Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
316L-1 Chemical Composition
Hochgeladen von
sfateugenOriginaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
316L-1 Chemical Composition
Hochgeladen von
sfateugenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Edelstahl
Der Begriff "Edelstahl" wird im Folgenden als Sammelbezeichnung fr nicht rostende austenitische Edelsthle benutzt. Der Chromgehalt (Cr) der austenitischen Edelsthle liegt bei 17 bis 20 %, whrend der Nickelanteil (Ni) mindestens 8 % betrgt. Dadurch wird die Bestndigkeit gegen Korrosion erreicht. Durch die Zugabe weiterer Legierungsbestandteile, wie Molybdn (Mo), Titan (Ti) etc., kann die Korrosionsbestndigkeit verbessert werden. Schwefel (S) verbessert die Zerspanbarkeit des Werkstoffs, vermindert aber die Schweiqualitt. Stickstoff (N) kann die mechanischen Eigenschaften verbessern. Die austenitischen Edelsthle sind gut verformbar, gut schweibar und sehr korrosionsbestndig. Sie haben auerdem gute Zhigkeitseigenschaften und sind auch bei tiefen Temperaturen bis -271 C einsetzbar. Die austenitischen Edelsthle sind im lsungsgeglhten Zustand nicht magnetisch. Beim Umformen kann Kaltverfestigung auftreten. Dabei kommt es zur Martensitbildung und schwachen Magnetisierbarkeit. Durch Lsungsglhen knnen die Kaltverfestigung und damit auch die Magnetisierbarkeit wieder rckgngig gemacht werden.
Stainless steel
The term "Stainless steel" is used for the following as a collective name for austenitic stainless steels. The chrom content (Cr) of austenitic stainless steels lies about 17 up to 20 %, whereas the nickel portion (Ni) is at least 8 %. Thereby the stability against corrosion is achieved. Through the addition of further alloy components, as molybdn (Mo), titan (Ti) etc., can this stability be improved. Sulphur (S) improves the cutting of the material but impaires the welding quality. Nitrogen (N) can improve the mechanical properties. The austenitic stainless steels are well formable, well weldable and very corrosion resistant. Moreover, they have good toughness properties and are also usable in low temperatures up to -271 C. The austenitic stainless steels are not magnetic when annealed. During shapening strain hardening can occur. Thereby it can come to martensite development and low magnetisability. Through annealing the strain hardening and the magnetism can be undone.
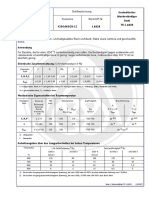
Chemische Zusammensetzung austenitischer Edelsthle. Chemical composition of austenitic stainless steels. W.-Nr. Mat. No. 1.4301 1.4305 1.4306 1.4307 1.4401 1.4404 1.4435 1.4539 1.4541 1.4571 Gruppe Group A2 A2 A2 A2 A4 A4 A4 A4 A2 A4 Kurzbezeichnung Abbreviation X 5 CrNi 18.10 X 10 CrNiS 18.9 X 2 CrNi 19.11 X 2 CrNi 18.9 X 5 CrNiMo 17.12.2 X 2 CrNiMo 17.13.2 X 2 CrNiMo 18.14.3 X 2 NiCrMoCuN 25.20.5 X 6 CrNiTi 18.10 X 6 CrNiMoTi 17.12.2 C % max. 0,07 0,12 0,03 0,03 0,07 0,03 0,03 0,03 0,08 0,08 Si % max. 1,0 1,0 1,0 1,0 1,0 1,0 1,0 1,0 1,0 1,0 Mn % max. 2,0 2,0 2,0 2,0 2,0 2,0 2,0 2,0 2,0 2,0 P % max. 0,045 0,065 0,045 0,045 0,045 0,045 0,045 0,030 0,045 0,045 S % max. 0,030 0,350 0,030 0,030 0,030 0,030 0,025 0,020 0,030 0,030 Cr % 17,0-19,0 17,0-19,0 18,0-20,0 17,5-20,0 16,5-18,5 16,5-18,5 17,0-18,5 19,0-21,0 17,0-19,0 16,5-18,5 Mo % 2,0-2,5 2,0-2,5 2,5-3,0 4,0-5,0 2,0-2,5 Ni % 8,5-10,5 8,0-10,0 10,0-12,5 8,0-10,0 10,5-13,5 11,0-14,0 12,5-15,0 24,0-26,0 9,0-12,0 10,5-13,5 Andere-Others % max. N 0,11 N 0,11, Cu 1 N 0,11 N 0,11 N 0,11 N 0,11 N 0,11 N 0,15; Cu 2 Ti 5x%C, 0,8 Ti 5x%C, 0,8
Physikalische Eigenschaften austenitischer Edelsthle. Physical qualities of austenitic stainless steels. W.-Nr. Mat. No. 1.4301 1.4305 1.4306 1.4307 1.4401 1.4404 1.4435 1.4539 1.4541 1.4571 Spez. Gewicht Spec. gravity g/mm 7,90 7,90 7,90 7,90 7,98 7,90 7,90 7,90 7,90 7,98 Elastizittsmodul Zugfestigkeit Wremausdehnung Elastic modulus Tensile strength Heat expansion 10-6 K-1 (20-100 C) kg/mm (20 C) N/mm 16,5 200 500-750 200 500-700 16,5 200 450-700 16,5 200 450-700 16,5 200 550-700 16,5 16,5 200 450-700 200 500-700 16,5 200 500-700 16,5 200 540-740 16,5 200 540-690 16,5 Wrmeleitfhigkeit Heat conductivity W/mK (20 C) 15 15 15 15 15 15 15 15 15 15 Spez. Wrme Spec. heat kJ/kgK (20 C) 500 500 500 500 500 500 500 500 500 500 Elektr. Widerstand Electric resistance mm/m (20 C) 0,73 0,73 0,73 0,73 0,75 0,75 0,75 0,73 0,73 0,75
Internationaler Werkstoff-Vergleich. International material comparison. Germany W.-Nr. 1.4301 1.4305 1.4306 1.4307 1.4401 1.4404 1.4435 1.4539 1.4541 1.4571 USA AISI 304 303 304L 304L 316 316L 316L 904L 321 316Ti UNS S 30400 S 30300 S 30403 S 31600 S 31603 S 31603 N 08904 S 32100 S 31635 Schweden SS 2332 2346 2352 2347 2348 2353 2562 2337 2350 Frankreich AFNOR Z 6 CN 18.09 Z 10 CNF 18.09 Z 2 CN 18.10 Z 6 CND 17.11 Z 2 CND 17.12 Z 2 CND 17.13 Z 1 NCDU 25.20 Z 6 CNT 18.10 Z 6 CNDT 17.12 England BS 304 S 15 303 S 31 304 S 11 316 S 31 316 S 11 316 S 11 321 S 31 320 S 31 Italien UNI X 5 CrNi 18.10 X 3 CrNi 18.11 X 5 CrNiMo 17.12 X 2 CrNiMo 17.12 X 2 CrNiMo 17.13 X 6 CrNiTi 18.11 X 6 CrNiMoTi 17.12 Spanien UNE F.3504-X 5 CrNi 18.10 F.3503-X 2 CrNi 18.10 F.3534-X 5 CrNiMo 17.12.2 F.3533-X 2 CrNiMo 17.13.2 F.3533-X 2 CrNiMo 17.13.2 F.3523-X 6 CrNiTi 18.10 F.3535-X 6 CrNiMoTi 17.12.2 Japan JIS SUS 304 SUS 304L SUS 316 SUS 316L SUS 316L SUS 321 SUS 316Ti Russland GOST 08Ch18N10 03Ch18N11 03Ch17N14M3 06Ch18N10T 10Ch17N13M2T
AISI = American Iron and Steel Institute, UNS = Unified Numbering System, SS = Swedish Standard, AFNOR = Association Franaise de Normalisation, BS = British Standard
nderungen ohne Vorankndigung vorbehalten / Subject to change without prior notice
Juni 2012
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Stahl BezeichnungDokument267 SeitenStahl BezeichnungerolNoch keine Bewertungen
- PanGas Titanschweisstechnik DDokument8 SeitenPanGas Titanschweisstechnik DTibor KeményNoch keine Bewertungen
- Material Table NiCr 23 Co 12 MoDokument2 SeitenMaterial Table NiCr 23 Co 12 MoWisnu WardhanaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Austenitisches Gusseisen 01Dokument32 SeitenAustenitisches Gusseisen 01Anonymous aigwY0jgzp100% (1)
- Handbuch CastolinDokument47 SeitenHandbuch CastolinPeterD100% (1)
- 3 Werkstoff GusseisenDokument41 Seiten3 Werkstoff GusseisenXantos YulianNoch keine Bewertungen
- Neumo Edelstahl DIN 11866 RohreDokument20 SeitenNeumo Edelstahl DIN 11866 RohreRuben PauwelsNoch keine Bewertungen
- MB109 Stahlsorten Fuer Oberflaechenveredeltes FeinblechDokument16 SeitenMB109 Stahlsorten Fuer Oberflaechenveredeltes FeinblechBernard TivadarNoch keine Bewertungen
- TGL 14414 - 02-1976Dokument16 SeitenTGL 14414 - 02-1976Janak MistryNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1 4550Dokument4 Seiten1 4550Faruk PojskicNoch keine Bewertungen
- Schnittdaten VariMillDokument45 SeitenSchnittdaten VariMillgoranb87Noch keine Bewertungen
- 1 4580Dokument4 Seiten1 4580horstiillingNoch keine Bewertungen
- ZCC Endmilling PDFDokument267 SeitenZCC Endmilling PDFstctool100% (1)
- ROTH - Axial Expansion JointDokument56 SeitenROTH - Axial Expansion Jointandmar2011Noch keine Bewertungen
- 235 Metallische WerkstoffeDokument12 Seiten235 Metallische WerkstoffeAntonio MerkourisNoch keine Bewertungen
- BRO FIN Elektroinstallationsrohre 2018 WebDokument28 SeitenBRO FIN Elektroinstallationsrohre 2018 WebSoimaresti DraganestiNoch keine Bewertungen
- BOHLER Survey of S GradesDokument57 SeitenBOHLER Survey of S Gradespipedown456Noch keine Bewertungen
- Din 28031 2003-06Dokument4 SeitenDin 28031 2003-06georgedjNoch keine Bewertungen
- 01 Duktilni Liveni Fazonski KomadiDokument70 Seiten01 Duktilni Liveni Fazonski Komadidusankg1Noch keine Bewertungen
- 2 NichteisenwerkstoffeDokument17 Seiten2 NichteisenwerkstoffeUsman HameedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tabla de AcerosDokument8 SeitenTabla de AcerosTXUSNoch keine Bewertungen
- SZ Kraftwerk DDokument20 SeitenSZ Kraftwerk DBorn ToSinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Stahllegierung DDokument24 SeitenStahllegierung Dchhakula07Noch keine Bewertungen
- 1 4571Dokument4 Seiten1 4571wilian_coelho3309Noch keine Bewertungen
- Werkstoffgruppen Metallischer WerkstoffeDokument6 SeitenWerkstoffgruppen Metallischer WerkstoffeABNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bdg-Normen Ne MetallDokument18 SeitenBdg-Normen Ne MetallimupathanNoch keine Bewertungen
- K110DE - Aisi D2Dokument16 SeitenK110DE - Aisi D2italangeloNoch keine Bewertungen
- Technisches Datenblatt Loctite 243Dokument4 SeitenTechnisches Datenblatt Loctite 243Chris HaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Castolin ElektrodeDokument62 SeitenCastolin ElektrodeIvan DulicNoch keine Bewertungen
- MÄDLER Sortimentsweiterung 2017 09 PDFDokument20 SeitenMÄDLER Sortimentsweiterung 2017 09 PDFAnonymous hsLOTgNoch keine Bewertungen
- 9 NormenvergleichDokument15 Seiten9 NormenvergleichadanicolaeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lernheft 2.3 LernendeDokument24 SeitenLernheft 2.3 Lernendevalricrom UnbekanntNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2011 RostfreieEdelstaehlDokument68 Seiten2011 RostfreieEdelstaehlm061990Noch keine Bewertungen
- FTBT TeststoffDokument4 SeitenFTBT TeststoffNiklasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rohrzubehoer Flansche KatalogDokument51 SeitenRohrzubehoer Flansche KatalogfuffinoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Din 50961 2012-04Dokument8 SeitenDin 50961 2012-04farhad pashaei mehr100% (1)
- Thyssen Datenblatt 1.4828Dokument4 SeitenThyssen Datenblatt 1.4828horstiillingNoch keine Bewertungen
- ALUDokument56 SeitenALUGustav NattererNoch keine Bewertungen
- Profile Im StahlbauDokument4 SeitenProfile Im Stahlbaumkiani2Noch keine Bewertungen
- Din 28053 PDFDokument8 SeitenDin 28053 PDFtudormoraruNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1.4301 ProkromDokument4 Seiten1.4301 Prokromangrypotato10Noch keine Bewertungen
- Industrie Kohle Buerste NDokument20 SeitenIndustrie Kohle Buerste NpiojeziorNoch keine Bewertungen
- Combiperm - Permanenet Magnet BrakeDokument12 SeitenCombiperm - Permanenet Magnet Brakeaiyubi2Noch keine Bewertungen
- v71 de File d643 17Dokument103 Seitenv71 de File d643 17sehmediaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Werkstofftabelle DEENDokument2 SeitenWerkstofftabelle DEENErivelton ScaldelaiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Stahltabelle v1 PDFDokument27 SeitenStahltabelle v1 PDFGastyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Wanddicken WerkstoffeDokument2 SeitenWanddicken Werkstofferalf_moeller958Noch keine Bewertungen
- BDG-NORMEN Fuer StahlgiessereienDokument21 SeitenBDG-NORMEN Fuer Stahlgiessereienandyhagger100% (1)
- Latz Ausführung Von Stahltragwerken 2012Dokument52 SeitenLatz Ausführung Von Stahltragwerken 2012fabian.hilgertNoch keine Bewertungen
- Verbindungs TechnikDokument24 SeitenVerbindungs TechnikPetar 'Grozni' KovačNoch keine Bewertungen
- Handbuch Kjellberg 2012 de enDokument260 SeitenHandbuch Kjellberg 2012 de enutku melihNoch keine Bewertungen
- Äquivalente StahlsortenDokument3 SeitenÄquivalente StahlsortenScribdTranslationsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Proiect MetalDokument24 SeitenProiect Metalmiu_vasile_valentin1259Noch keine Bewertungen
- Cu Ni 10 Fe 1 MNDokument9 SeitenCu Ni 10 Fe 1 MNskisharkNoch keine Bewertungen
- Brochure Wire IS10Dokument1 SeiteBrochure Wire IS10Danut RusNoch keine Bewertungen
- Kaltzaehe StaehleDokument69 SeitenKaltzaehe Staehle9914102Noch keine Bewertungen
- Metalle: Struktur und Eigenschaften der Metalle und LegierungenVon EverandMetalle: Struktur und Eigenschaften der Metalle und LegierungenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Brünieren: Ein Überblick zu historischen und neueren Verfahren Mit über 90 Rezepturen und zahlreichen Anleitungen 48 FarbfotosVon EverandBrünieren: Ein Überblick zu historischen und neueren Verfahren Mit über 90 Rezepturen und zahlreichen Anleitungen 48 FarbfotosNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nanostrukturierte Aluminiumfluoridschichten: Über das neuartige Niedertemperatur Sol-Gel Verfahren und die charakteristischen EigenschaftenVon EverandNanostrukturierte Aluminiumfluoridschichten: Über das neuartige Niedertemperatur Sol-Gel Verfahren und die charakteristischen EigenschaftenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cistus EbookDokument15 SeitenCistus EbookKarl Hinkel100% (1)
- Ein Kreuz Des Georgios Laskaris in Den Berliner Museen Victor ElbernDokument13 SeitenEin Kreuz Des Georgios Laskaris in Den Berliner Museen Victor ElbernneddyteddyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Frauen HaditheDokument9 SeitenFrauen Hadithekareem_815226Noch keine Bewertungen
- Mikrobiologische Grundlagen 030909Dokument2 SeitenMikrobiologische Grundlagen 030909ortnerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Latein LernenDokument24 SeitenLatein LernenJohannes Von KniggeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Multifase EDURDokument24 SeitenMultifase EDURLïlïana GarciaNoch keine Bewertungen