wo Philip sei.” Ich möchte gerne wissen, ob es hier eine schnelle Internetverbindung
gibt.
DEMAND AND REQUESTS
usually modal verb “sollen” is used. In case you’d like to sound more IF HAUPTSATZ = INTERROGATIVE CLAUSE + (?)
polite, just use the verb “mögen”.
Darf ich Sie fragen, ob Sie soziale Netzwerke nutzen?
“Er sagte: Philip, sei nicht so laut!”
“Er sagte, Philip solle nich so laut sein.”
Z.B:
Indikativ oder Konjunktiv? A: Gehst du gern ins Kino?
Indicative is mostly used in spoken language. B: Kannst du das bitte wiederholen? / Was hast du gefragt?
we can assume that we believe and/or agree with the original speaker. A: Ich mochte wissen, ob du gern ins Kino gehst. / Kannst du mir sagen, ob du
Subjunctive is used mainly in written language gern in Kino gehst?
simply repeating what the original speaker said (whether we believe
him/her or not).
GRAMMATIK Seite 1
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Neues Prüfungsformat Hören und Schreiben Deutsch-Test für den Beruf B1 DTB/BSK B1: 16 Übungen für den Subtest Hören und Schreiben B1 mit LösungenVon EverandNeues Prüfungsformat Hören und Schreiben Deutsch-Test für den Beruf B1 DTB/BSK B1: 16 Übungen für den Subtest Hören und Schreiben B1 mit LösungenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Englisch ( Englisch für Alle ) Englisch Lernen für Reisende: Englisch deutsch buch mit 400 Phrasen zum Erlernen des englischen Wortschatzes für ReisendeVon EverandEnglisch ( Englisch für Alle ) Englisch Lernen für Reisende: Englisch deutsch buch mit 400 Phrasen zum Erlernen des englischen Wortschatzes für ReisendeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Goethe SprechenDokument57 SeitenGoethe SprechenFatimeNoch keine Bewertungen
- 150 Irregular German VerbsDokument20 Seiten150 Irregular German VerbsSilvia FischerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Top 100 Verbs, Nouns and Adjectives With Examples - Top 100 VerbsDokument5 SeitenTop 100 Verbs, Nouns and Adjectives With Examples - Top 100 VerbspunjabtarunNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1 - Die AusspracheDokument2 Seiten1 - Die AusspracheFatima KhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- German Communicative Activities PDFDokument158 SeitenGerman Communicative Activities PDFJulia OrtizNoch keine Bewertungen
- German Notes SRMDokument26 SeitenGerman Notes SRMtyagiaryan1975100% (1)
- Aula 5 - Lesen (Goethe T1 Und T4)Dokument11 SeitenAula 5 - Lesen (Goethe T1 Und T4)Julianne BraynerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Verben Mit PräpositionenDokument6 SeitenVerben Mit PräpositionenYshael ColomaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Scan 10 Sep 2020Dokument6 SeitenScan 10 Sep 2020Ashima Goel100% (1)
- DTonlineA2 Wortschatz K12 TURDokument8 SeitenDTonlineA2 Wortschatz K12 TURhknkcr46Noch keine Bewertungen
- BFR KoVo Lektion5 Test PDFDokument2 SeitenBFR KoVo Lektion5 Test PDFAna Maria NeacșuNoch keine Bewertungen
- A1 - Sprechen Teil 3 PDFDokument5 SeitenA1 - Sprechen Teil 3 PDFPadmavothi BharadwajNoch keine Bewertungen
- Wortliste 1 enDokument15 SeitenWortliste 1 enzuleyha2003.sglNoch keine Bewertungen
- Get Ready 6Dokument9 SeitenGet Ready 6Ashima Goel100% (1)
- B1 PreparationDokument8 SeitenB1 PreparationShinto BabuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Perfekt Schwacher Verben Aktivitaten Spiele 109636Dokument1 SeitePerfekt Schwacher Verben Aktivitaten Spiele 109636Lasigo MokafiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Einfache Texte Ferienparadies Schwarzwald Einszueins Mentoring Inhalt Und Sprachenintegriert - 83114Dokument3 SeitenEinfache Texte Ferienparadies Schwarzwald Einszueins Mentoring Inhalt Und Sprachenintegriert - 83114BTorbaveczCsillaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Verben Mit PräpositionenDokument5 SeitenVerben Mit PräpositionenMurilo PastorelloNoch keine Bewertungen
- Grammatik - Kopiervorlagen - L1 - A2 - Gesamt 1Dokument1 SeiteGrammatik - Kopiervorlagen - L1 - A2 - Gesamt 1Rajan ShahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Goethe Prüfung A1.2 - SchreibenDokument14 SeitenGoethe Prüfung A1.2 - SchreibenBeatriz NevesNoch keine Bewertungen
- DT-online A1 LWS K05 TurDokument5 SeitenDT-online A1 LWS K05 TurÖmer Utku KahramanNoch keine Bewertungen
- MOTIVE Lektion 30 Test LoesungenDokument4 SeitenMOTIVE Lektion 30 Test LoesungenAlexandra100% (1)
- Adjektivendung b1Dokument5 SeitenAdjektivendung b1Samia ZerdabiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Verben Mit PräpositionenDokument3 SeitenVerben Mit PräpositionenMarijana SpaseskaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nicht Und Kein ÜbungDokument1 SeiteNicht Und Kein ÜbungAlbert WeskerNoch keine Bewertungen
- DTZ UEbungssatz 1 Erwachsene - PDF 2Dokument8 SeitenDTZ UEbungssatz 1 Erwachsene - PDF 2khairieaalfahadNoch keine Bewertungen
- A1 Schreiben Prüfung A1 DatenbankDokument7 SeitenA1 Schreiben Prüfung A1 DatenbankThanh NguyễnNoch keine Bewertungen
- A2 Deutsch InfoDokument64 SeitenA2 Deutsch InfotikeNoch keine Bewertungen
- 01 Was Machen Sie in Ihrer Freizeitlehrerkommentar PDFDokument5 Seiten01 Was Machen Sie in Ihrer Freizeitlehrerkommentar PDFAnonymous FuoPUE100% (1)
- L7 A1 HoerenDokument3 SeitenL7 A1 HoerenDương Phương ThảoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tablica Nemeckix Glagolov Silnogo SpryazheniyaDokument5 SeitenTablica Nemeckix Glagolov Silnogo SpryazheniyaAnushNoch keine Bewertungen
- PronombresDokument2 SeitenPronombresPedro Manuel Oliver FernándezNoch keine Bewertungen
- b1 Arbeitsblatt Kap1-02 PDFDokument1 Seiteb1 Arbeitsblatt Kap1-02 PDFRoman ChepezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Erste Stunde A1.2Dokument3 SeitenErste Stunde A1.2Huynh Nguyen Song ThuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Arbeitsblatt-A1-KAP-4-Guten AppetitDokument8 SeitenArbeitsblatt-A1-KAP-4-Guten AppetitAylDemNoch keine Bewertungen
- A1 Deutsch ÜbungDokument8 SeitenA1 Deutsch ÜbungConstantineNoch keine Bewertungen
- Test III Mujori II März KL IX - Gruppe A 2022 1Dokument3 SeitenTest III Mujori II März KL IX - Gruppe A 2022 1Gudi CanajNoch keine Bewertungen
- Arbeitsblatt Akkusativpronomen - With Answer KeyDokument6 SeitenArbeitsblatt Akkusativpronomen - With Answer KeyIndu JosephNoch keine Bewertungen
- Konjugationen Deutsch (Conjugaciones)Dokument4 SeitenKonjugationen Deutsch (Conjugaciones)Carlos Andres Chumacero100% (1)
- 02 TestsDokument17 Seiten02 TestsMelinda Ocskay100% (1)
- German LanguagesDokument2 SeitenGerman LanguagesJuliaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Konjunktionen ÜbungenDokument18 SeitenKonjunktionen ÜbungenCarlos Jaimes AguilarNoch keine Bewertungen
- A2 Klausur PDFDokument14 SeitenA2 Klausur PDFHarmanpreet 151Noch keine Bewertungen
- Satzstruktur Auf DeutschDokument1 SeiteSatzstruktur Auf DeutschMagali Acevedo100% (1)
- Deutsch A1Dokument22 SeitenDeutsch A1Neha GoswamiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Linksammlung Für Deutsch A2.1Dokument4 SeitenLinksammlung Für Deutsch A2.1Esra BaşkanNoch keine Bewertungen
- German Syllabus July 2022Dokument13 SeitenGerman Syllabus July 2022Vedanti KumbharNoch keine Bewertungen
- GCSE German Speaking Theme Questions 2023Dokument4 SeitenGCSE German Speaking Theme Questions 2023AshleyNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1000 Worter GrundwortschatzDokument32 Seiten1000 Worter GrundwortschatzИрина КучеренкоNoch keine Bewertungen
- German Verb Conjugation With ExampleDokument1 SeiteGerman Verb Conjugation With ExampleRaaz SharmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- E 9 Ferien Und PerfektDokument74 SeitenE 9 Ferien Und PerfektPedro AcabadoNoch keine Bewertungen
- A1 Phieu Boc Sprechen Teil2 - Duc ToanDokument6 SeitenA1 Phieu Boc Sprechen Teil2 - Duc ToanDuc-3D-18 Phạm Ngọc AnhNoch keine Bewertungen
- GenitivDokument3 SeitenGenitivThu Vân 3Đ - 20 Nguyễn ThịNoch keine Bewertungen
- Auf Jeden Fall A1.2 Loesungen KB ABDokument7 SeitenAuf Jeden Fall A1.2 Loesungen KB ABMaria del AlamoNoch keine Bewertungen
- A1 PRÜFUNG 6-WPS OfficeDokument22 SeitenA1 PRÜFUNG 6-WPS OfficeGerman PrivateNoch keine Bewertungen
- German Test 2 PDFDokument20 SeitenGerman Test 2 PDFChristina YaworskaNoch keine Bewertungen
- L5 A1 LesenDokument6 SeitenL5 A1 LesenDương Phương ThảoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Übungsdiktate: Gleich und ähnlich klingende Konsonanten. Regeln zur Rechtschreibung mit Beispielen und Wortlisten: Deutsch - ganz praktisch Band 6Von EverandÜbungsdiktate: Gleich und ähnlich klingende Konsonanten. Regeln zur Rechtschreibung mit Beispielen und Wortlisten: Deutsch - ganz praktisch Band 6Noch keine Bewertungen
- Modal VerbenDokument1 SeiteModal VerbenAlexandria Theresa F.B.Noch keine Bewertungen
- KASUSDokument1 SeiteKASUSAlexandria Theresa F.B.Noch keine Bewertungen
- Substantivierte VerbenDokument1 SeiteSubstantivierte VerbenAlexandria Theresa F.B.Noch keine Bewertungen
- Satz StrukturDokument2 SeitenSatz StrukturAlexandria Theresa F.B.Noch keine Bewertungen
- ADVERBIENDokument1 SeiteADVERBIENAlexandria Theresa F.B.Noch keine Bewertungen
- INDEFINITPRONOMENDokument4 SeitenINDEFINITPRONOMENAlexandria Theresa F.B.Noch keine Bewertungen
- Redemittel BeschwerdenDokument2 SeitenRedemittel BeschwerdenAlexandria Theresa F.B.Noch keine Bewertungen
- Passiv SatzeDokument4 SeitenPassiv SatzeAlexandria Theresa F.B.Noch keine Bewertungen
- Redemittel Für DiskussionenDokument4 SeitenRedemittel Für DiskussionenAlexandria Theresa F.B.Noch keine Bewertungen
- Deutsch Als Fremdsprache - AdjektivdeklinationDokument3 SeitenDeutsch Als Fremdsprache - AdjektivdeklinationCimarron1989Noch keine Bewertungen
- Lektion 2Dokument8 SeitenLektion 2MEDIA WORLDNoch keine Bewertungen
- GR 321 Steigerung AdjektivDokument1 SeiteGR 321 Steigerung AdjektivDipesh NiroulaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pronume Personal - OdtDokument12 SeitenPronume Personal - Odtmilenium11Noch keine Bewertungen
- FR Lsa Loes 2021Dokument15 SeitenFR Lsa Loes 2021Hải YếnNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2033 NomenDokument7 Seiten2033 Nomeniamjeyashree552Noch keine Bewertungen
- Kon-Takt1 3Dokument3 SeitenKon-Takt1 3Tamas BardosNoch keine Bewertungen
- ModalverbenDokument2 SeitenModalverbenDea Fils SorellNoch keine Bewertungen
- To Be GermanDokument4 SeitenTo Be GermanMadalina CheroiuNoch keine Bewertungen
- UntitledDokument168 SeitenUntitledAmir Rostami100% (1)
- Modalverbem Im PräteritumDokument1 SeiteModalverbem Im PräteritumBianca MourãoNoch keine Bewertungen
- GER A2.2.0205G The Verb LassenDokument25 SeitenGER A2.2.0205G The Verb LassenGTNoch keine Bewertungen
- Konjugation "Beginnen" - Alle Formen Des Verbs, Beispiele, Regeln (-V-) Netzverb WörterbuchDokument5 SeitenKonjugation "Beginnen" - Alle Formen Des Verbs, Beispiele, Regeln (-V-) Netzverb Wörterbuchmurat ozanNoch keine Bewertungen
- 原因从句和介词短语Dokument17 Seiten原因从句和介词短语朱浩Noch keine Bewertungen
- Akkusativ Und Dativ Arbeitsblatter Grammatikerklarungen - 40420Dokument3 SeitenAkkusativ Und Dativ Arbeitsblatter Grammatikerklarungen - 40420Roshni Melwani50% (2)
- B-Grammatik b1-b2 L 246 SungenDokument23 SeitenB-Grammatik b1-b2 L 246 SungenKrisztina PrágaiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Arbeitsblatt RelativDokument3 SeitenArbeitsblatt RelativZhai OribiadaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Infinitiv Mit ZuDokument23 SeitenInfinitiv Mit ZuSoifahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tga1 1 InhaltDokument2 SeitenTga1 1 InhaltFrancesco Gattuso100% (1)
- Klasse DeutschDokument5 SeitenKlasse DeutschlukasNoch keine Bewertungen
- DazDokument170 SeitenDazClara Mjk100% (1)
- Verben Mit Prapositionen II JahrDokument5 SeitenVerben Mit Prapositionen II JahrBile Vitanova AngelovaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Generative Grammatik VORLESUNGDokument98 SeitenGenerative Grammatik VORLESUNGhalmekNoch keine Bewertungen
- Indirekte RedeDokument3 SeitenIndirekte RedeRais AsvatullinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Deutsch Test 100Dokument5 SeitenDeutsch Test 100roxanaclau100% (2)
- 646251.bildung Und Gebrauch Des Adjektivs in Der Deutschen Gegenwartssprache 2Dokument127 Seiten646251.bildung Und Gebrauch Des Adjektivs in Der Deutschen Gegenwartssprache 2ivanana tomiNoch keine Bewertungen
- 016 023 Kap02 PDFDokument8 Seiten016 023 Kap02 PDFSto StolicaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Extra Übungen (Indefinit-, Possessivpronomen) .Hausaufgaben - Lektion3Dokument3 SeitenExtra Übungen (Indefinit-, Possessivpronomen) .Hausaufgaben - Lektion3rizzaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Adjektivdeklination-Vorlagen 34907Dokument11 SeitenAdjektivdeklination-Vorlagen 34907yoNoch keine Bewertungen
- D - Duden - Neue RechtschreibungDokument5 SeitenD - Duden - Neue Rechtschreibungbanish2Noch keine Bewertungen