Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Grenzwerte Von Funktionen - Ableitung
Hochgeladen von
amoalleramos069Originaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Grenzwerte Von Funktionen - Ableitung
Hochgeladen von
amoalleramos069Copyright:
Verfügbare Formate
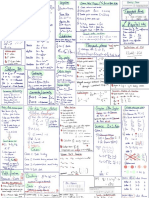
Ableitung Grundidee : Wir wollen die Steigung in an der Stelle Xo herausfinden .
1 f(x) = x]
Vorgehen :
Wir wählen einen zweiter Punkt auf der Funktion f
,
f(xoth) liegt (Stelle Xoth)
g
Steigung
--------
I der in der Nähe Die
.
T
! der Sekante ist eine Näherung der Steigung der Funktion .
4f(x)
---------! Steigung kann bestimmt werden durch den Differenzquotient
S
Yo Xoth f(x)
(xo +))
* f -
= =
m
h
2
- (Xd= X
,
->
(oth =
(xoth" =
x 02 + 2x0) + 42
~ -
Xo + 2xohth
f(x) X
Für f(x) = x2 m=
=
h
2xoth
,
=
f(x) = X
Um
f (xoth) = (xoth) = Xo + 3x2h 3x +
43 +
von der Näherung der Sekante zur exakten Lösung der
Tangente über zugehen ,
macht man einer Grenzübergang
f(x0 + h) -
f(x)
=
(X) =
yig h - (x) =
&folclim
fxot-fl
h
M
3 2
1 x f(x) =Xh
=im 3x) + 3x h Beispiel für
xo + .
+ -
kürzen
Differential-
4
f (X) =
j2Xth=2x0
hoffizient
=3x0 + 3x 04 + 42
2
= 3x ,
Pascalsche Dreieck
T 7
f(x) = XY f(x) = x5
(a+b)" a2 2ab + 62
f(xz) = XY
1 = +
f (X) = Y5
12
b) a + 3ab + 3as" + 33
133
T (a + =
- Exoth" E =
" + Exo3h + Exo +40th"-*** + Exoth5
Im
=4 0 -
~
5
X + 5x2h + 20x34" + cox +5xoh"th
I
- x
a" + 436 + 6262 + 6" h
1
4647(+ b)" =
↳
5
= a + 5a"s + road" + 10963 + 5ab" + 35
(+
5x043 +44
205 7
1 5 10
=4 x + 0x24 + 4x042 + 13 = 5x0"+ Toxo3h +10x0242 +
"
=5x
"X ,
f(x)
=
f(x)
0
2X
>2
3x Ableitung für Potenzfunktionen
xb
Beweis g'(X) = Mg(x+h)h
(x)
4x] Faktorregel g(x) f(x) CER
4 1
g
-
Exponenten
-
xY mit natürlichen : = c :
,
:
5x , 4
5 7
X5
-)'(x) limcf(yth)-cfy
-
1
j'(x) = c .
=
xn nxh
-
= C
. Im f(xth)-fy
Summeregel : h(x) = f(x) + g(x) =c .
f'(x)
L' (x) f' (x) +g'(x)
Beweis = S(xth)
=
Sex
5(X
-
:
4
Differenzregel : h(x) f(x)
L (x
=
= f'(x) y'(x)
-
g(x
-
- h
3
=in f(xth)-f2x)+g(xt-y
.
100 no .
5 Potenregel : f(x) = XY
= f'(x) + g' (x)
a) f(x) = 2 x+ 3x2b) +(x) = 5 2) f(x) = Lax d) +2x) = anxv f(x) = 1 -
y"
2) f(x) = 4x + 4 f(f'(x) = X g)f'(x) = 6x2 Ox 4) f'(x) =
3ax + b+
a n - M
=a
am
+ m
au am = an
Wiederholung S
.
101
Nit a"6
: ( b) "
.
.
=
.
=
M
-" -5
f'(x) 5x6 (an = at
x a) f(x) =
, =
y = -
= f(x) 5
E X) 6) f(x) 5
-
-
- =
= 3 yx 22x
-
= Y
. -
5 3 x
fix=i=EX fix F 6x* 2x7
x 6) =
- . -
=
* =
xt
"
3 ( *
4
x+ y 2x 3x "
+1 =- x y
3
=
d) X +
f(x)
-
f(x)
= *
= = X -
= 1 + -
4x
* =
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- FahrzeugtechnikDokument131 SeitenFahrzeugtechnikAnonymous KjM8mKwbNoch keine Bewertungen
- BMW E28 518 520i WerkstatthandbuchDokument336 SeitenBMW E28 518 520i Werkstatthandbuchcristi_badea_6Noch keine Bewertungen
- Salzburg Train MapDokument1 SeiteSalzburg Train MapKuen WongNoch keine Bewertungen
- Din 7349Dokument6 SeitenDin 7349Peter Pan100% (1)
- Faszination Fliegen: Die zivile Luftfahrt und der Flughafen Rhein-Main in den 1930er-JahrenVon EverandFaszination Fliegen: Die zivile Luftfahrt und der Flughafen Rhein-Main in den 1930er-JahrenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Vestido 50s Burda 133-072012-SchnittDokument17 SeitenVestido 50s Burda 133-072012-SchnittMercè Rodellas Canudas100% (1)
- Durufle-Tantum ErgoDokument2 SeitenDurufle-Tantum ErgoViktoriya KonchakovskayaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Map City Altdorf - VectorDokument1 SeiteMap City Altdorf - VectorNieuczesany100% (1)
- VollständigerDokument3 SeitenVollständigerXinru XuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Designfunktion Sonderverkauf Flash MagazinDokument17 SeitenDesignfunktion Sonderverkauf Flash MagazindesignfunktionNoch keine Bewertungen
- Klaus Hurrelmann PDFDokument1 SeiteKlaus Hurrelmann PDFDumboFinnNoch keine Bewertungen
- REB 23003 2009 FormeluebersichtDokument2 SeitenREB 23003 2009 FormeluebersichtGeorge Sîrbu100% (1)
- Mathe ExamDokument2 SeitenMathe ExamFlorian NixNoch keine Bewertungen
- Zeitung - Ausgabe 04/2010 - Nr. 10 DeutschDokument20 SeitenZeitung - Ausgabe 04/2010 - Nr. 10 Deutschgrafenwoehr_comNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mathe LernzettelDokument11 SeitenMathe Lernzettelfriederike.srlNoch keine Bewertungen
- SpickDokument3 SeitenSpickAnonymous 1JLCy9gNoch keine Bewertungen
- tm4 Mitschrieb ss2017Dokument49 Seitentm4 Mitschrieb ss2017Kalin MladenovNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fourier ReihenDokument7 SeitenFourier ReihenSalma KermassNoch keine Bewertungen
- Figur 4 - Belastungsarten - 1475680157Dokument2 SeitenFigur 4 - Belastungsarten - 1475680157manuepar01220Noch keine Bewertungen
- Zeitung - Ausgabe 9 03/2010Dokument20 SeitenZeitung - Ausgabe 9 03/2010grafenwoehr_comNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mitutoyo OberflaechenrauheitsmessungDokument2 SeitenMitutoyo OberflaechenrauheitsmessungFlorian DirnböckNoch keine Bewertungen
- Zeitung 04/2009 - November/DezemberDokument18 SeitenZeitung 04/2009 - November/Dezembergrafenwoehr_comNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lösung MonotonieverhaltenDokument1 SeiteLösung MonotonieverhaltenBenjamin EiflerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Zeitung Grafenwoehr - Com - 01/2010Dokument24 SeitenZeitung Grafenwoehr - Com - 01/2010grafenwoehr_comNoch keine Bewertungen
- Stille Nacht Heilige NachtDokument1 SeiteStille Nacht Heilige NachtChristophe BornetNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fahrpläne Stadtwerke AugsburgDokument2 SeitenFahrpläne Stadtwerke AugsburgValentino StellaNoch keine Bewertungen
- SternkartenDokument5 SeitenSternkartenNiklas ObermayerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Zeitung - Ausgabe 05/2010 - Nr. 11 DeutschDokument22 SeitenZeitung - Ausgabe 05/2010 - Nr. 11 Deutschgrafenwoehr_comNoch keine Bewertungen
- Map Aachen HBF DEDokument1 SeiteMap Aachen HBF DEchristophe.briereNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lageplan - Uke 3Dokument1 SeiteLageplan - Uke 3F FNoch keine Bewertungen
- November AbrechnungDokument2 SeitenNovember AbrechnungmaiamargishviliNoch keine Bewertungen
- S 1FormelsammlungmitSchemaundErklärungenfür Dummies"Dokument1 SeiteS 1FormelsammlungmitSchemaundErklärungenfür Dummies"orcunNoch keine Bewertungen
- Petec Katalog 2019 It PDFDokument68 SeitenPetec Katalog 2019 It PDFEnzo LongoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Blouson Dita Schnitt-1zu1Dokument1 SeiteBlouson Dita Schnitt-1zu1Lesedi MolelekiNoch keine Bewertungen
- AnalysisDokument11 SeitenAnalysisRiad K.Noch keine Bewertungen
- AchernDokument2 SeitenAchernQiu YmNoch keine Bewertungen
- (Earthdawn) (Map) Barsaives Entfernungen by SturmfalkeDokument1 Seite(Earthdawn) (Map) Barsaives Entfernungen by SturmfalkehgjtuiNoch keine Bewertungen
- U-Bahn Liniennetz Nürnberg-FürthDokument1 SeiteU-Bahn Liniennetz Nürnberg-FürthCristinaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Monsun 18,5-22Dokument28 SeitenMonsun 18,5-22Maxf BueNoch keine Bewertungen
- Flash 2010 11 15pdfDokument16 SeitenFlash 2010 11 15pdfFLASH-COLOGNENoch keine Bewertungen
- Formelsammlung - Korrigiert - 2021-06-07Dokument17 SeitenFormelsammlung - Korrigiert - 2021-06-07muhammad chairyl maulaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Schlaft Mei Dörfle Im SchneeDokument1 SeiteSchlaft Mei Dörfle Im SchneeFiona Meinhardt-KasparekNoch keine Bewertungen
- Scheibenräder: Mit SteilschulterDokument2 SeitenScheibenräder: Mit SteilschulterFrancisco UrizarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lageplan Uke 2Dokument1 SeiteLageplan Uke 2cgqrgs4gd7Noch keine Bewertungen
- Lageplan - Uke 4Dokument1 SeiteLageplan - Uke 4Michaela GrahnNoch keine Bewertungen
- Stadtplan KaiserslauternDokument2 SeitenStadtplan KaiserslauternViktor SpeicherNoch keine Bewertungen
- Teil6 Kanalbau 2012 DTDokument10 SeitenTeil6 Kanalbau 2012 DTbatka2Noch keine Bewertungen
- Der Lindenbaum - Schubert - Analyse - Ohne Bezug Zu Text Und InhaltDokument4 SeitenDer Lindenbaum - Schubert - Analyse - Ohne Bezug Zu Text Und Inhaltoeu36618Noch keine Bewertungen
- 7 Guillaume Dufay Nuper - RosarumDokument10 Seiten7 Guillaume Dufay Nuper - RosarumGianmarco ScrivanoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Form LagetoleranzenDokument1 SeiteForm LagetoleranzensaeidNoch keine Bewertungen
- RegeldetailuriDokument1 SeiteRegeldetailuriVasile IsipNoch keine Bewertungen
- WZT 2 - Gestaltung Von Umformwerkzeugen IDokument15 SeitenWZT 2 - Gestaltung Von Umformwerkzeugen INurullah KocaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Prometheus InterpretationDokument1 SeitePrometheus InterpretationEmily BaurothNoch keine Bewertungen
- Zusammenfassung PDFDokument4 SeitenZusammenfassung PDFhasti maghsoudipourNoch keine Bewertungen
- Slotcars PDFDokument39 SeitenSlotcars PDFTissières SamuelNoch keine Bewertungen
- 6300L Carrier FDokument118 Seiten6300L Carrier Fvmg guindastesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Zustandsgrößen 15.09.2021Dokument2 SeitenZustandsgrößen 15.09.2021Nejla MemićNoch keine Bewertungen
- DM-Toys Neuheiten 2023-1Dokument2 SeitenDM-Toys Neuheiten 2023-1hhhuNoch keine Bewertungen
- LHH Ferienhits 2022 Web KleinDokument2 SeitenLHH Ferienhits 2022 Web KleinSploopiNoch keine Bewertungen
- RadiatorDokument1 SeiteRadiatorPritesh ChauhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Usar Network Plan Diagram en DataDokument1 SeiteUsar Network Plan Diagram en DataNils LodderNoch keine Bewertungen
- HVV Usar-Plan 240408 115049Dokument1 SeiteHVV Usar-Plan 240408 115049peterpaul999pNoch keine Bewertungen
- D913B RCF 1Dokument6 SeitenD913B RCF 1Mohd Abu AjajNoch keine Bewertungen
- Manual Vipow BAT1140Dokument32 SeitenManual Vipow BAT1140chlorasNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2.2 Operating-AndmaintenancemanualDokument22 Seiten2.2 Operating-AndmaintenancemanualThy Hà TuyếtNoch keine Bewertungen
- ZEPHYRA-doc Technique AnhDokument68 SeitenZEPHYRA-doc Technique AnhDavid LynxNoch keine Bewertungen
- De - Haenchen Programm KontaktDokument23 SeitenDe - Haenchen Programm KontaktDmitry BezdnikovNoch keine Bewertungen